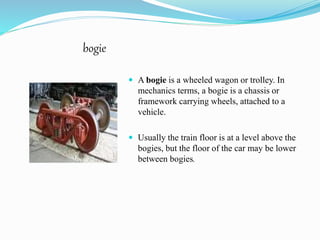
The document provides information about the Carriage and Wagon workshop in Alambagh, Lucknow. It discusses the workshop's history and facilities. The workshop specializes in overhauling, repairing, and restoring coaches and wagons. It performs maintenance like wheel replacement, brake testing, and suspension oil changes. The document also describes different types of coaches and rolling stock, as well as the various levels of train maintenance.