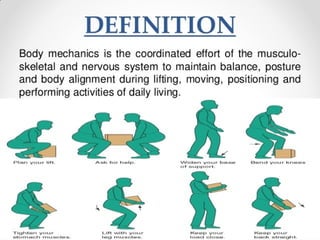
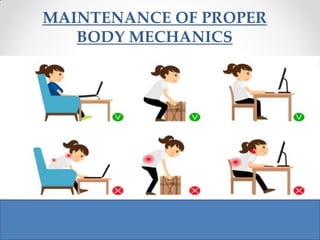
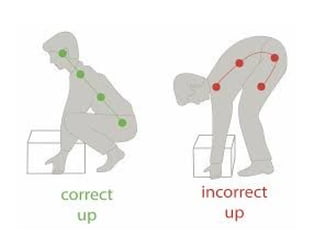
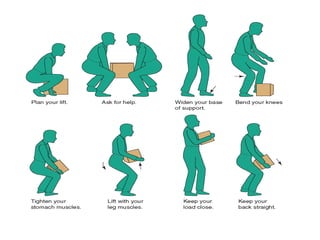
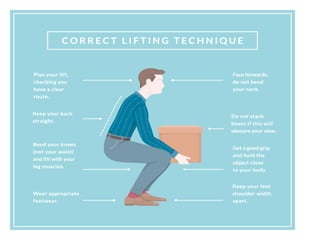
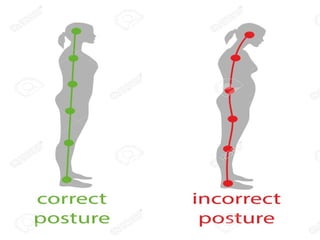
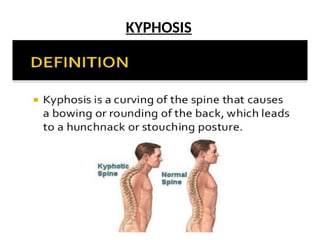
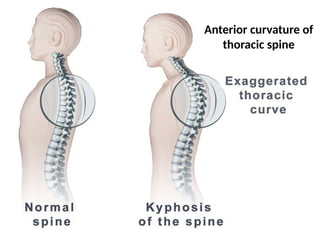
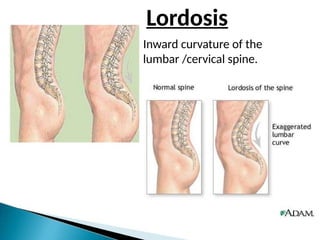
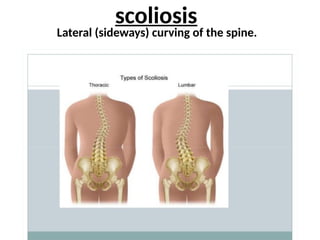
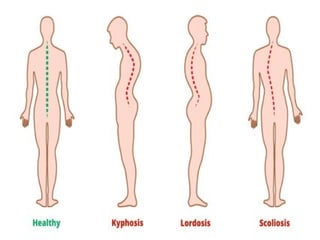
The document discusses the principles of body mechanics, which involve the efficient use of the body to maintain posture and balance while preventing injury through proper alignment and movement techniques. It outlines factors affecting mobility, including age, energy levels, lifestyle, fear, pain, and disability, as well as hazards associated with immobility like pneumonia and pressure ulcers. The document also addresses postural abnormalities, such as kyphosis, lordosis, and scoliosis.