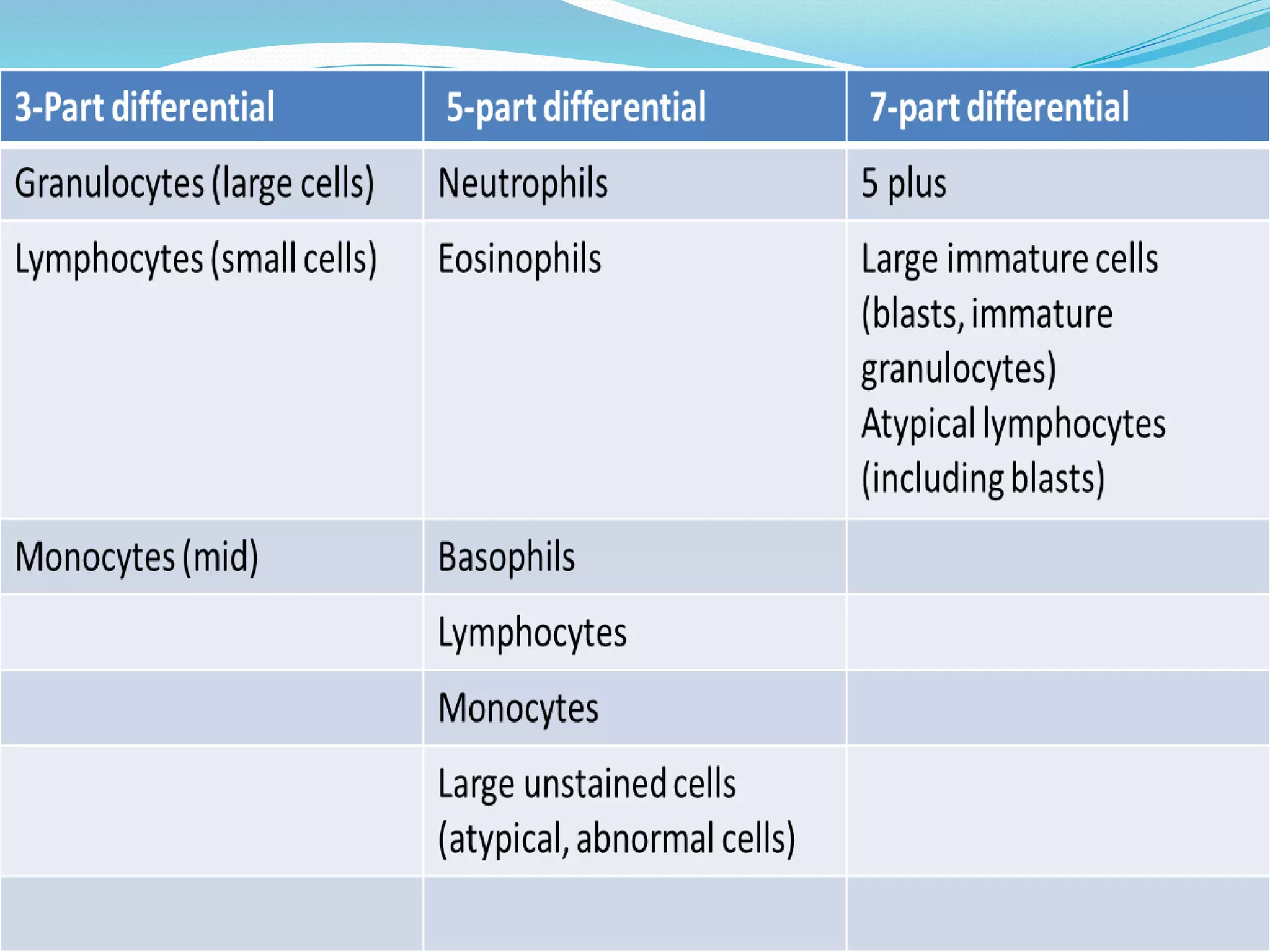
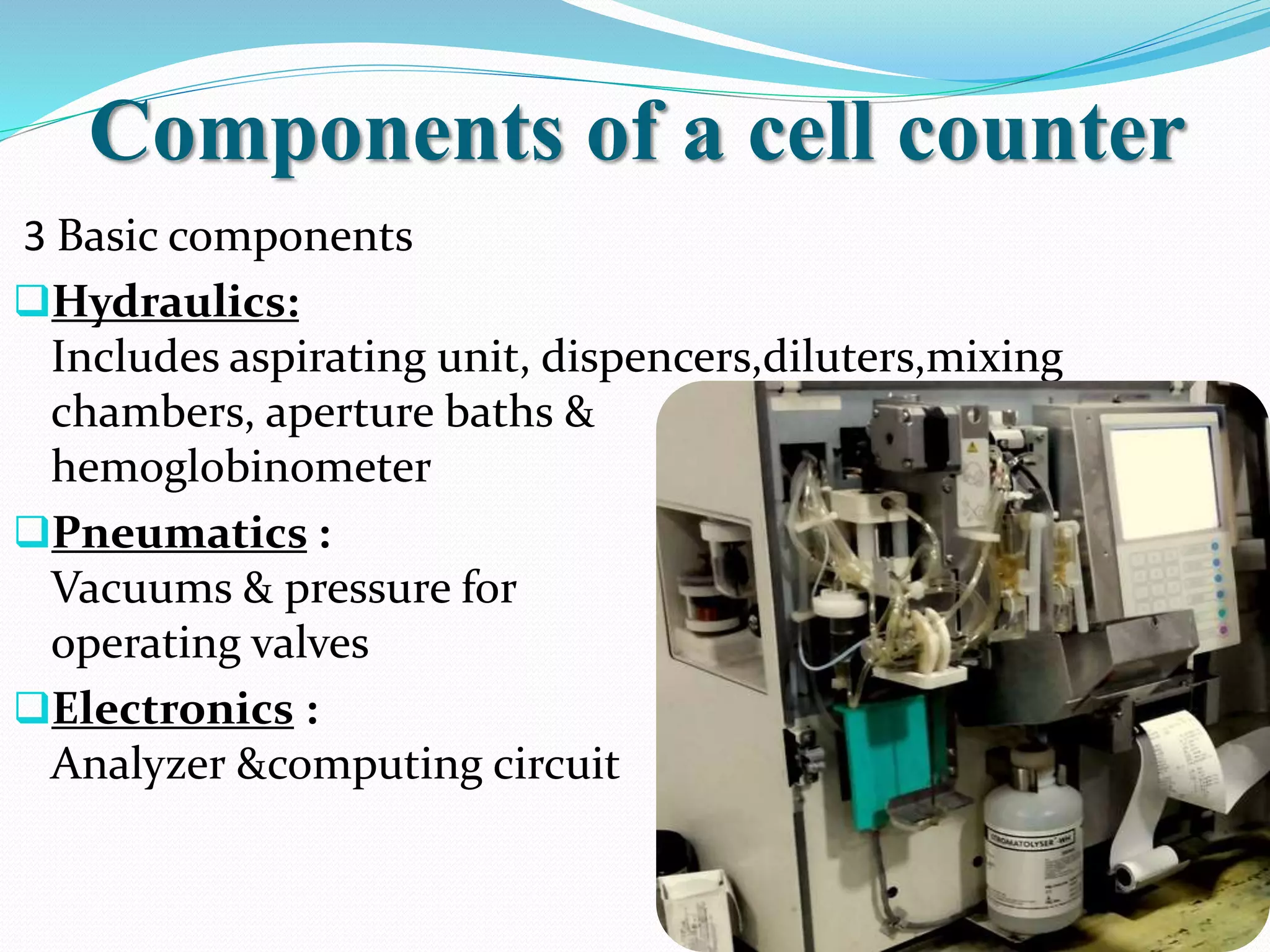
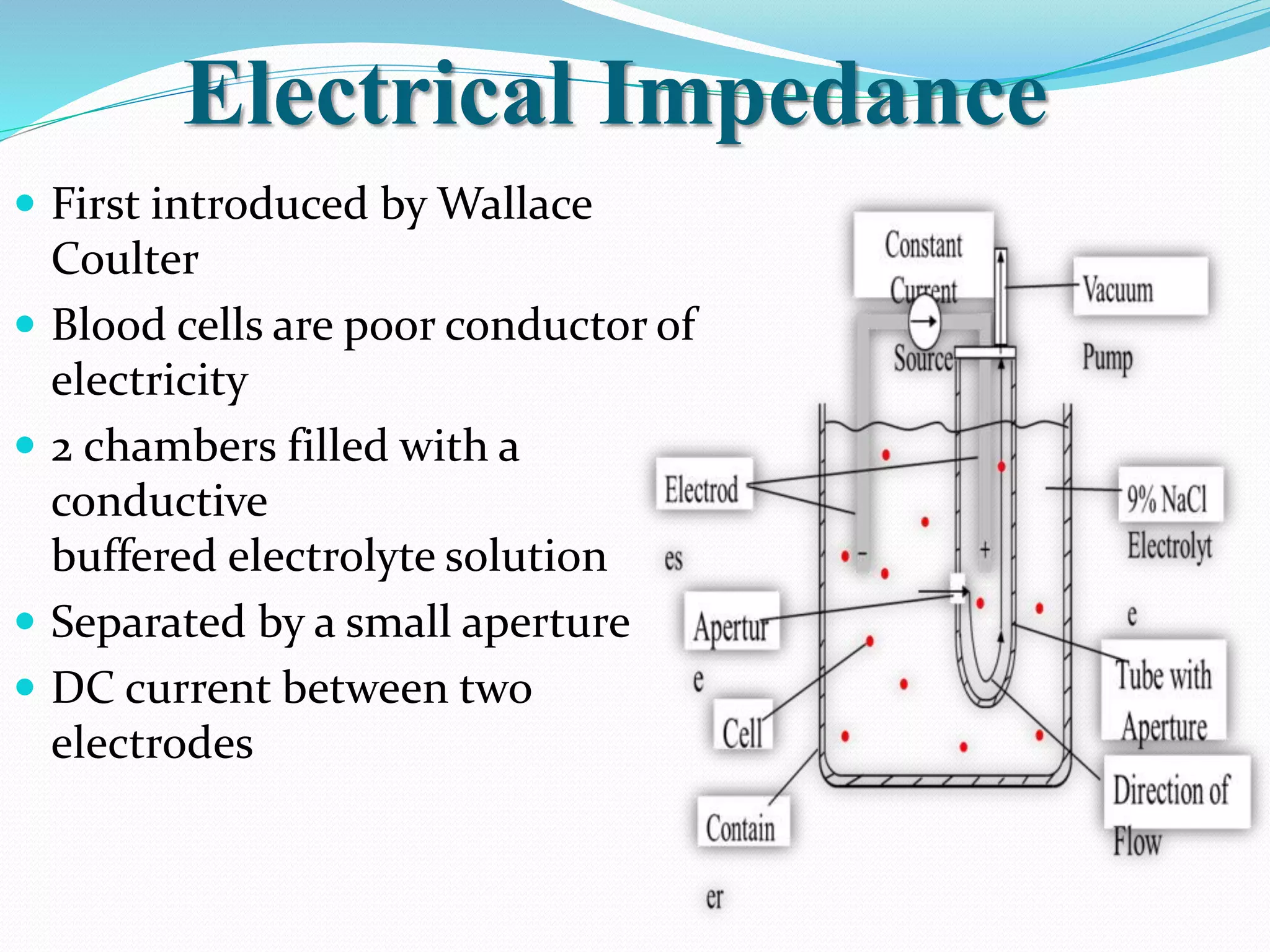
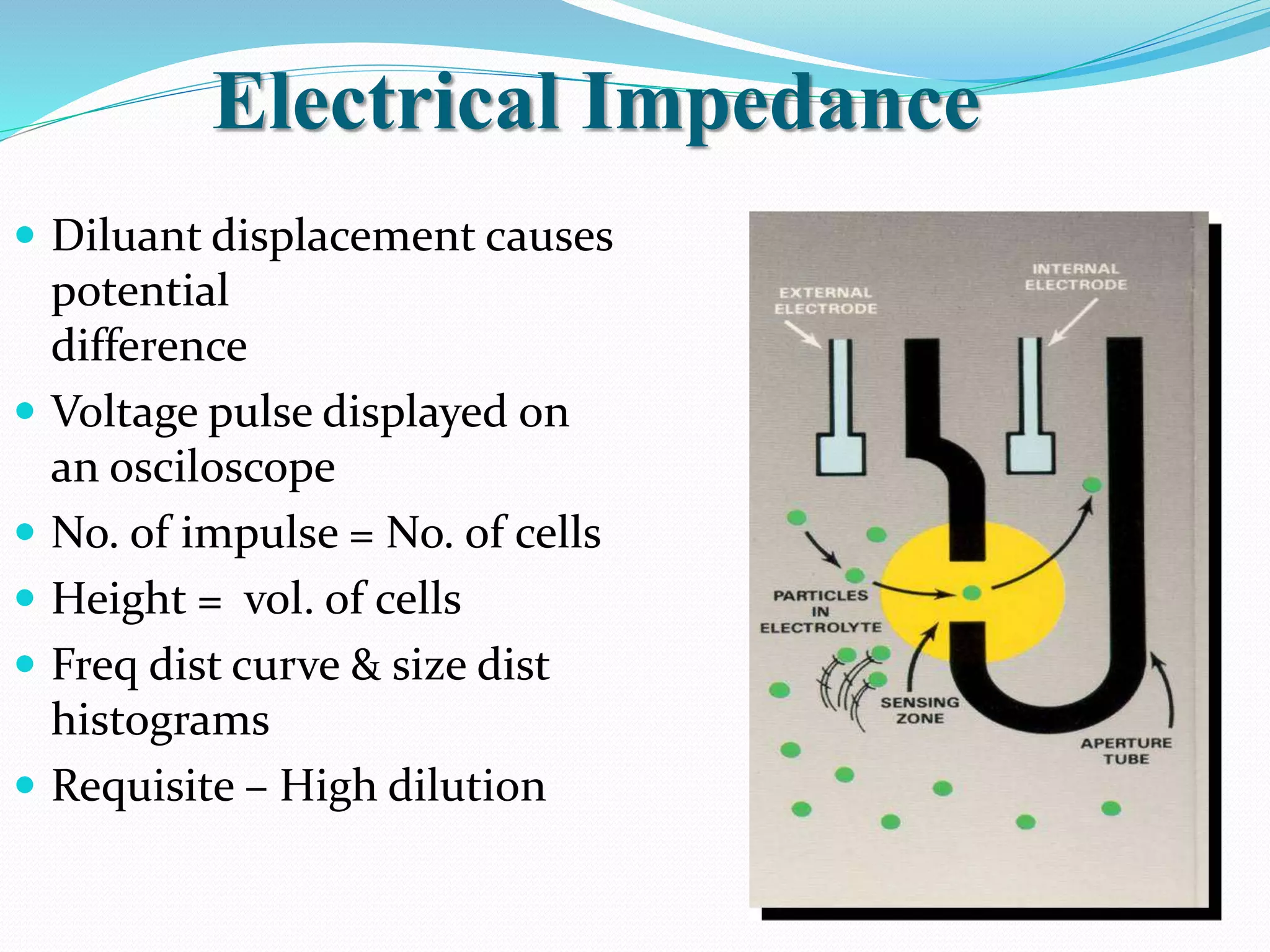
