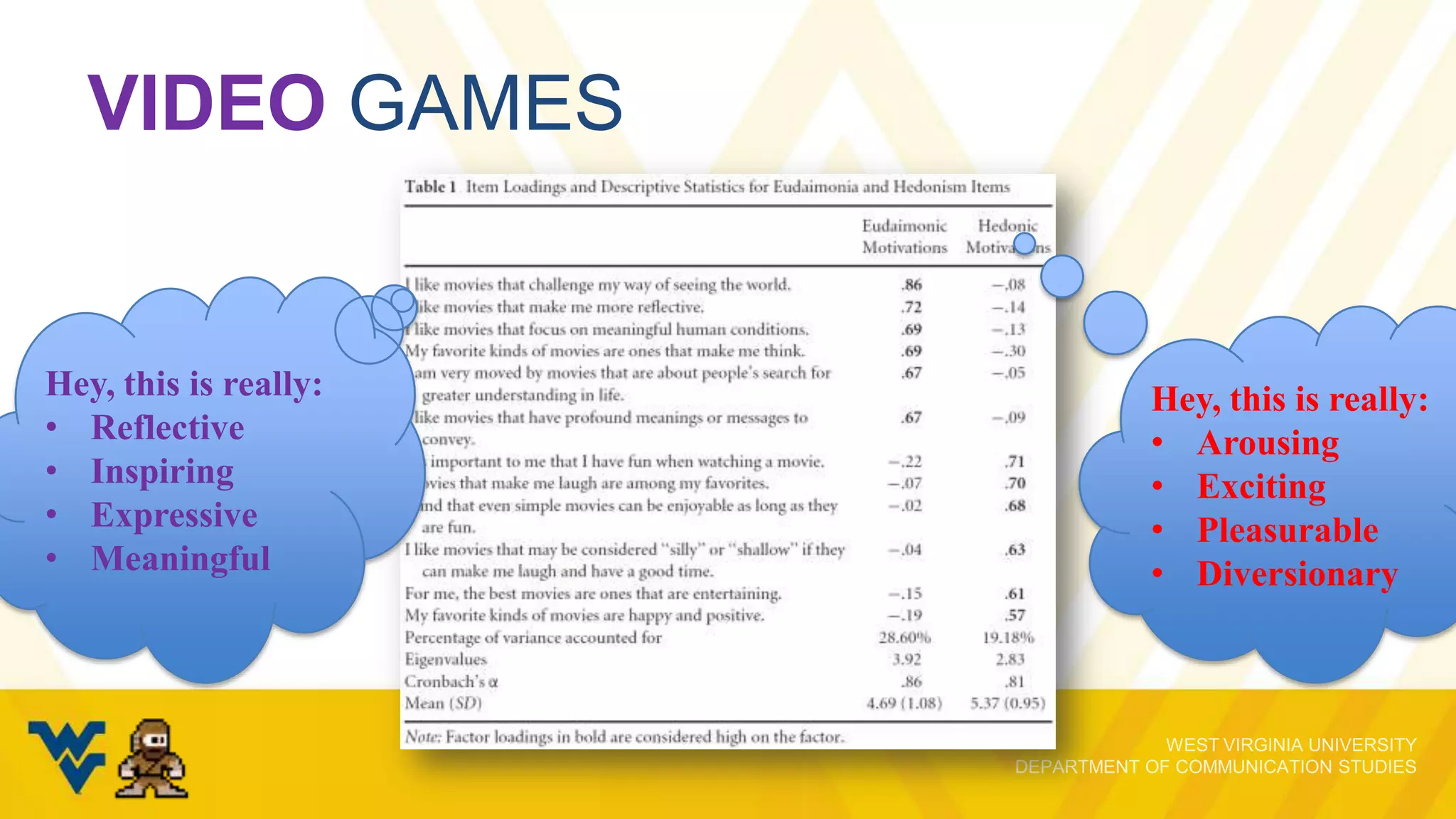
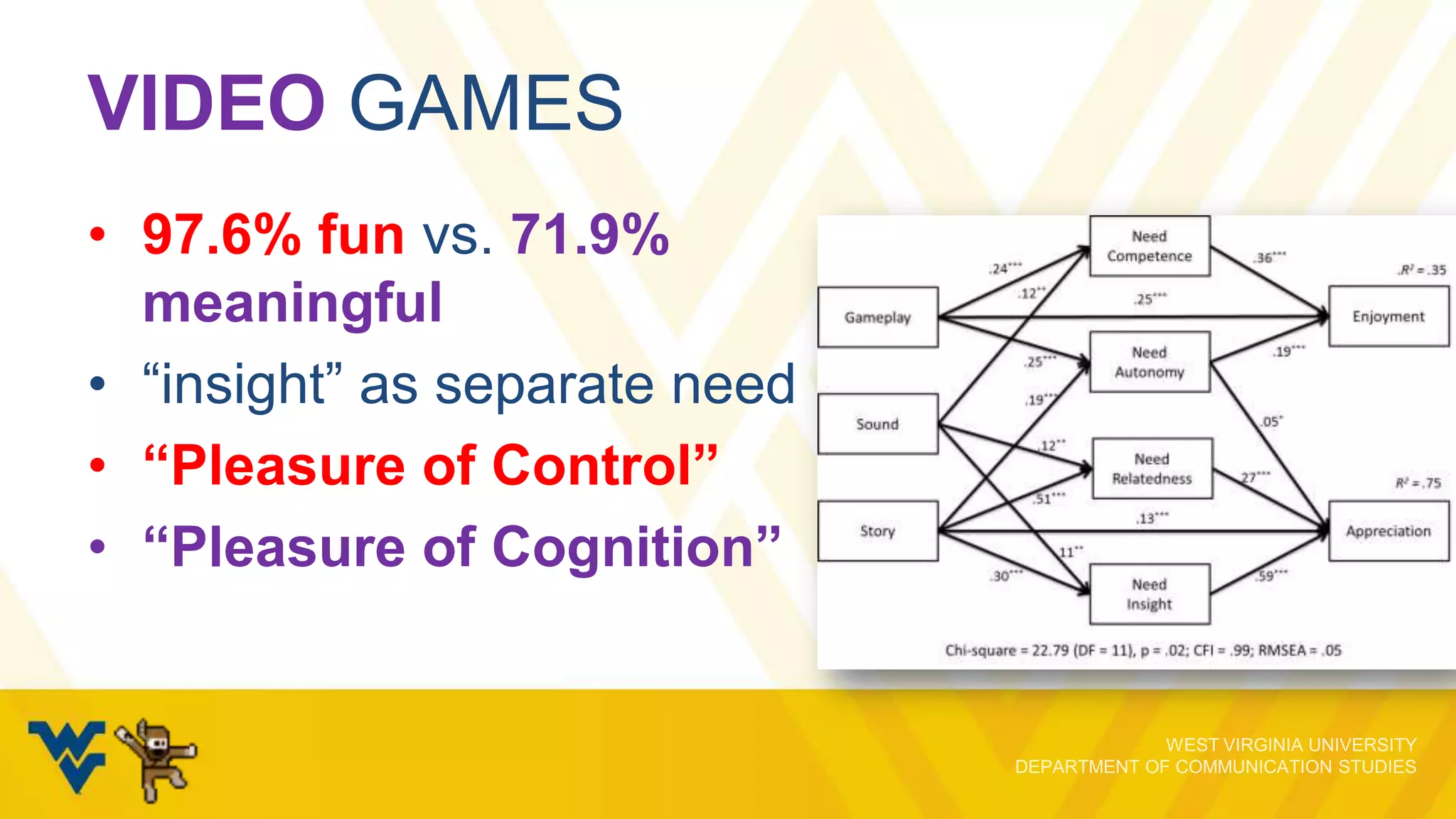
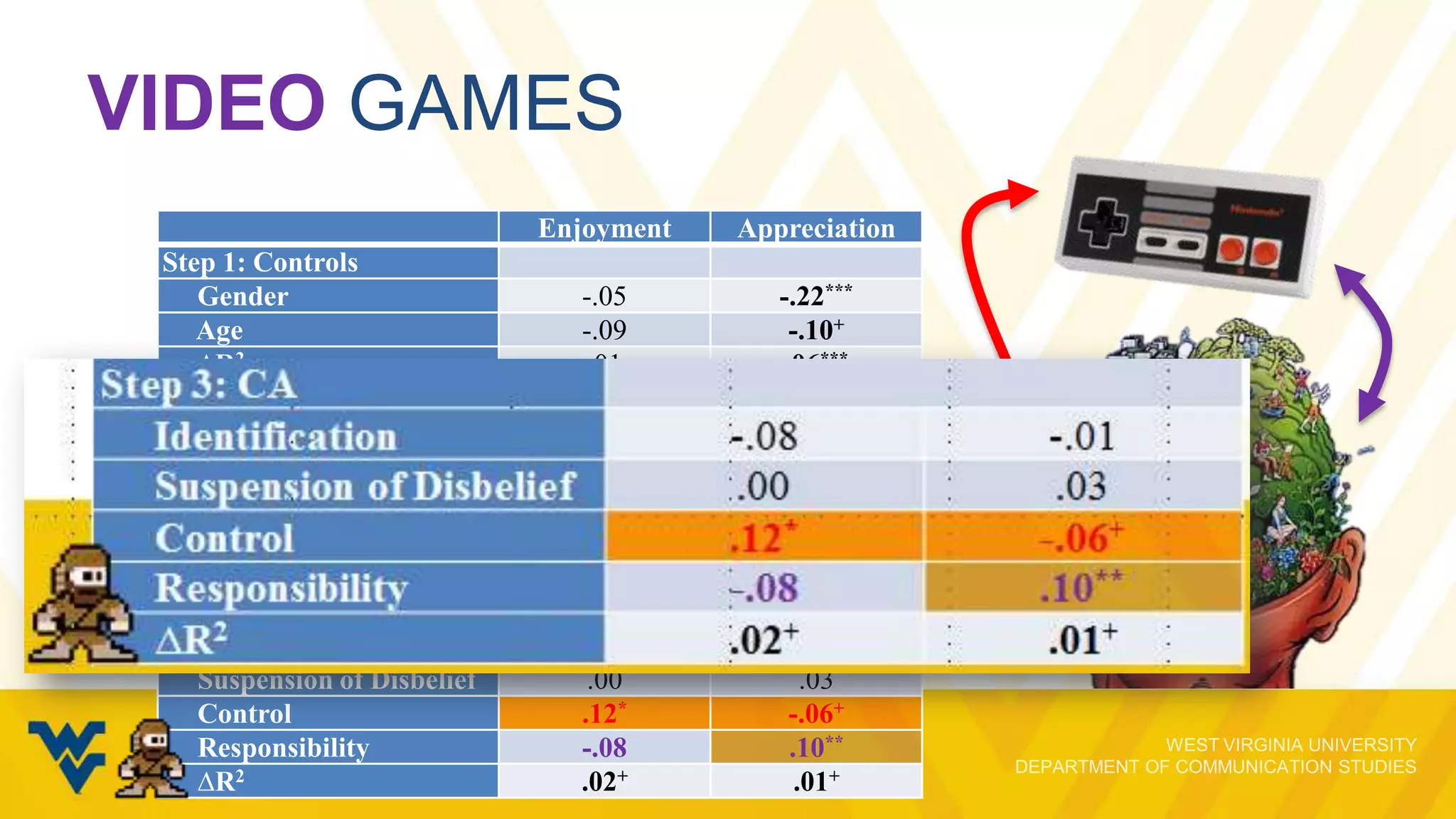
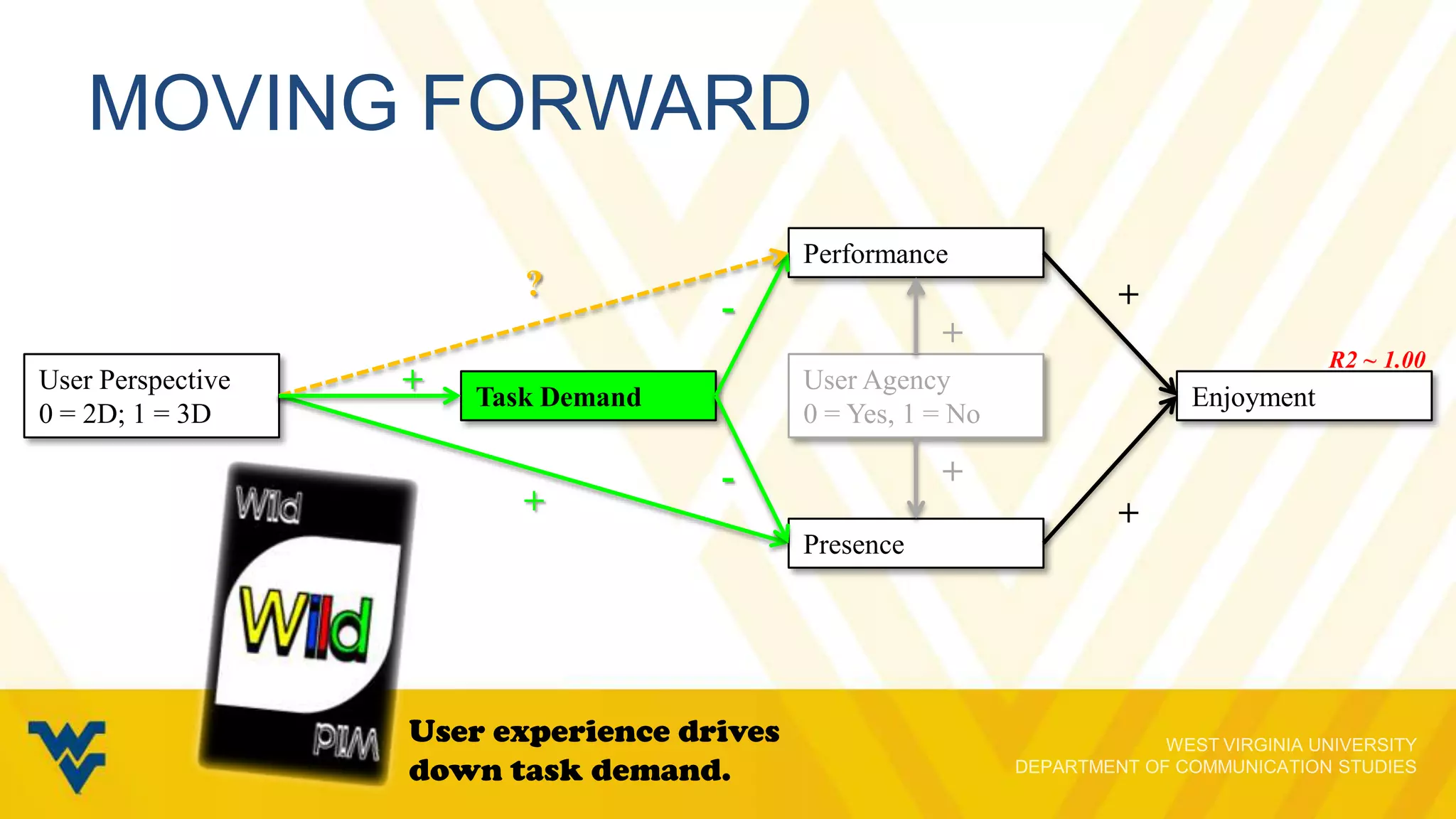
