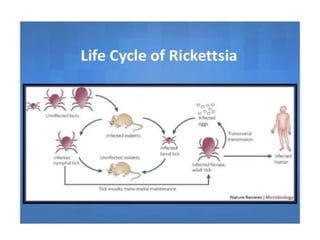
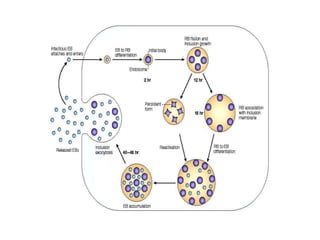
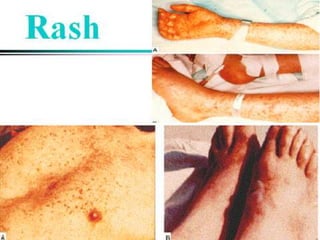
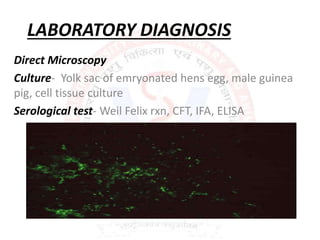
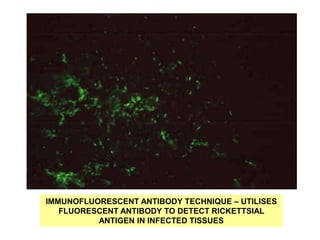
Rickettsia are obligate intracellular parasites that infect arthropods like ticks and mites. They are transmitted to humans via arthropod bites and infect endothelial cells. This causes thrombosis and occlusion of blood vessels, leading to organ damage and acute febrile illness with rash. Some examples include: Rocky Mountain spotted fever caused by R. rickettsii transmitted by ticks; and epidemic typhus caused by R. prowazekii transmitted by body lice. Diagnosis involves microscopy, culture in animals or cells, and serological tests like Weil-Felix and immunofluorescence. Treatment is with doxycycline or tetracycline.