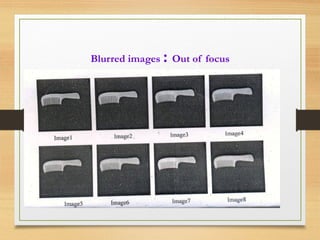
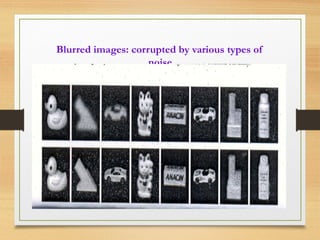
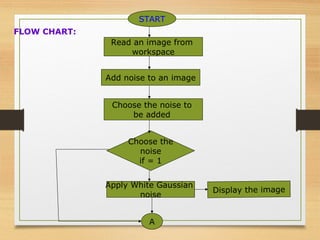
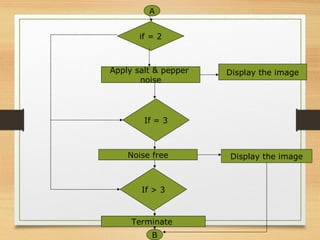
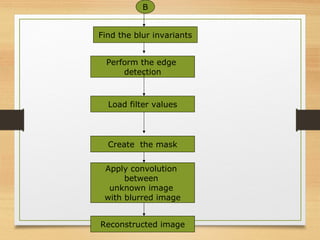
The document discusses a project focused on recognizing blurred images using orthogonal moments, which offer improved robustness to noise compared to existing methods based on complex moment invariants. It outlines the challenges of image degradation due to various factors like lens aberration and atmospheric conditions, and presents a systematic approach for image recognition and reconstruction. The proposed system aims to enhance accuracy in applications such as image security, 3D scene analysis, and automatic tracking.