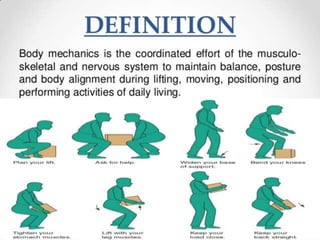
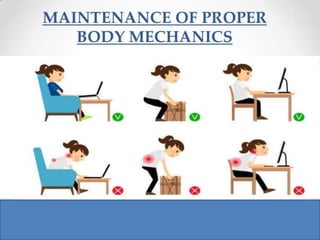
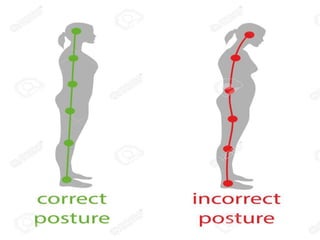
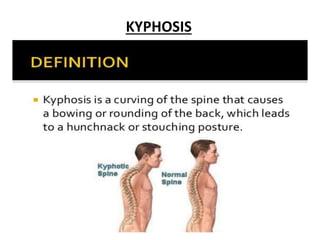
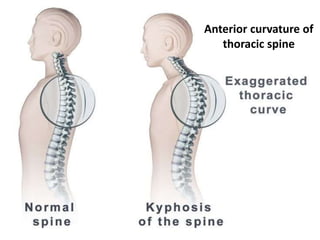
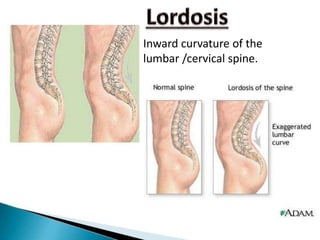
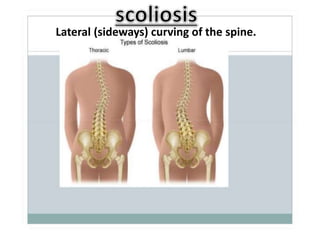
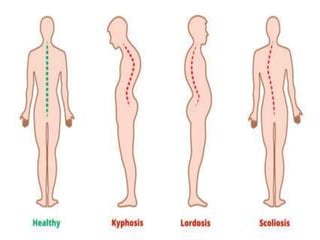
Body mechanics refers to the efficient use of the body as a machine for locomotion and movement. It is related to proper functioning of bones, joints, muscles, nerves, and the brain to maintain posture and balance. Some key principles of good body mechanics include facing the direction of movement to prevent spine twisting, dividing tasks between arms and legs to reduce back injury risk, and using rolling and turning which require less force than lifting. Maintaining proper alignment and mobility is also important for reducing fatigue and injury risk. Factors like age, energy level, lifestyle, fear, pain and disabilities can impact a person's mobility. Prolonged immobility can increase risks of issues like pneumonia, blood clots, pressure sores,