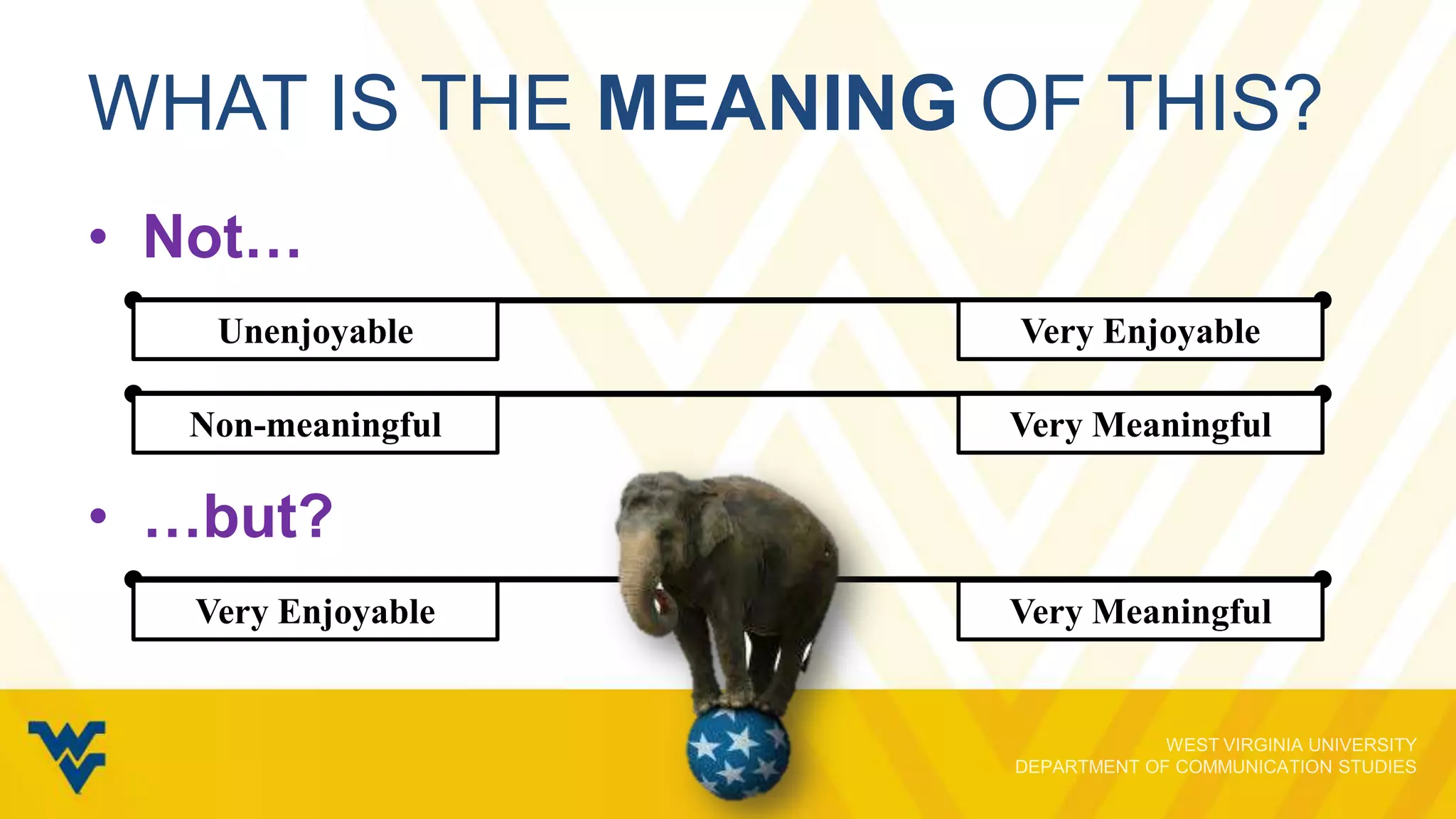
The document discusses the evolving relationship between video game play and narrative, emphasizing how interactivity influences players' engagement and perception. It explores various cognitive skills that affect gameplay, the motivations behind gameplay selection, and the distinction between enjoyment and appreciation in gaming experiences. The presentation underscores the importance of understanding both the psychological aspects of gaming and the implications for narrative retention and emotional involvement.



