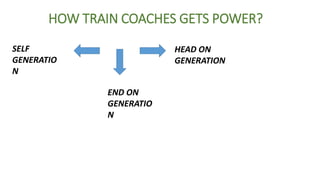
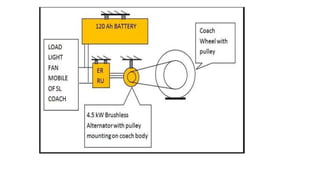
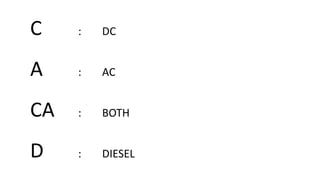
The document discusses train maintenance procedures in India. It describes the different types of maintenance schedules for trains, including washing (every 2,500 km), light maintenance every month, heavy maintenance every 3 months, and overhauls every 9-18 months. The document also outlines the different types of coaches used in Indian trains, including ICF and LHB coaches, and summarizes the key differences between them. Finally, it provides a brief overview of how train coaches receive power, including through head-on generation, self-generation, and end-on generation.