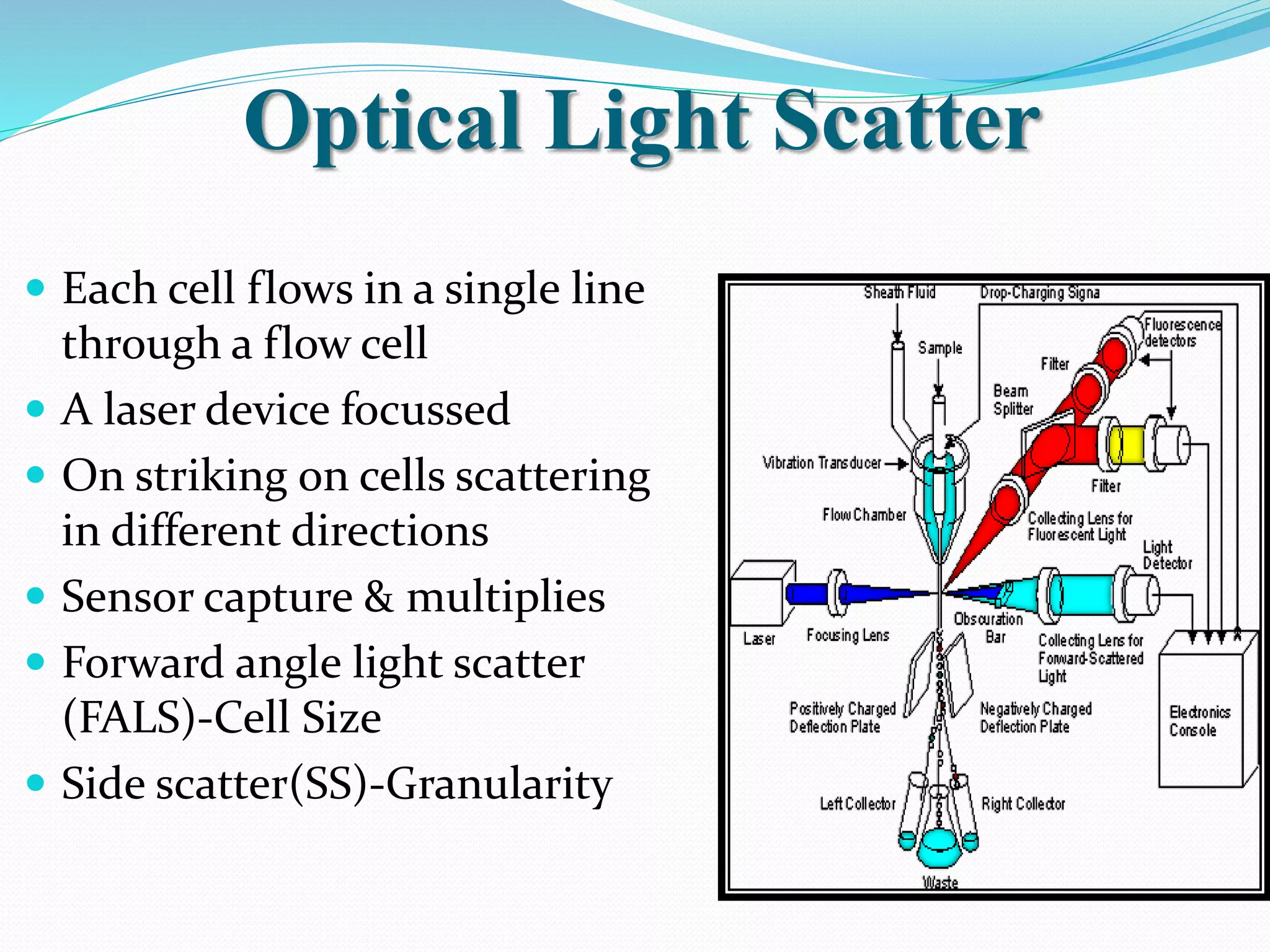
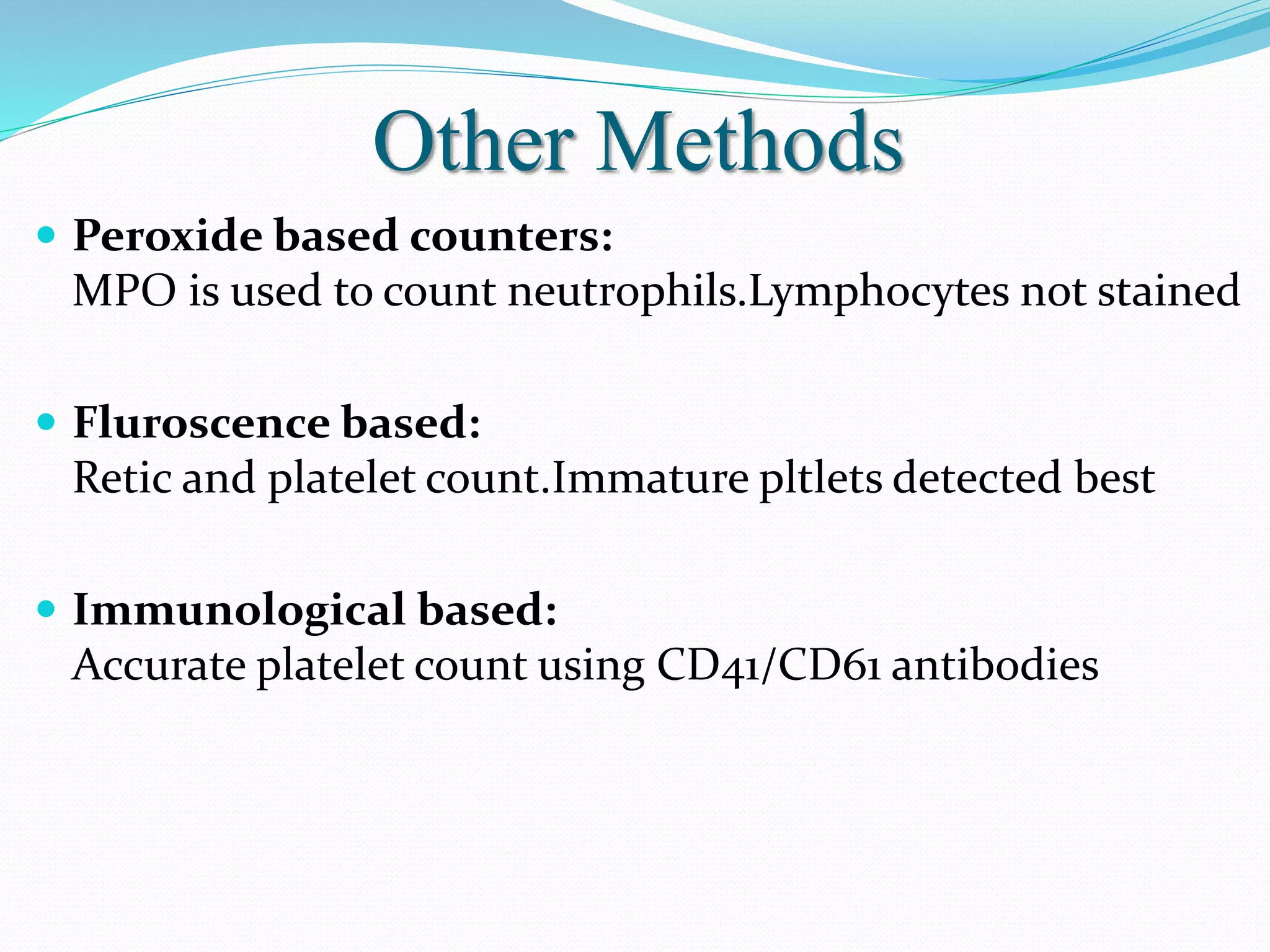
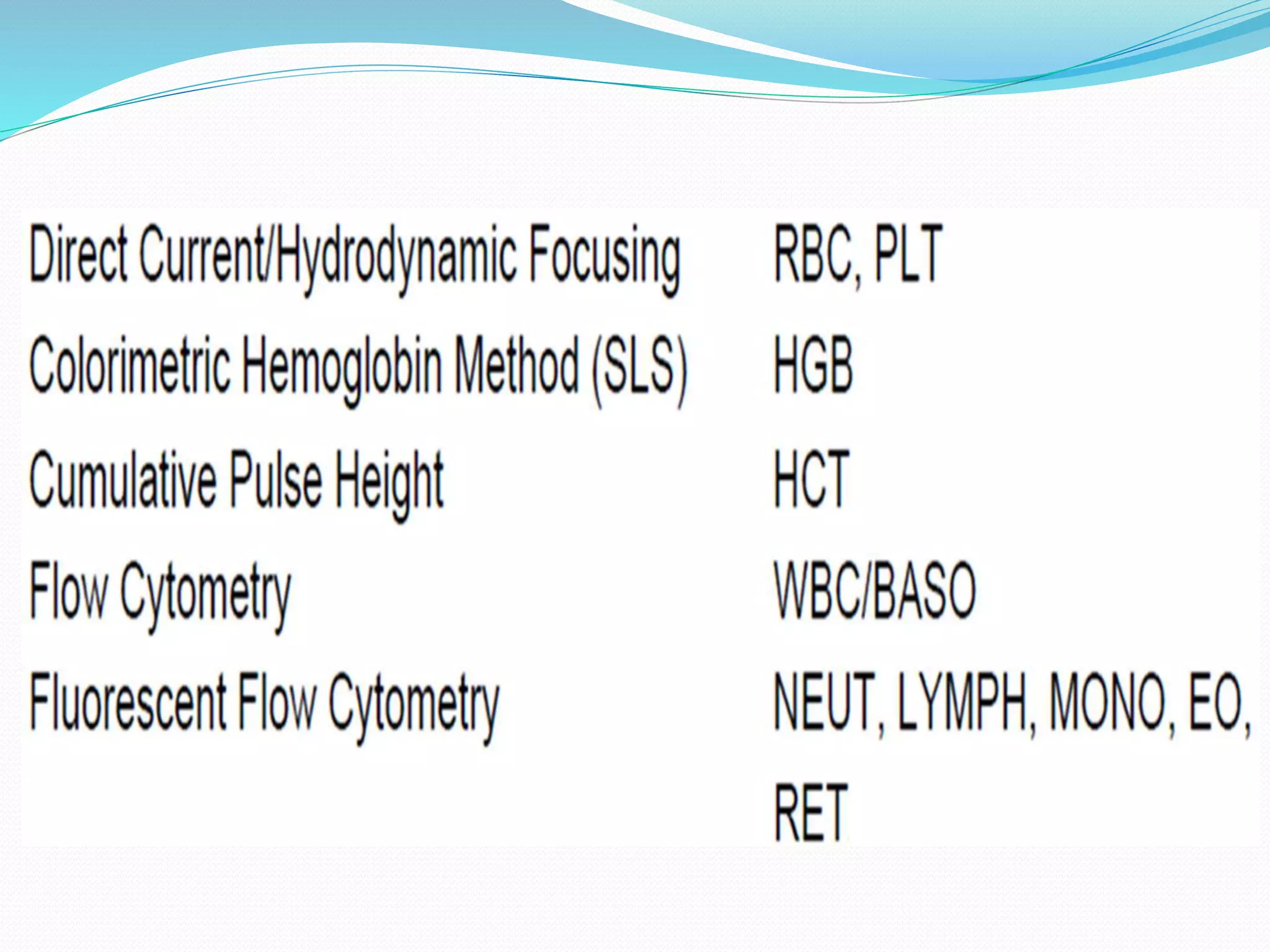
