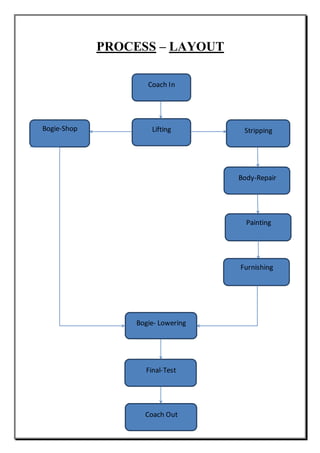
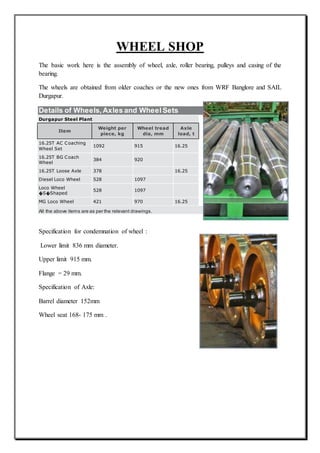
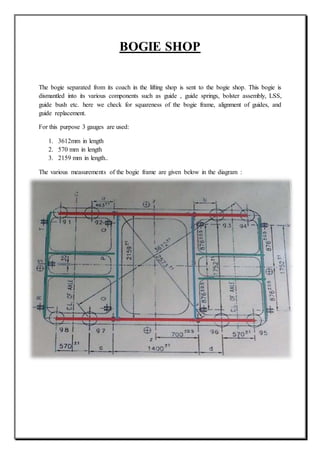
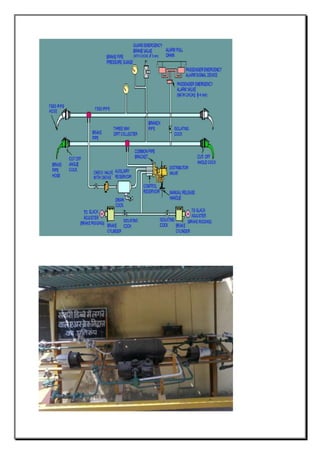
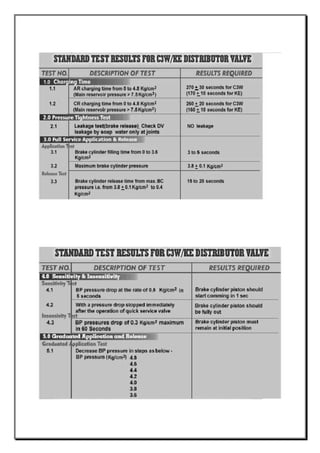
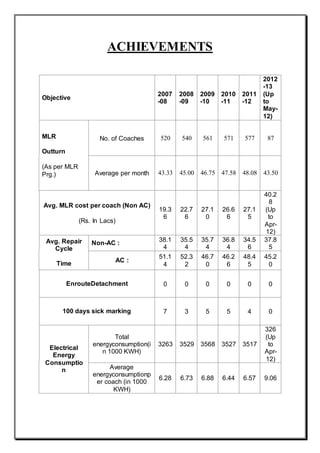
The document provides an overview of the process of mid-life rehabilitation (MLR) of railway coaches at the Coach Rehabilitation Workshop in Bhopal, India. The MLR process involves completely stripping and repairing coaches that are 12-15 years old. Key steps include separating the bogie and shell, stripping components to identify corrosion, heavy corrosion repair, painting, refurbishing interior furnishings, and reassembling. Specialized shops support each step of the process, from lifting and stripping, to body repair, painting, carpentry works, and reinstallation of components. Upon completion, coaches undergo testing before returning to service with an "as new" condition.