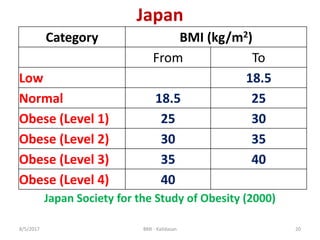
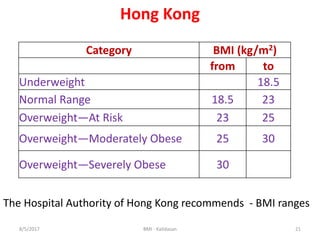
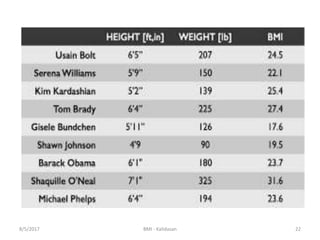
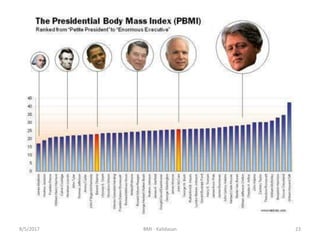
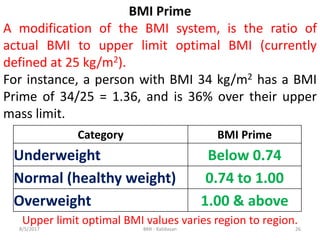
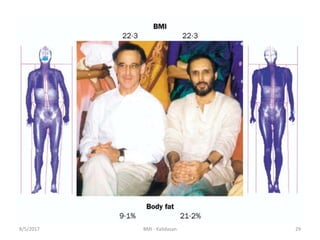
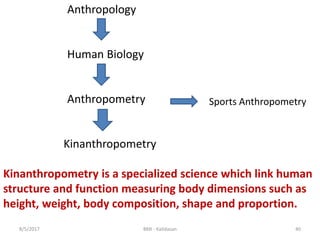
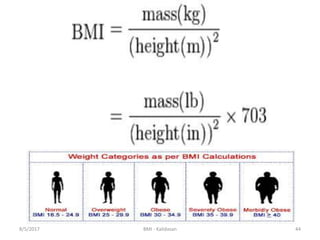
The document discusses Body Mass Index (BMI) which is a measure of body fat based on height and weight. It was initially devised in 1830 by Adolphe Quetelet and the term "BMI" was coined in 1972 by Ancel Keys. The document provides details on calculating BMI, BMI categories and cut-offs, limitations of BMI, diseases associated with overweight and obesity, and alternatives to BMI for measuring body composition. It also discusses the history and applications of anthropometry and kinanthropometry in assessing body measurements.
![Body Mass Index [BMI] (or) Quetelet index
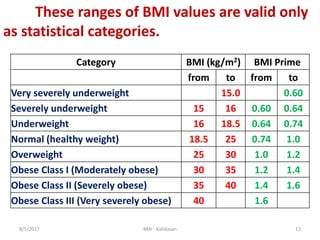
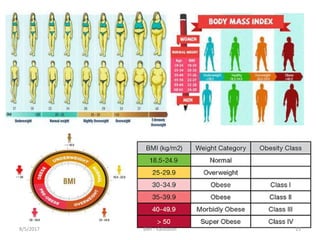
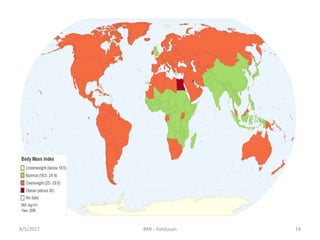
It is calculated from once height and weight.
BMI is measure of body fat based on height
and weight.
It is a useful measure of
overweight
obesity
28/5/2017 BMI - Kalidasan](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bmi-kalidasan-170805034256/85/Body-Mass-Index-2-320.jpg)