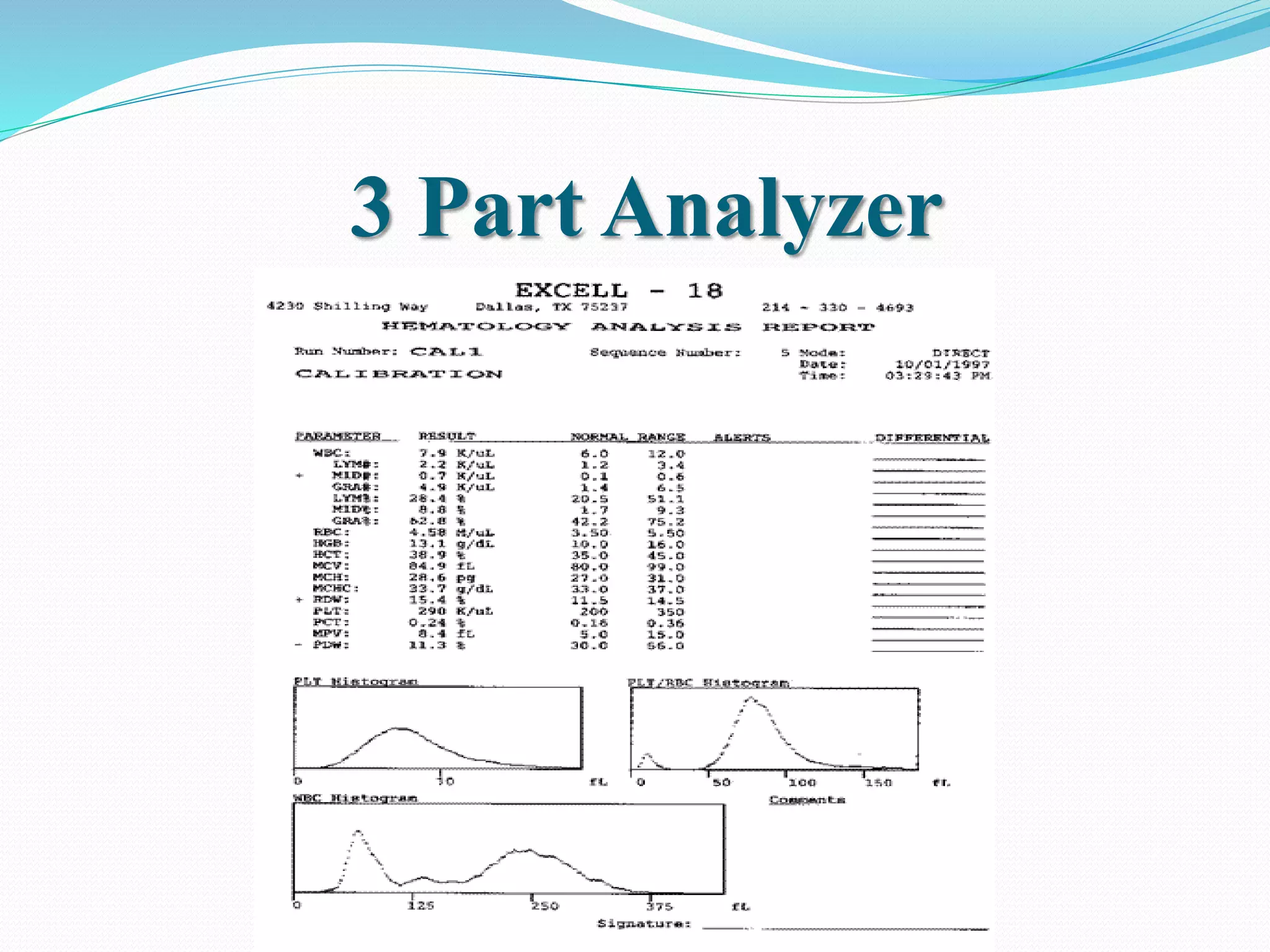
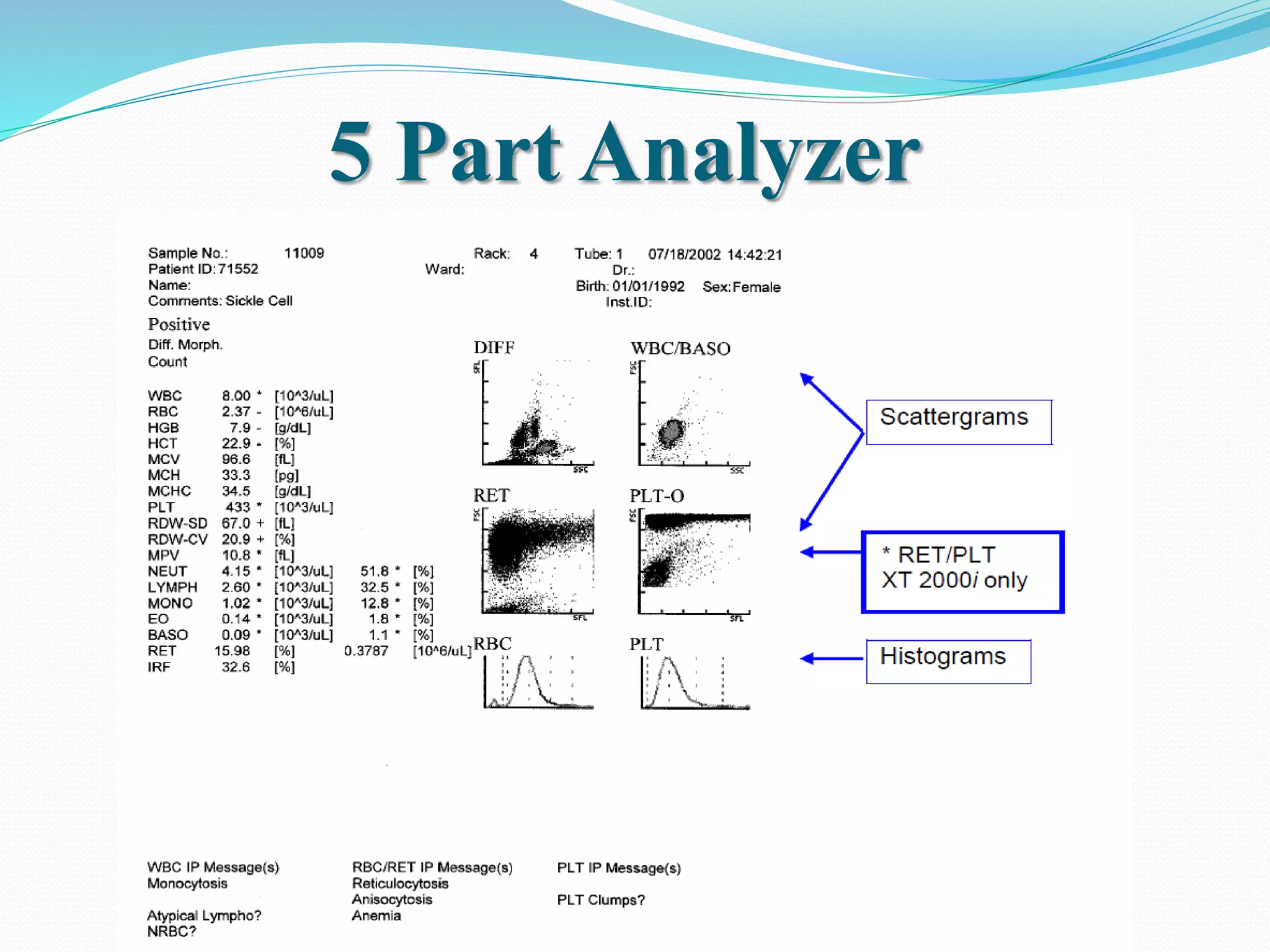
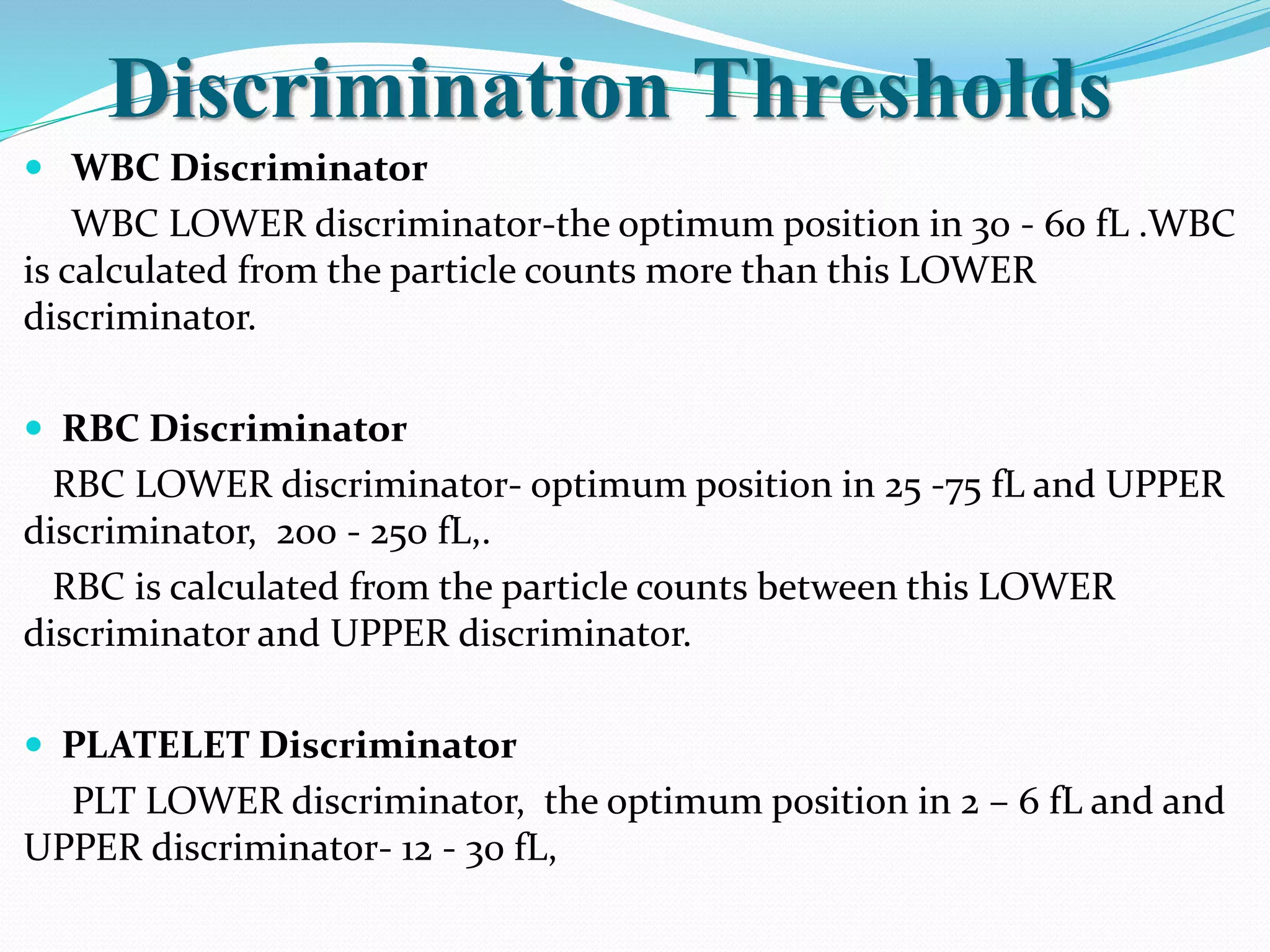
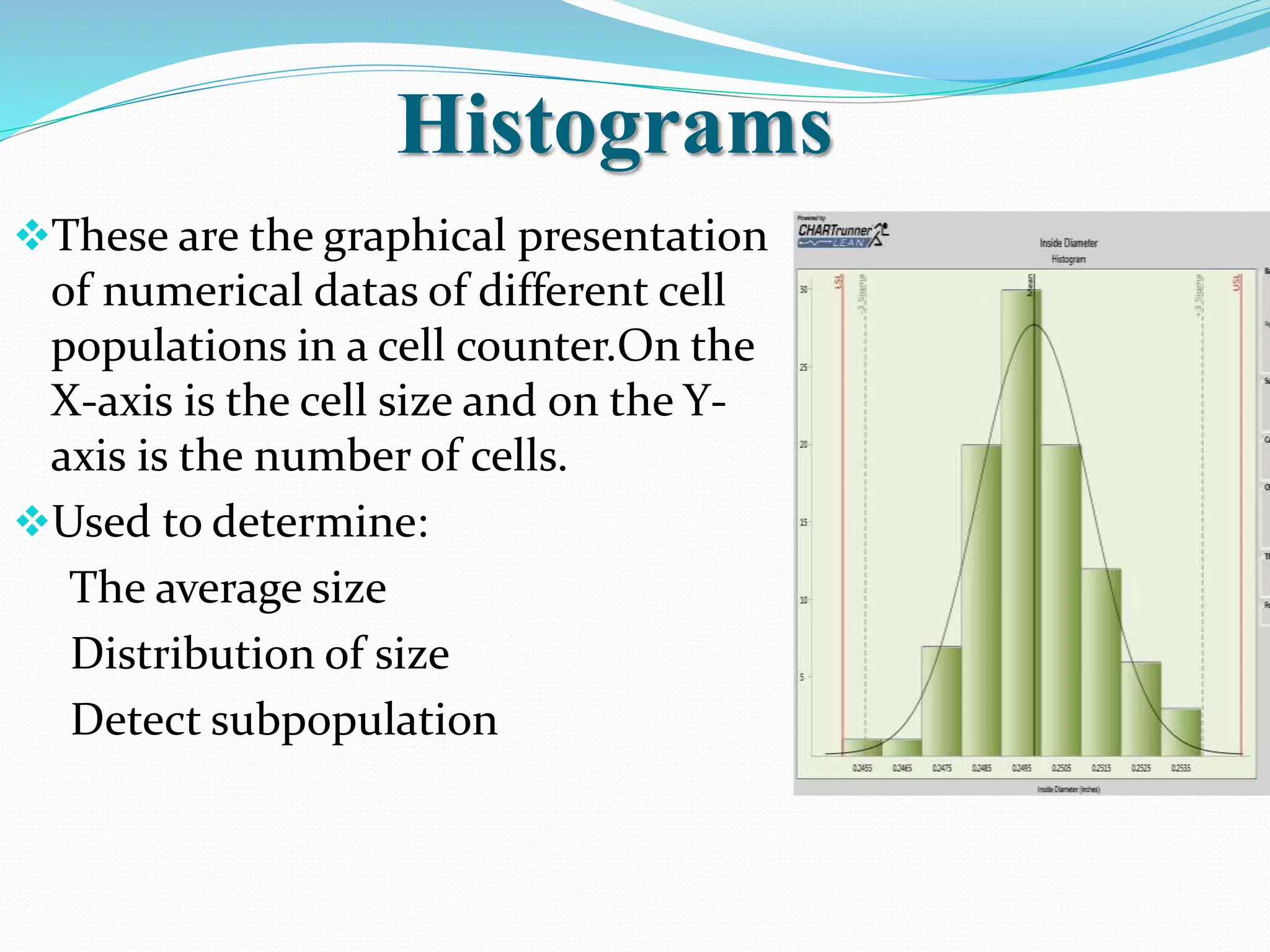
