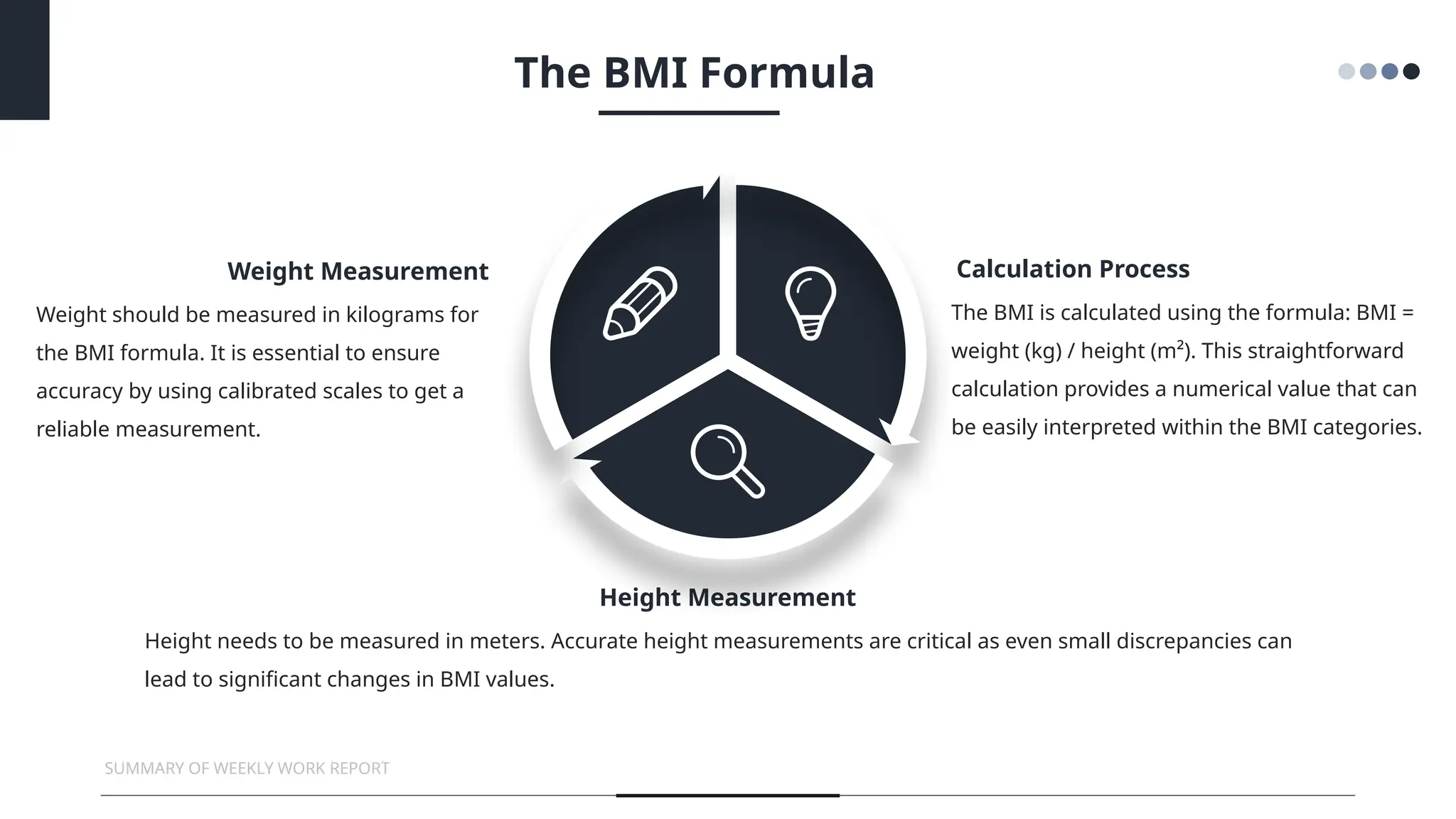
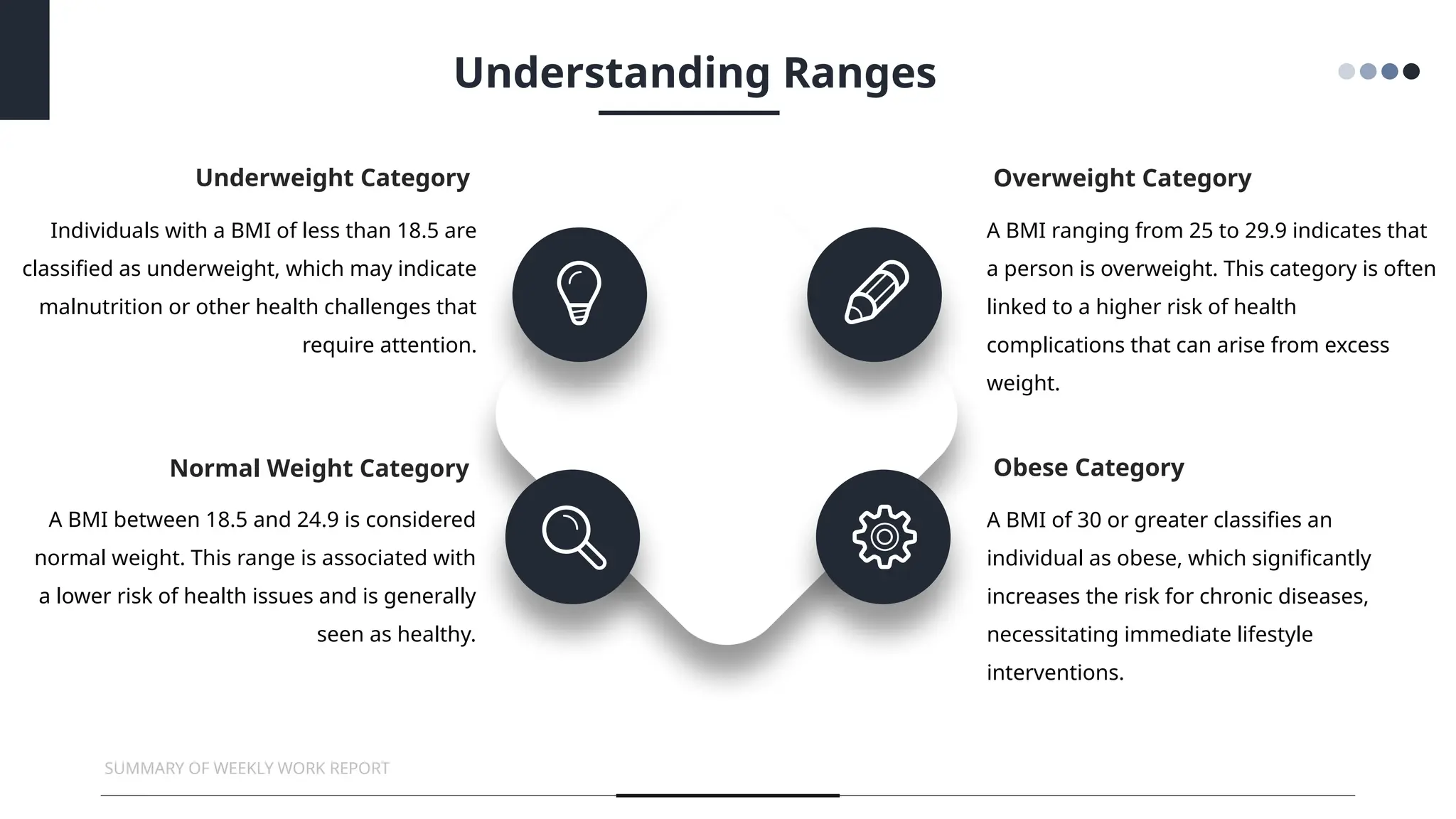
The document provides an overview of Body Mass Index (BMI), discussing its calculation, categories, and significance for health assessment. It highlights the limitations of BMI, such as its inability to differentiate between muscle and fat, and emphasizes the importance of monitoring BMI alongside other health markers. The conclusion urges individuals to consult healthcare professionals for personalized health advice and to adopt healthier lifestyle practices.