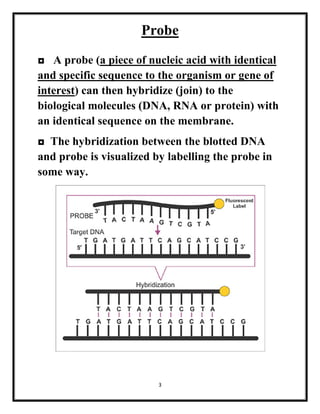
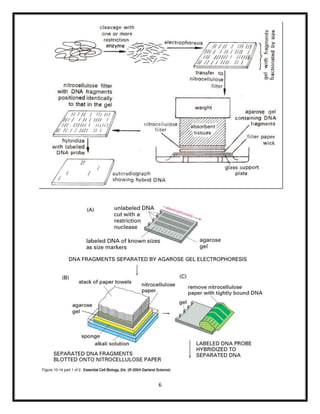
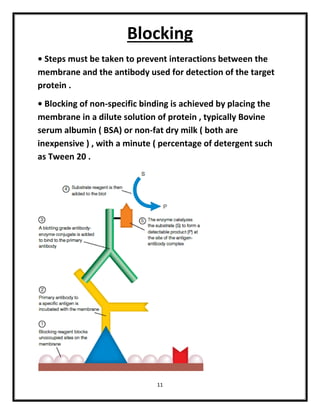
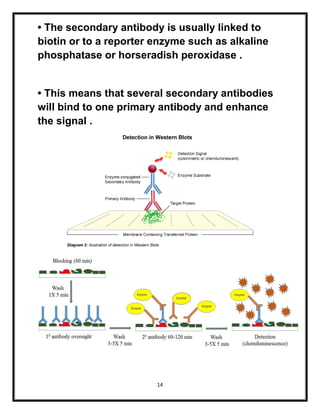
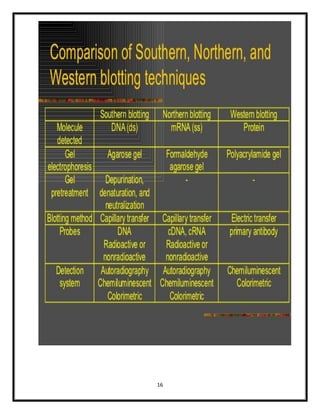
The document explains various blotting techniques used in molecular biology, including Southern, Northern, Western, and Eastern blotting, each designed to transfer different biological molecules like DNA, RNA, or proteins to membranes for analysis. It describes the fundamental processes involved such as gel electrophoresis, transfer, hybridization with probes, and detection methods. Advantages and disadvantages of these techniques are also discussed, highlighting their applications in studying gene expression and protein modifications.