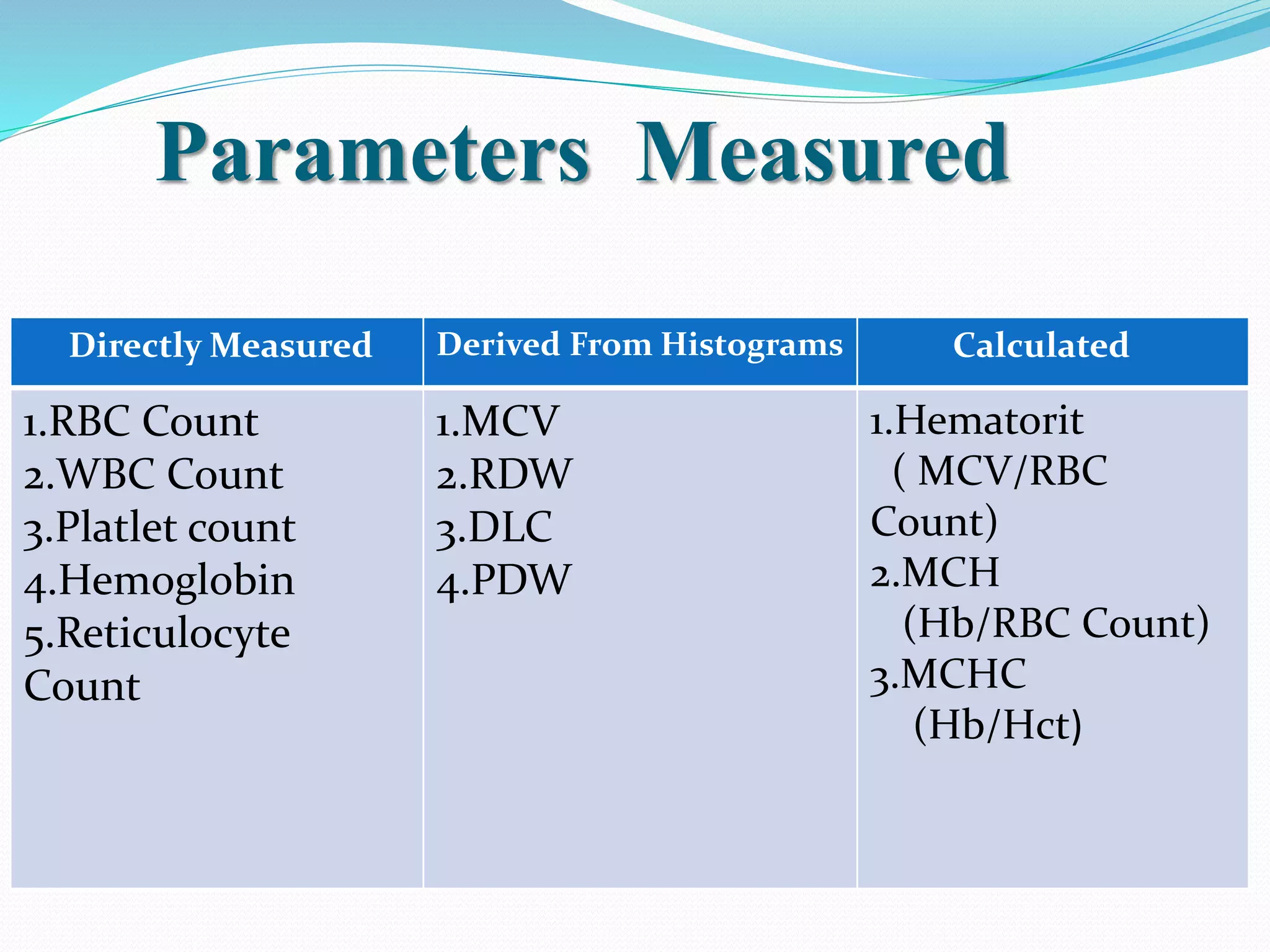
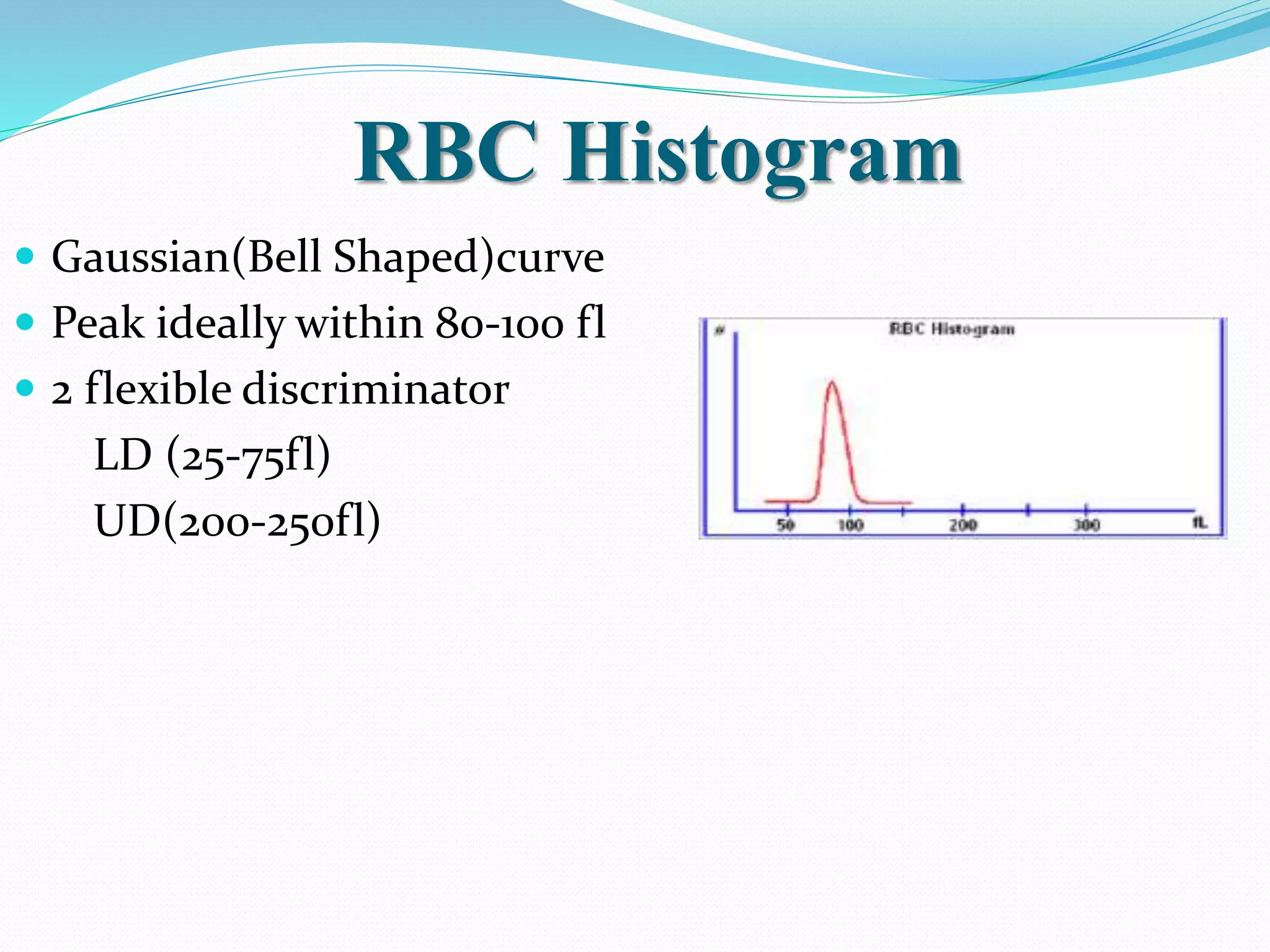
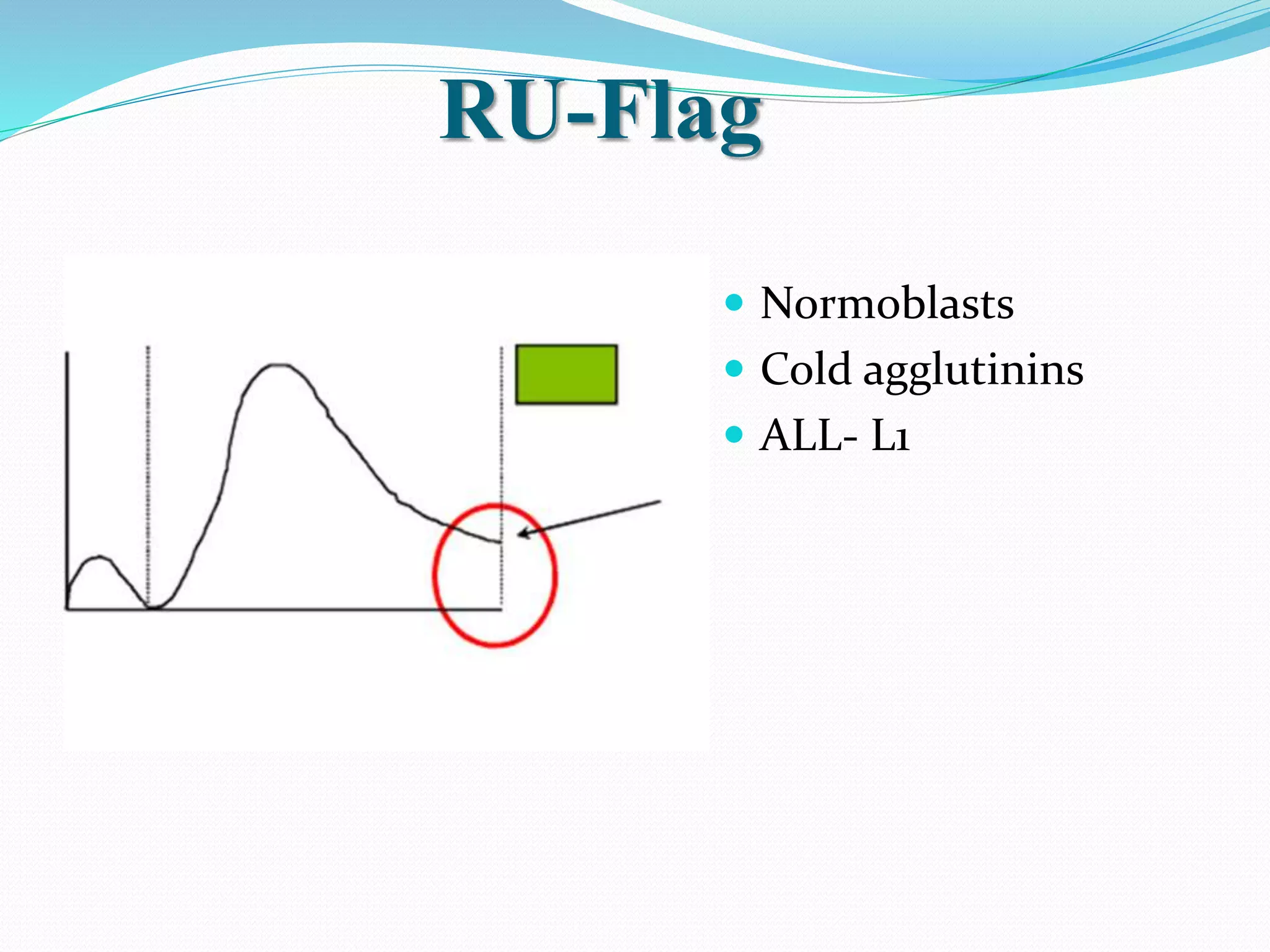