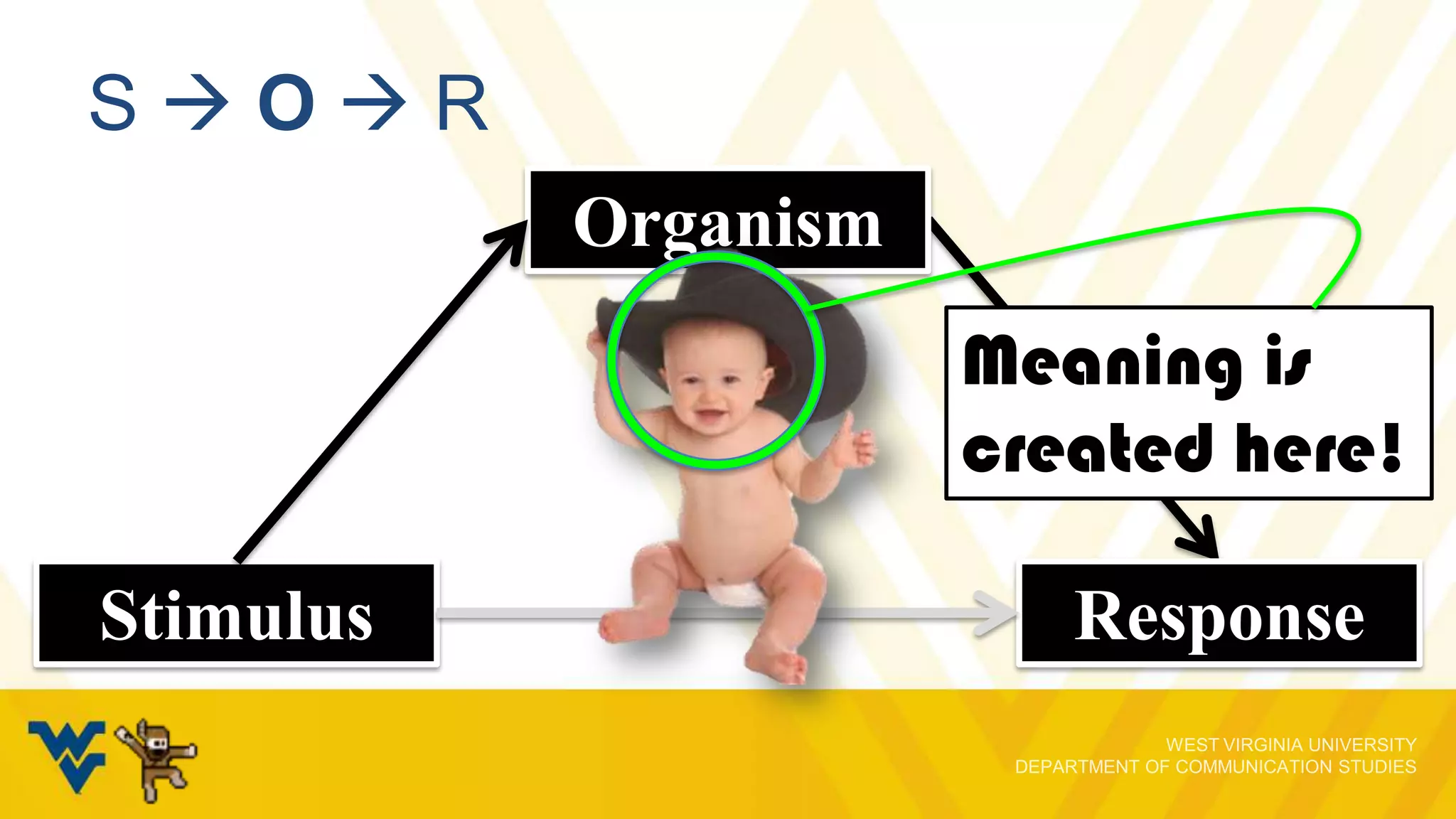

![SOR
• So, do we get to BE Batman, or do we get to
PLAY Batman? Can’t we do BOTH? [NO]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bowmaniuguesttalkfinal21114-140121224630-phpapp02/75/What-is-the-Meaning-of-this-Understanding-the-contentious-relationship-between-videogame-play-and-videogame-narrative-6-2048.jpg)

















![FOR MORE INFORMATION
• Nick Bowman, Ph.D. [CV]
Twitter (@bowmanspartan)
Skype (nicholasdbowman)
nicholas.bowman@mail.wvu.edu
Media and
Interaction Lab
Need references
for cited materials?
Contact me!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bowmaniuguesttalkfinal21114-140121224630-phpapp02/75/What-is-the-Meaning-of-this-Understanding-the-contentious-relationship-between-videogame-play-and-videogame-narrative-35-2048.jpg)
![COLLABORATORS AND
INSPIRATIONS
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Andrew Billings
Frank Biocca
Jennings Bryant
Mun-Yun Chung
Mary Beth Oliver
Art Raney
Ryan Rogers
•
•
•
•
•
•
John Sherry
Brett Sherrick
Ron Tamborini
Rene Weber
Julia Woolley
[everyone mentioned
via Twitter!]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bowmaniuguesttalkfinal21114-140121224630-phpapp02/75/What-is-the-Meaning-of-this-Understanding-the-contentious-relationship-between-videogame-play-and-videogame-narrative-36-2048.jpg)