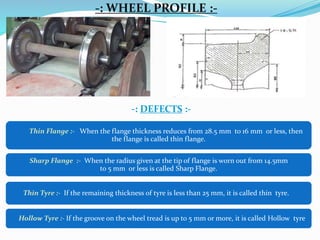
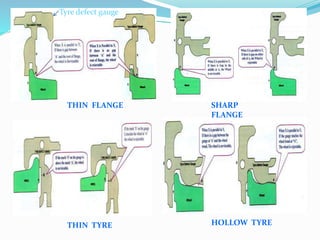
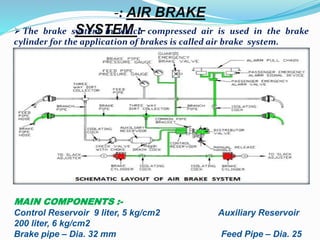
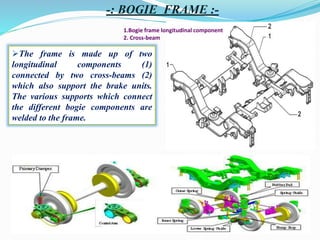
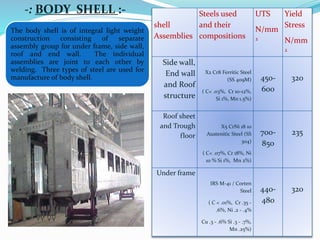
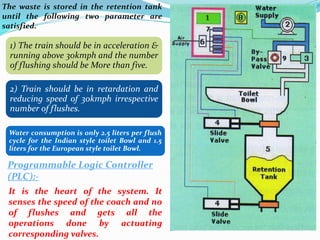
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the Indian Railways, detailing its establishment, maintenance schedules, and essential components of train coaches, such as the wheel profile, air brake system, and body structure. It highlights the evolution and scale of the railway network, being the largest public sector enterprise and informing on various maintenance procedures, including periodic overhauling and controlled discharge toilet systems. Additionally, it mentions the infrastructure and operational details, including water tanks and safety protocols for train operation.