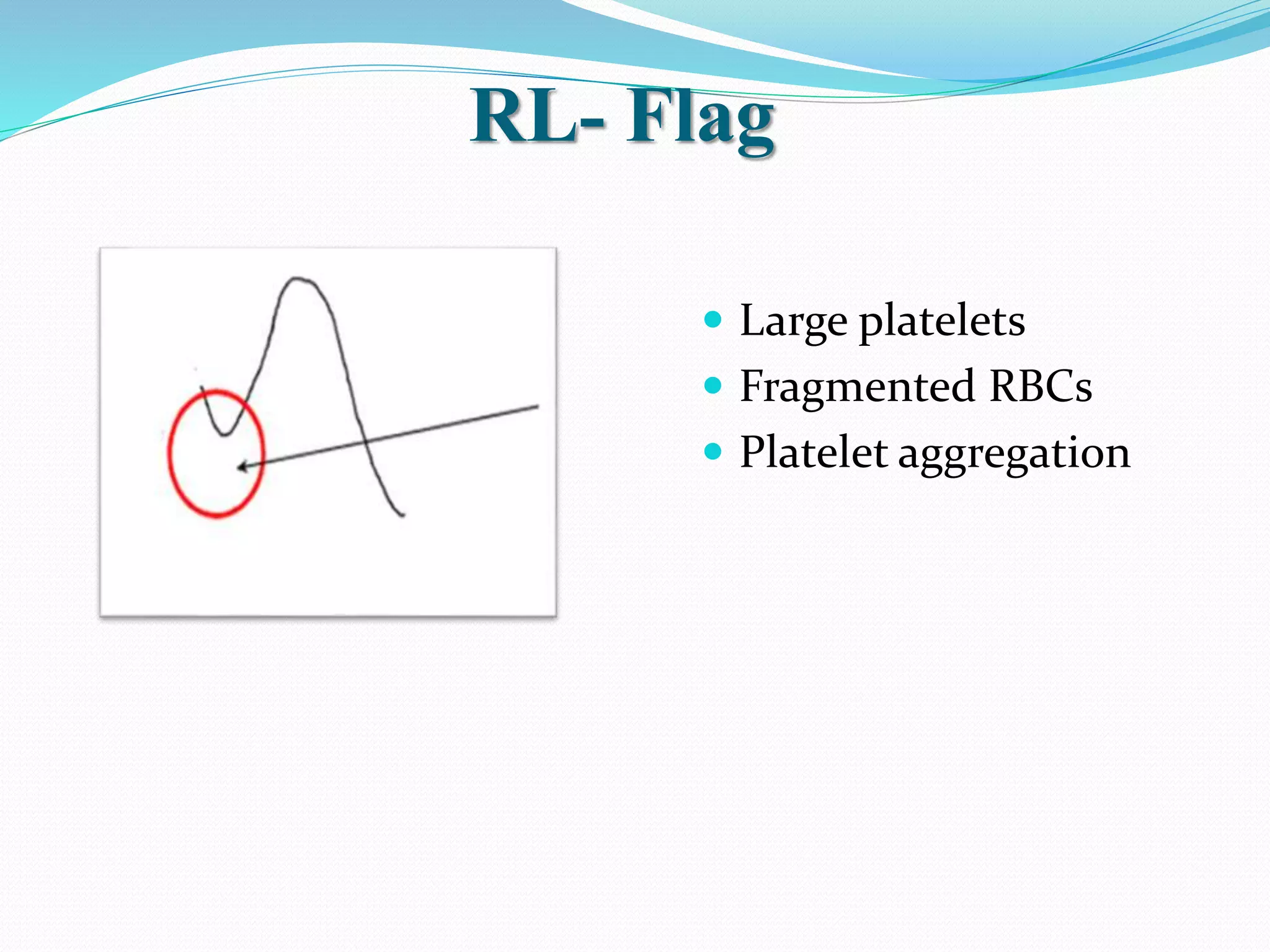
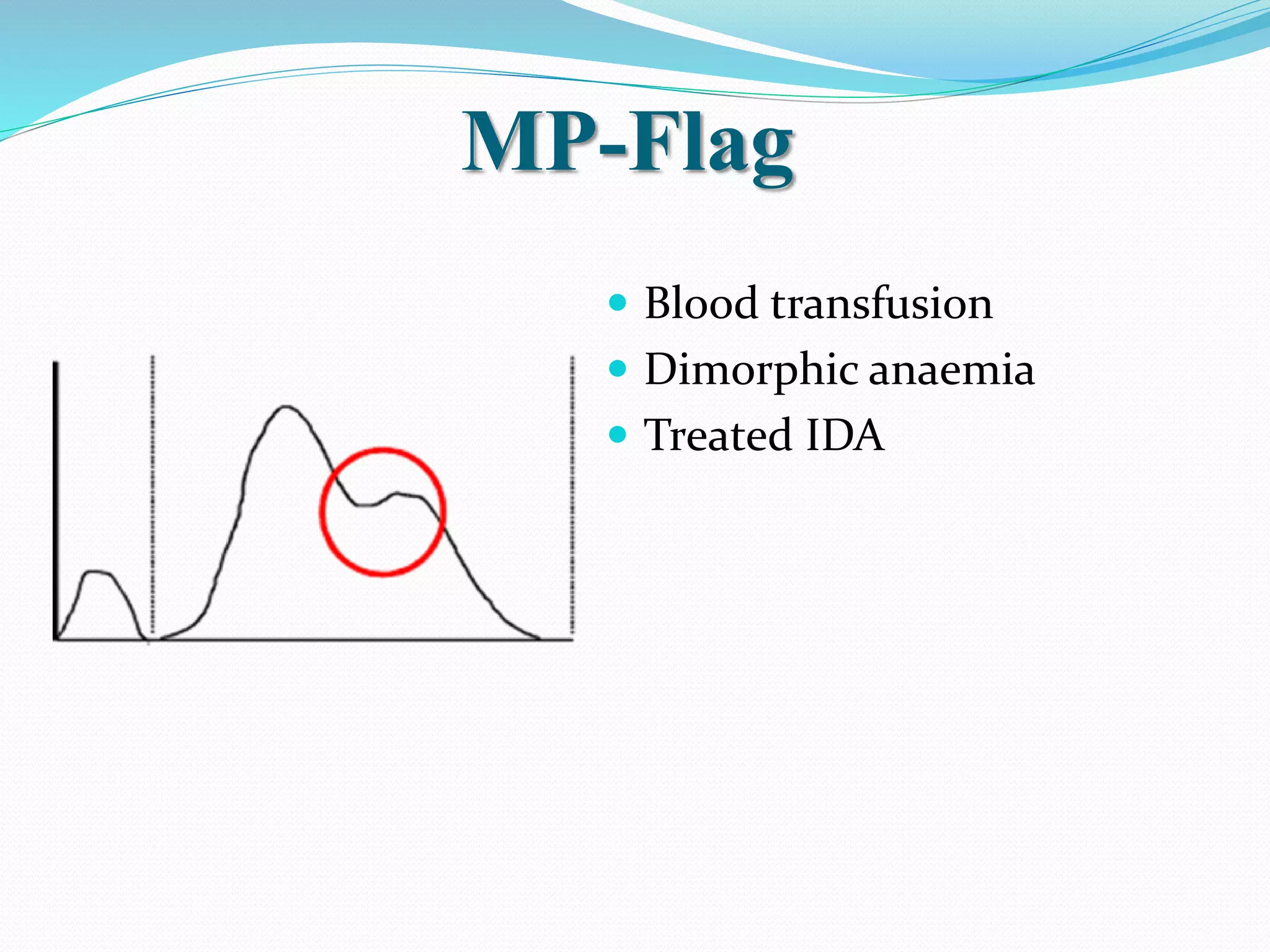
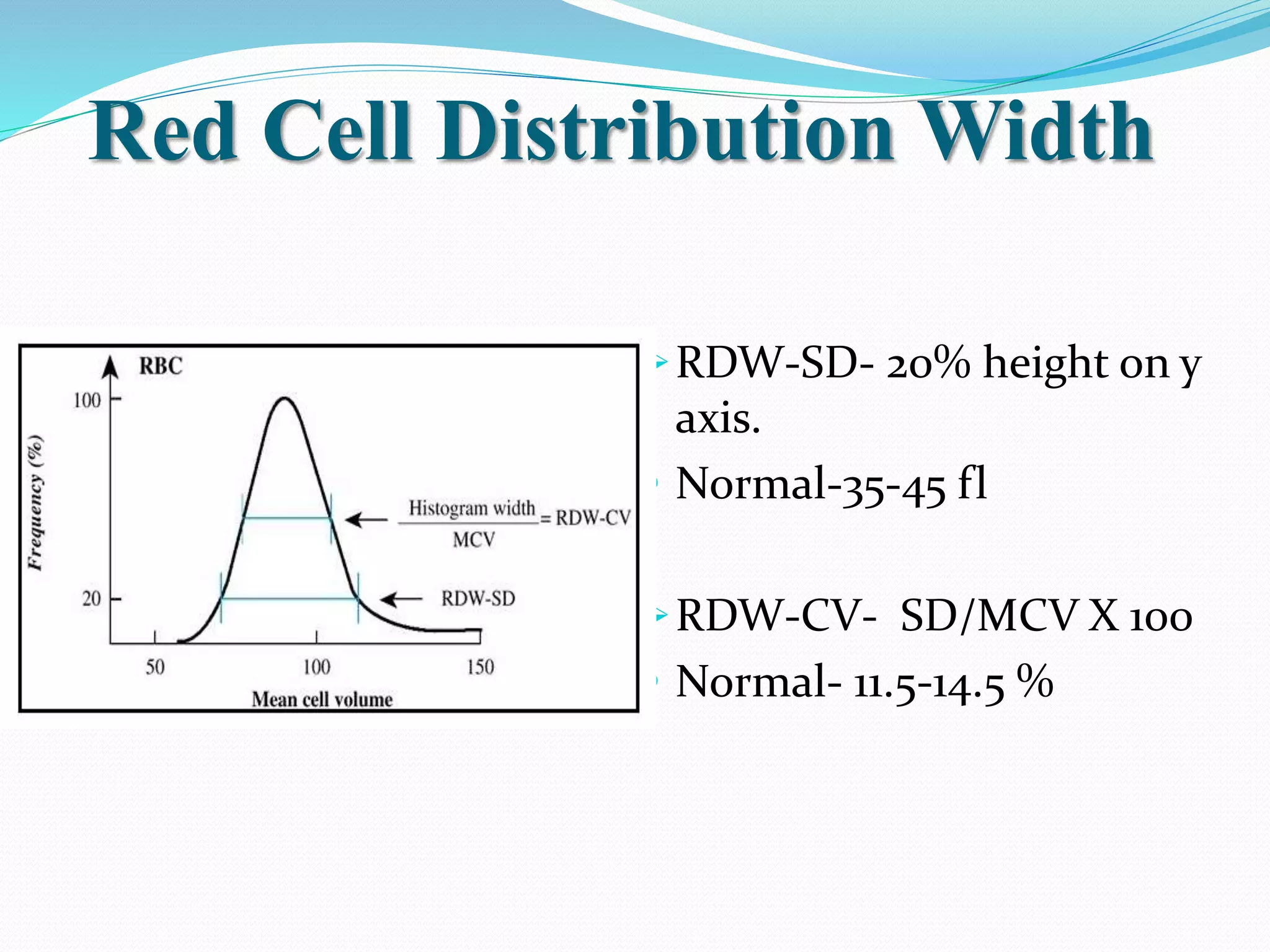
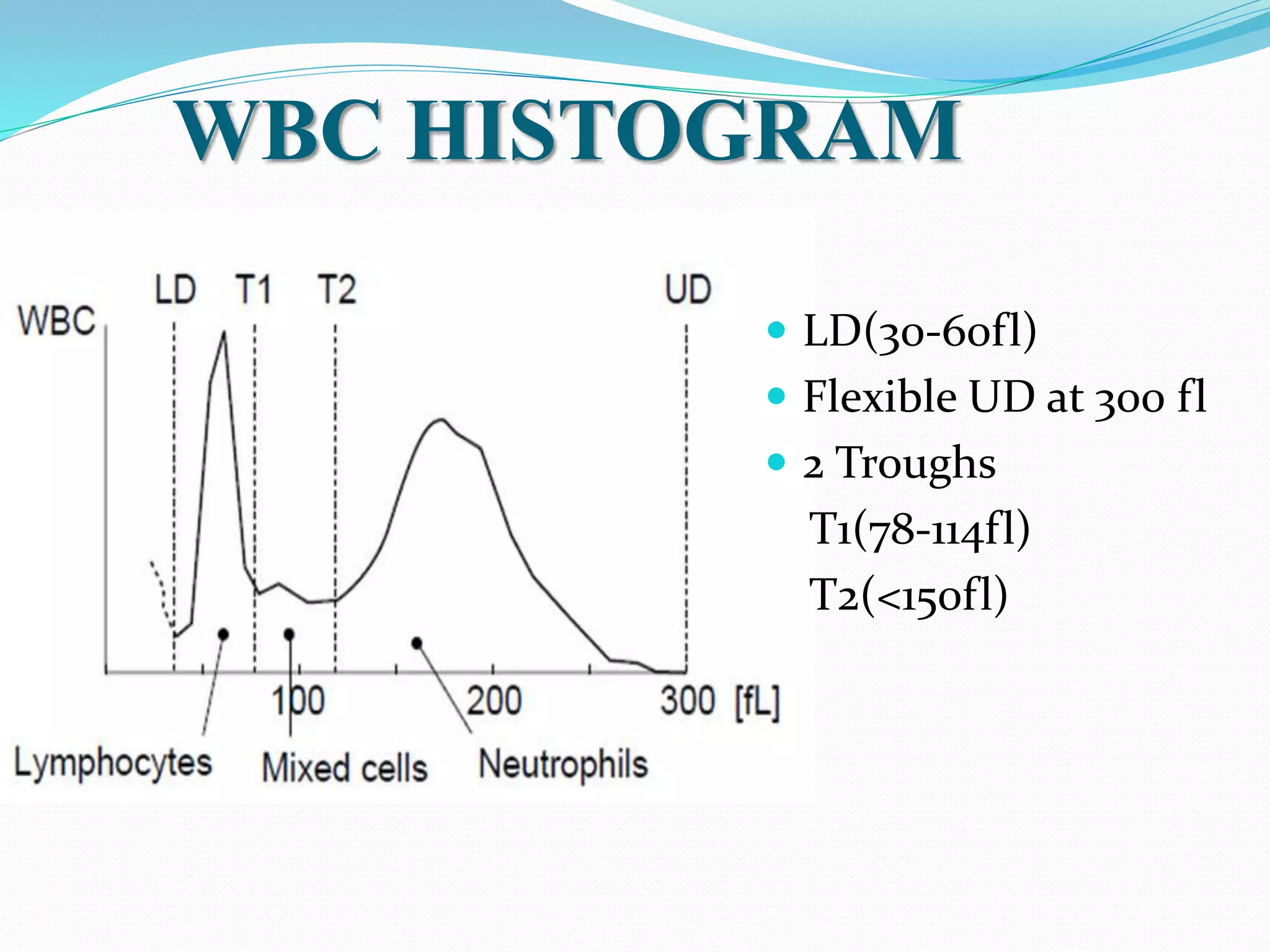
