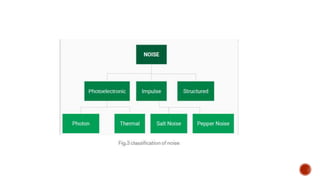
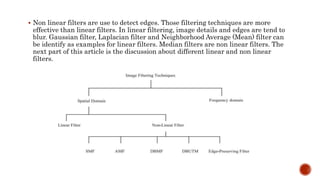
Digital image processing techniques can be used to enhance images by modifying pixel values using filters. Filters are classified as either spatial or frequency domain filters, with non-linear filters being more effective at edge detection than linear filters. The median filter is a common non-linear filter that replaces pixel values with the median of neighboring pixels to reduce salt-and-pepper noise. Image restoration techniques aim to reduce noise and recover lost resolution, such as by using deconvolution in the frequency domain to undo the effects of blurring.









![ A(x,y) = H(x,y) + B(x,y) Where, A(x,y)= function of noisy image, H(x,y)= function of
image noise , B(x,y)= function of original image.But in theoretical terms, a picture
that we look at is a function of image intensity at a particular position in the
image. I.e I(x,y) is an image function where I = Intensity at position (x,y) in an
image.
Types of digital images:
There are typically three types of digital images.
Binary Images
Gray Scale Images
Color Images
So, it can be stated as, f: [a,b] * [c,d] -> [min,max]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vs-221031165757-8dd10af2/85/vs-pptx-11-320.jpg)