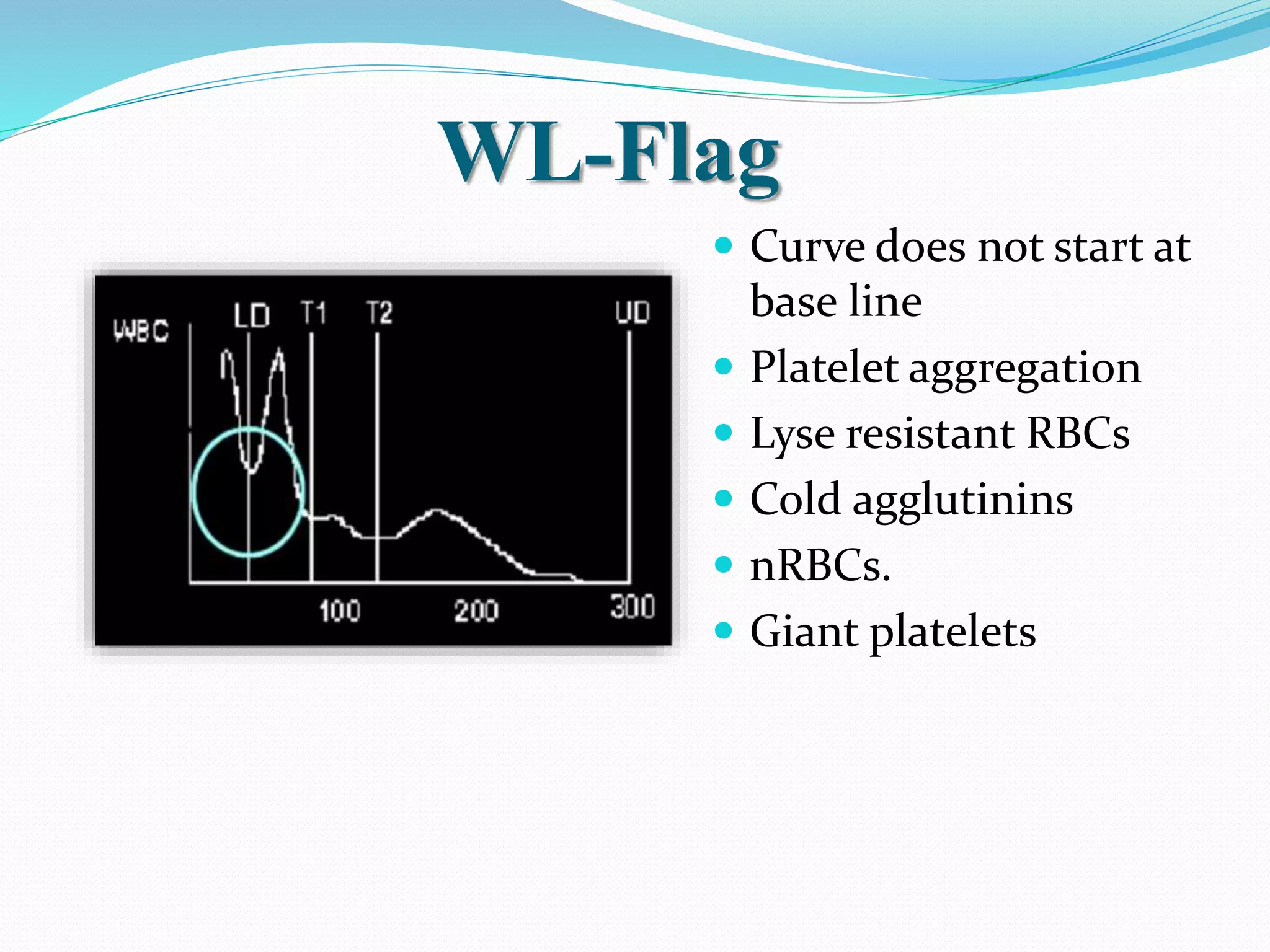
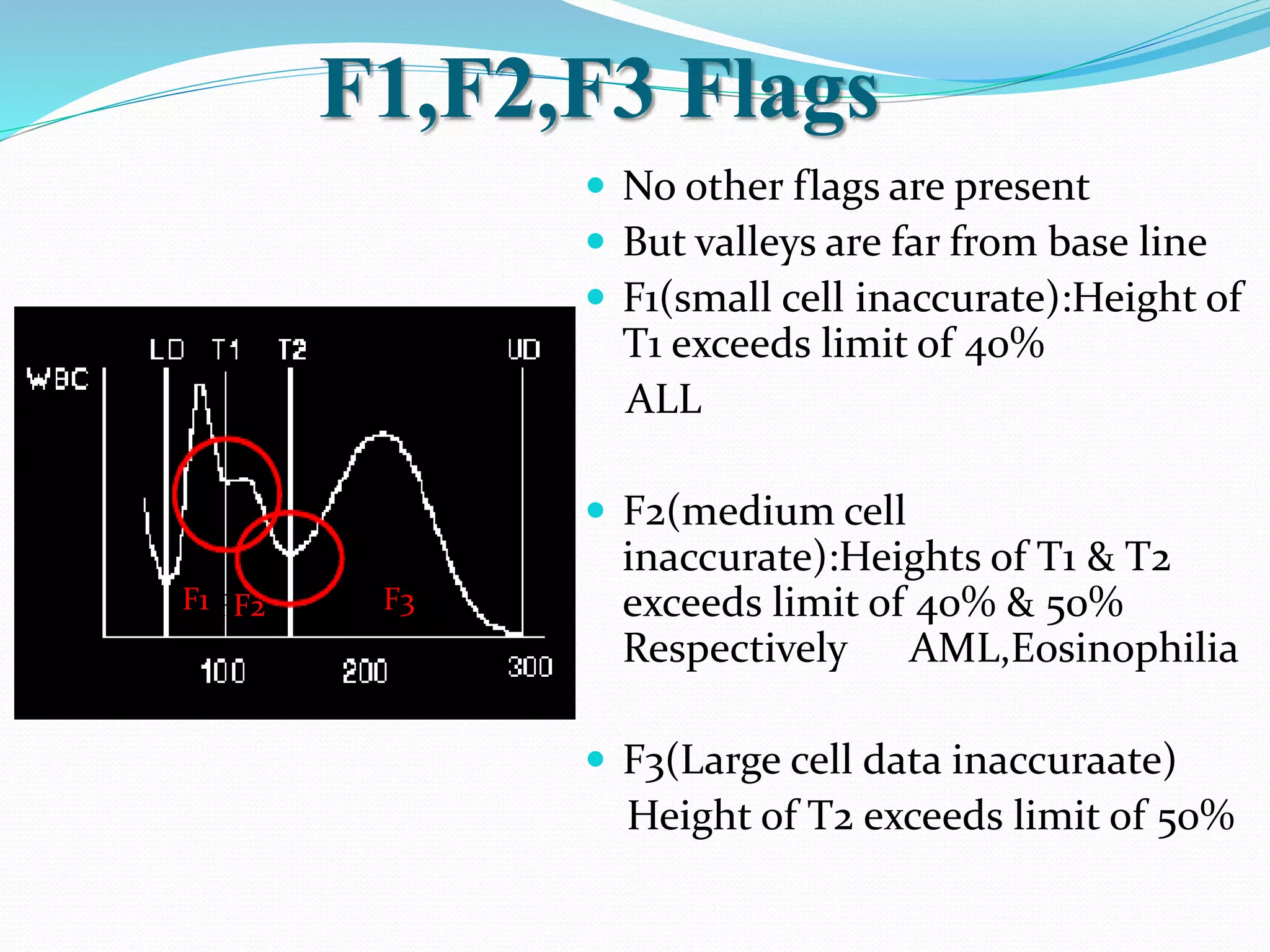
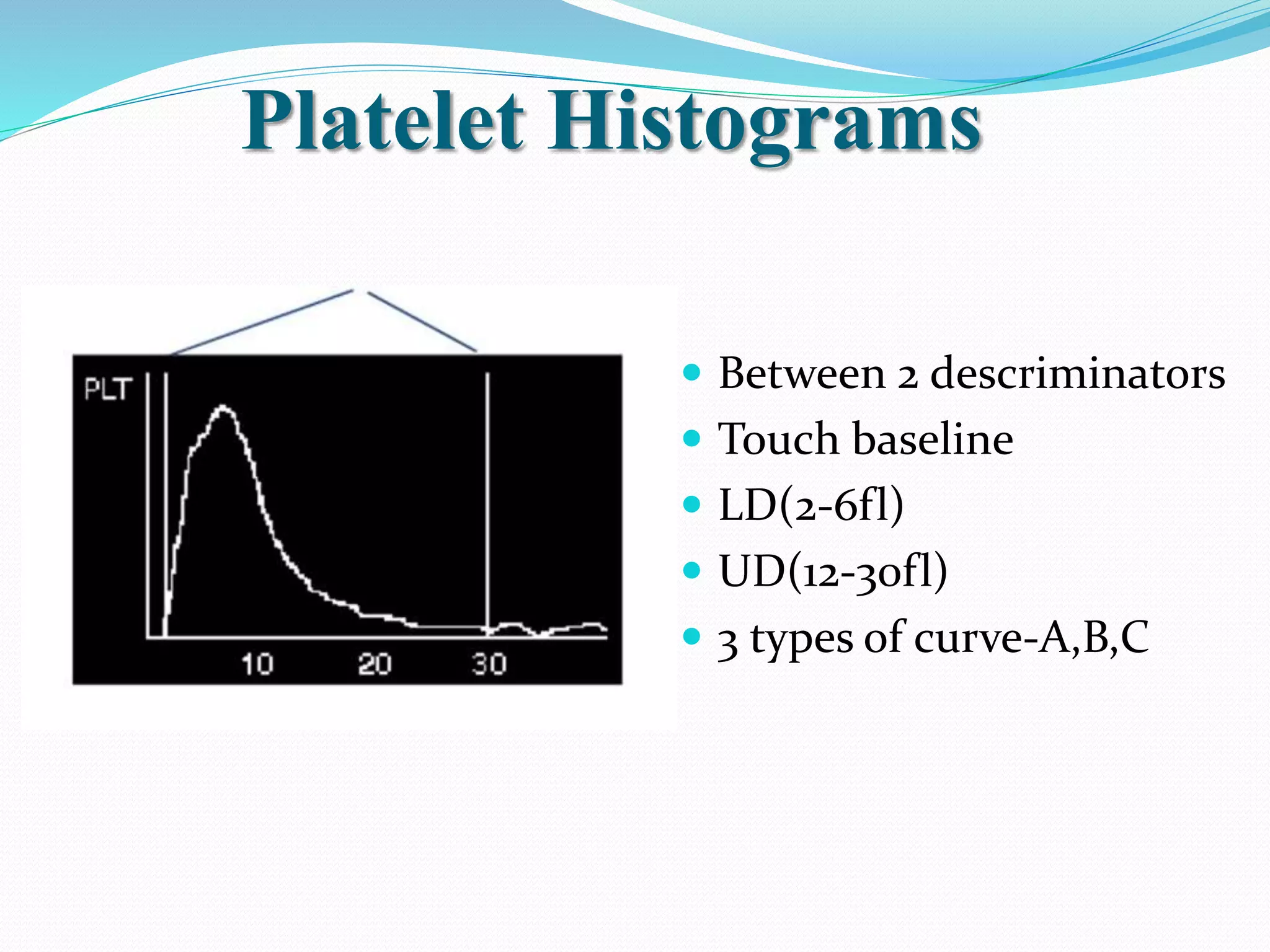
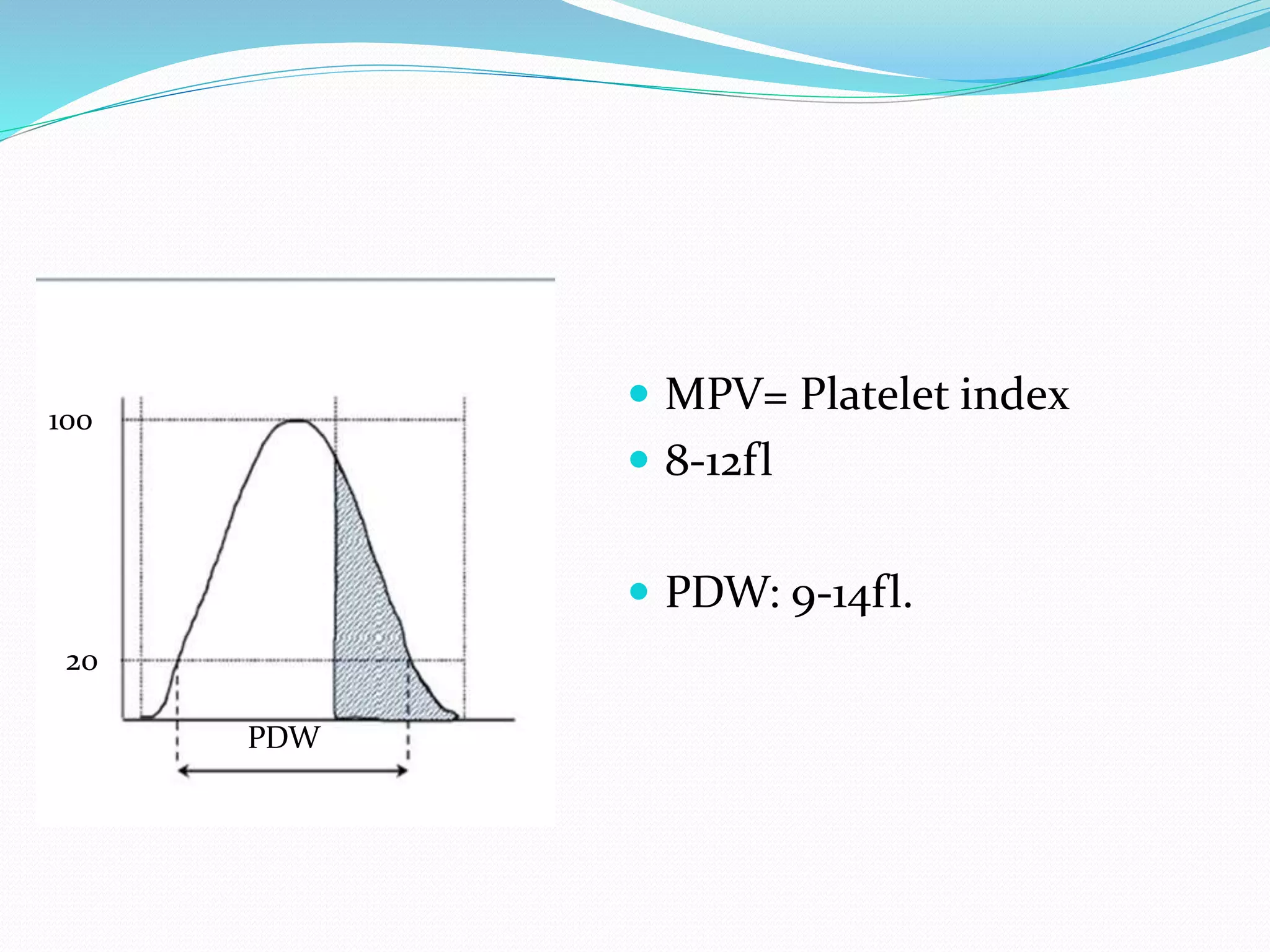
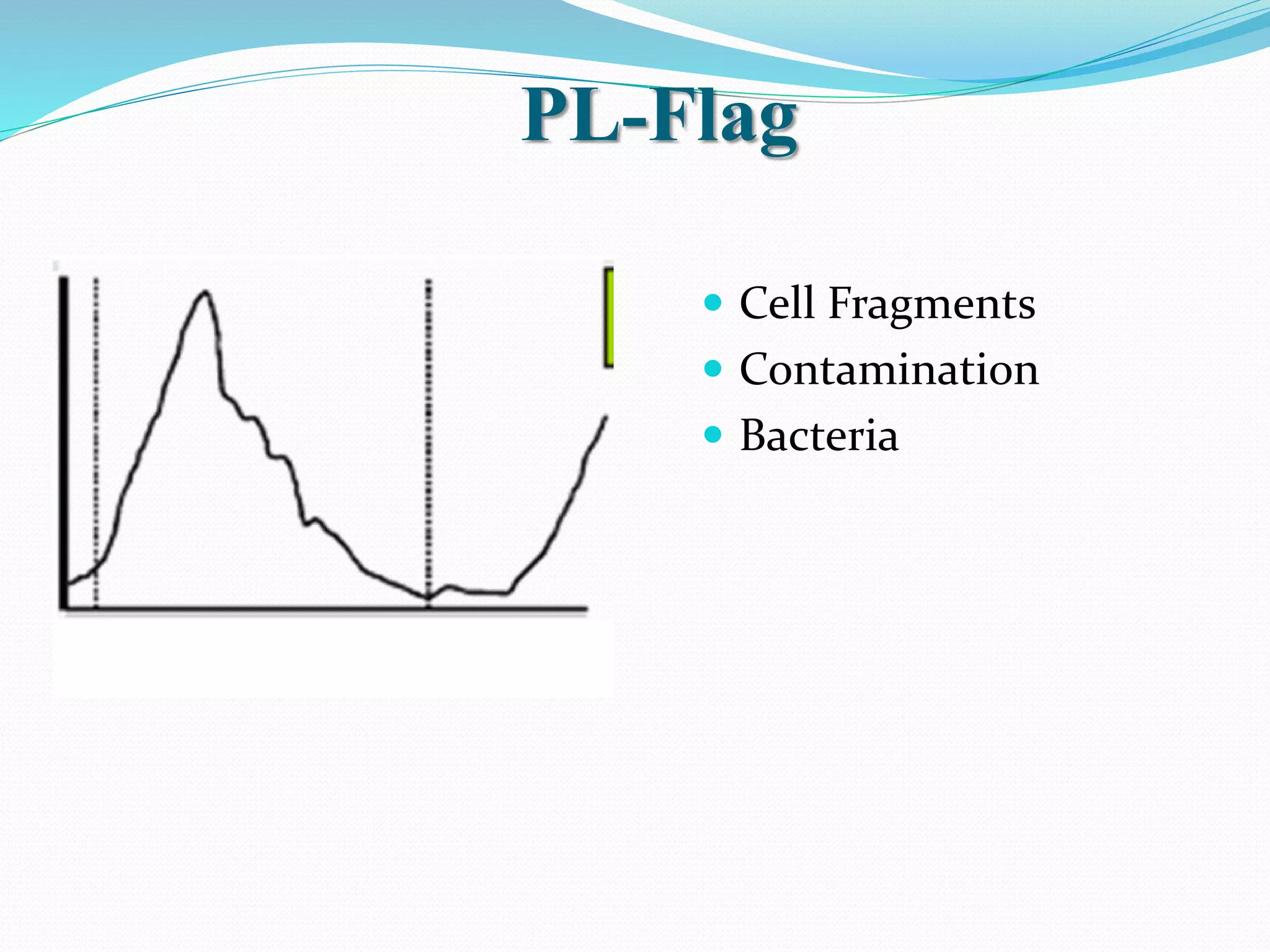
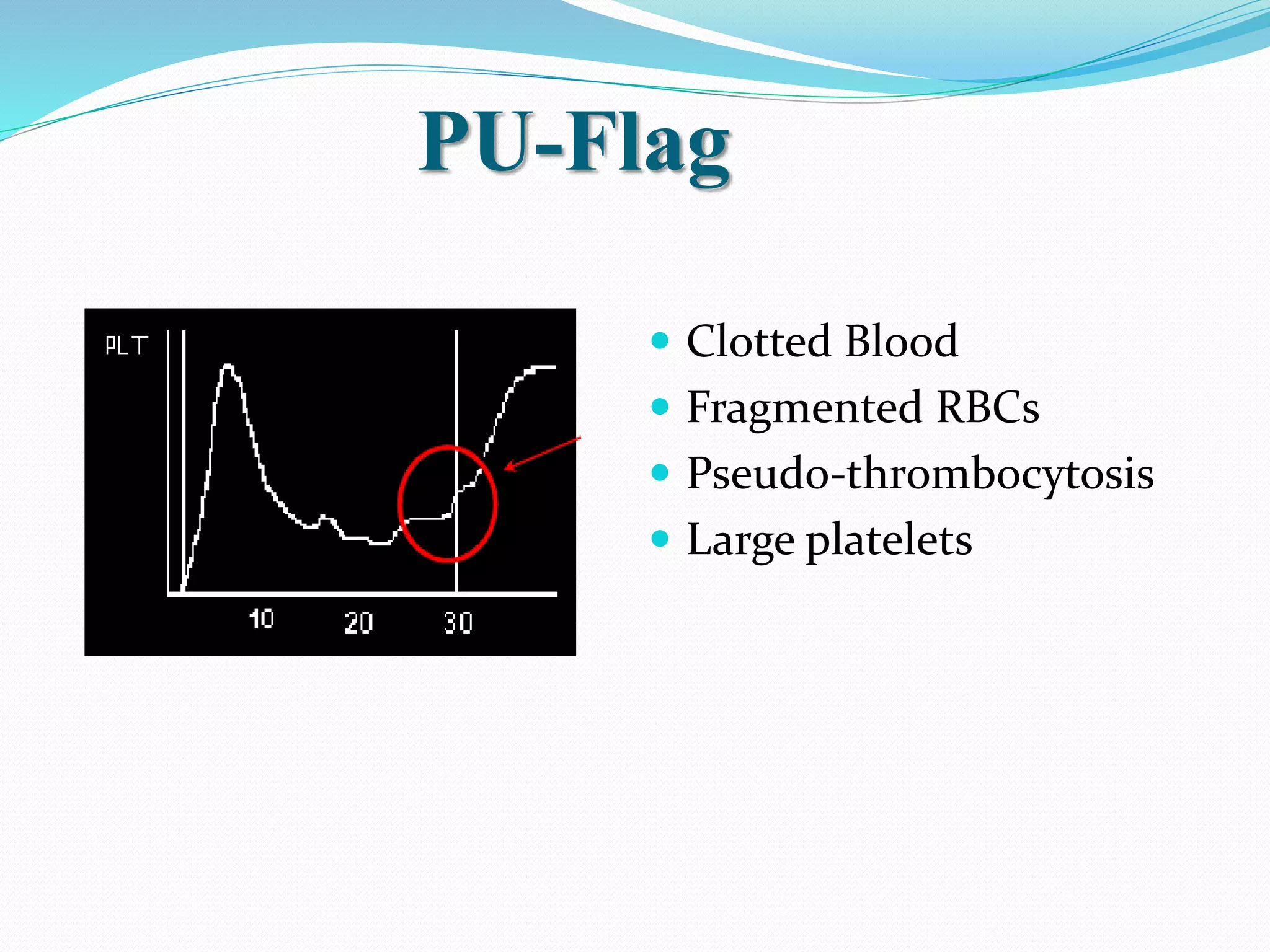
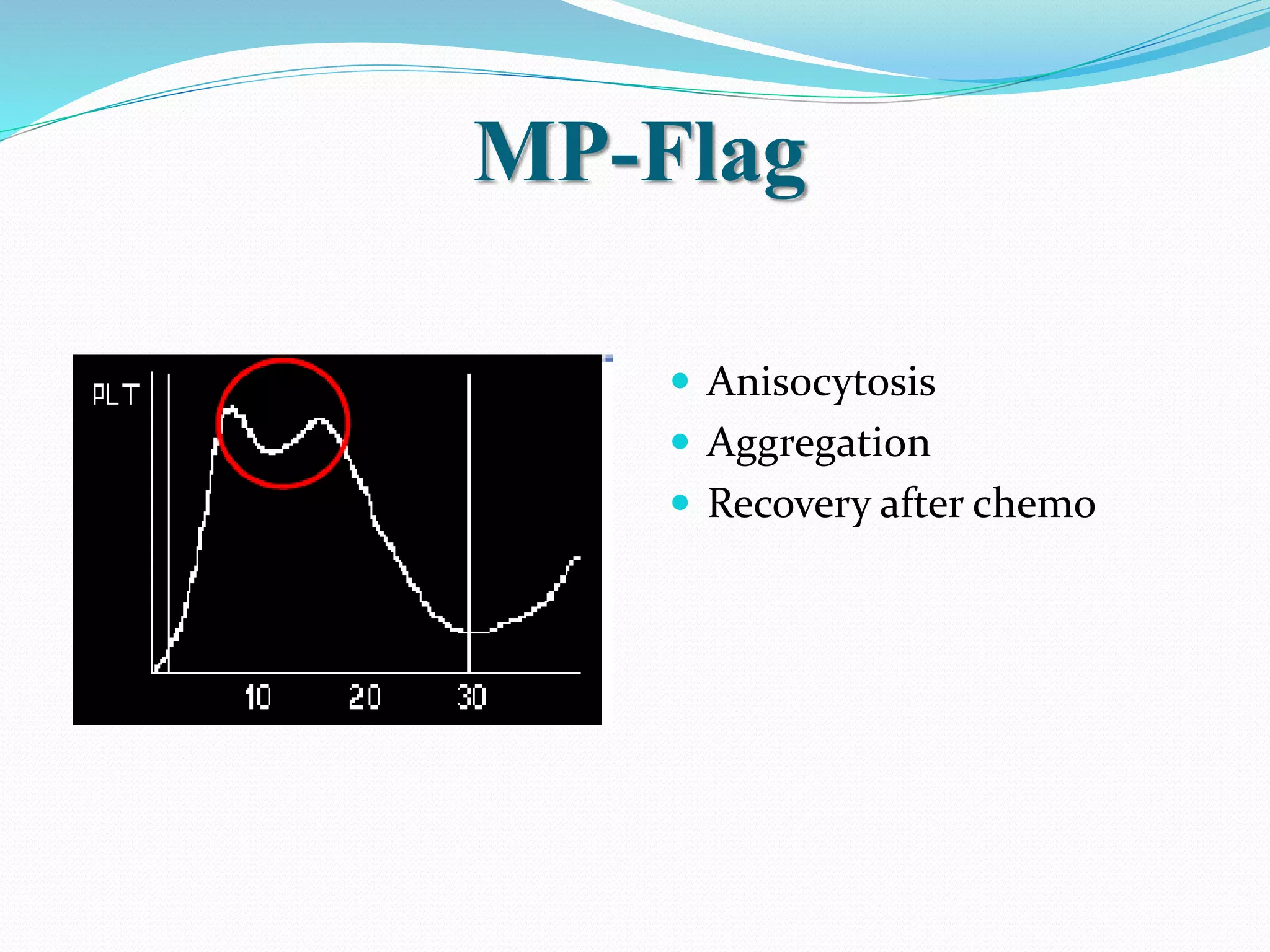
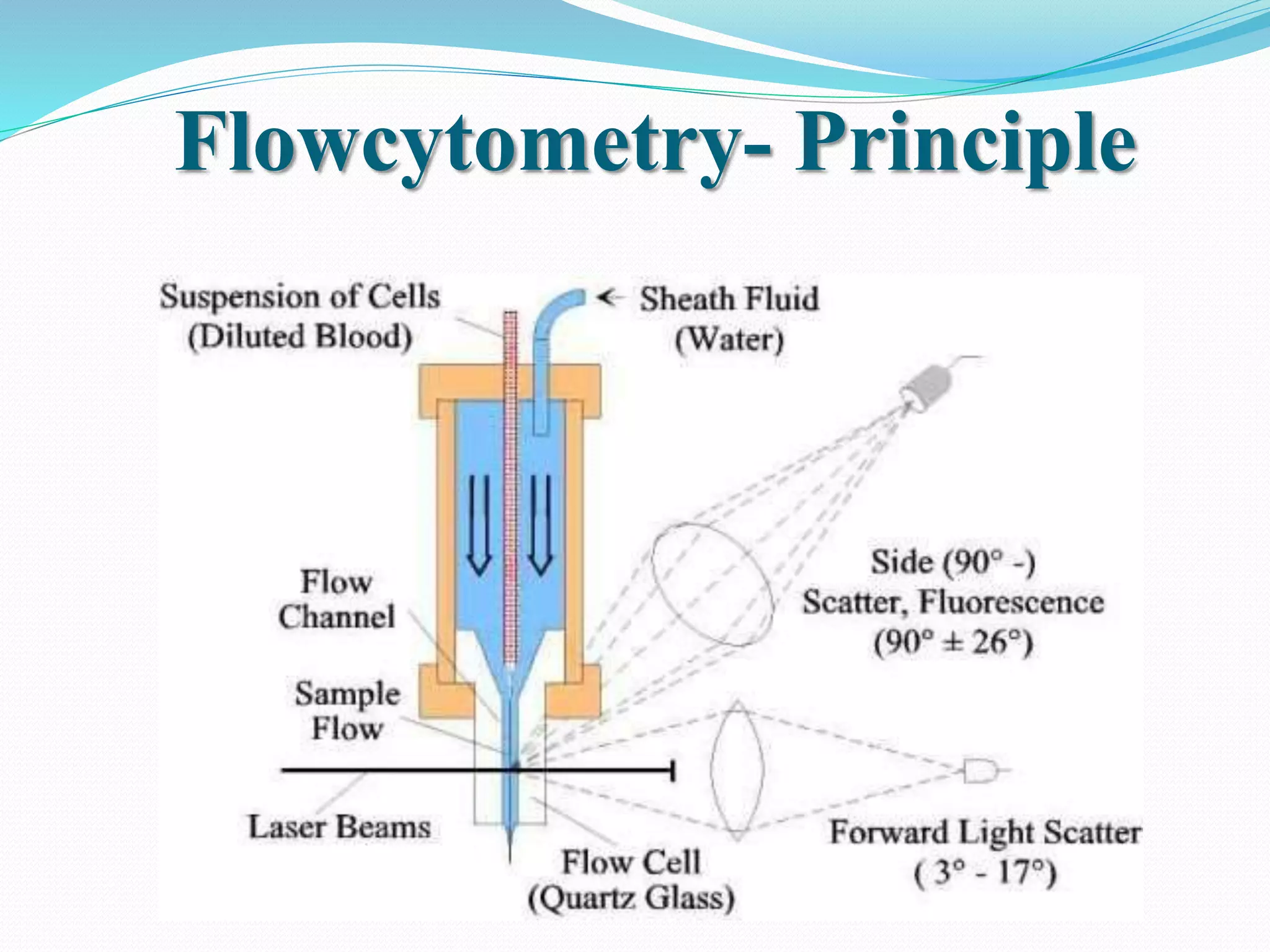
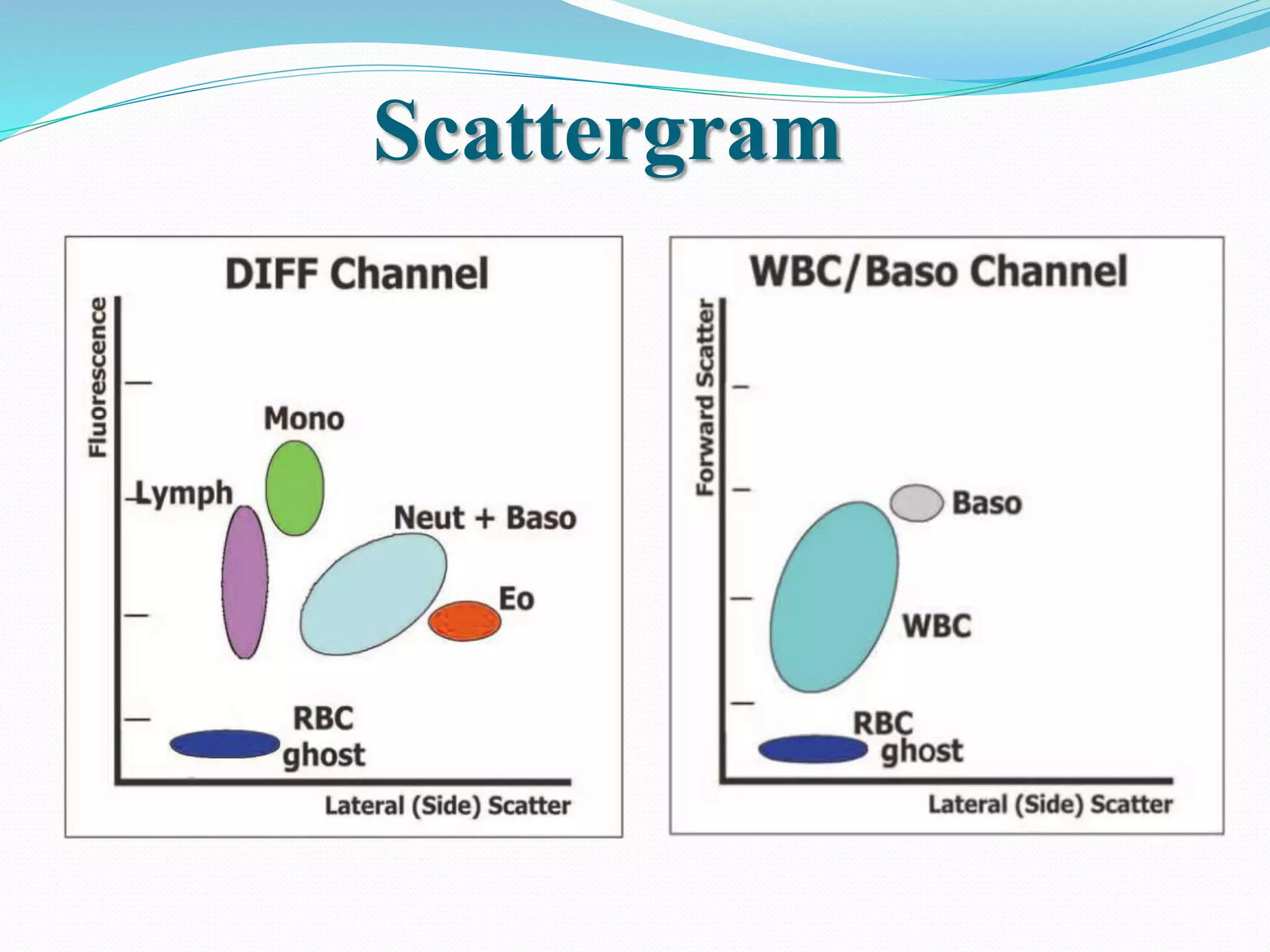
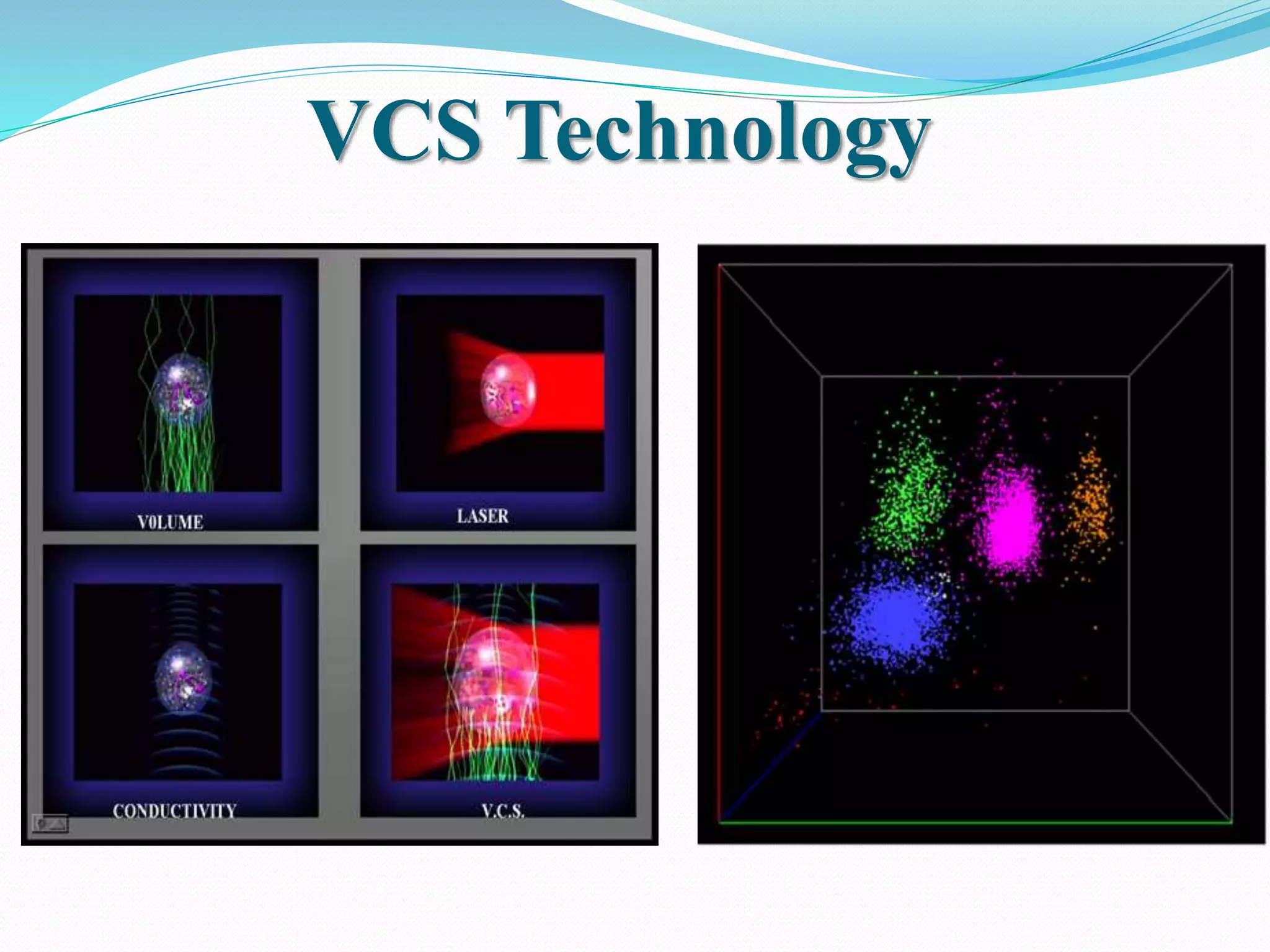
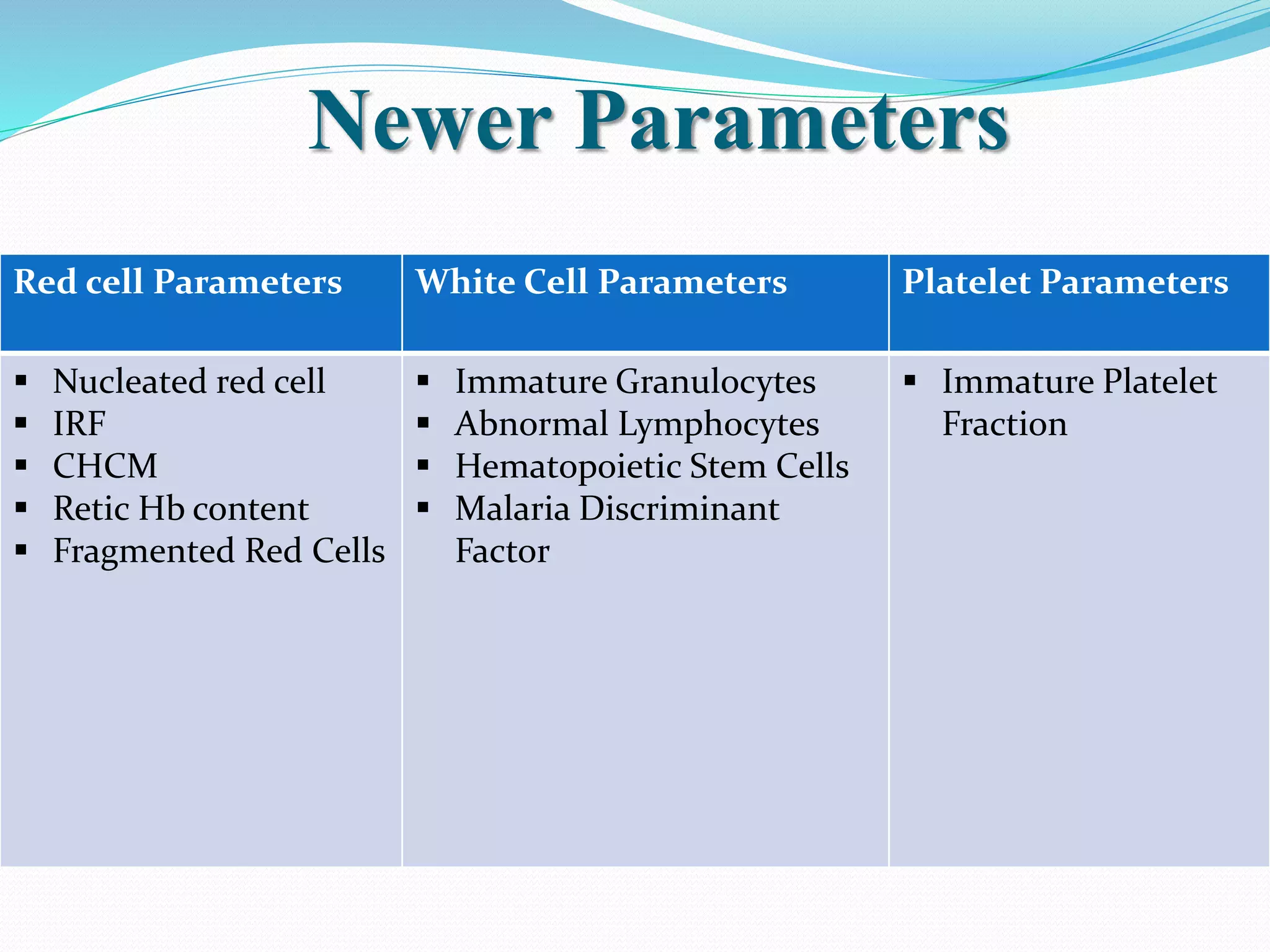
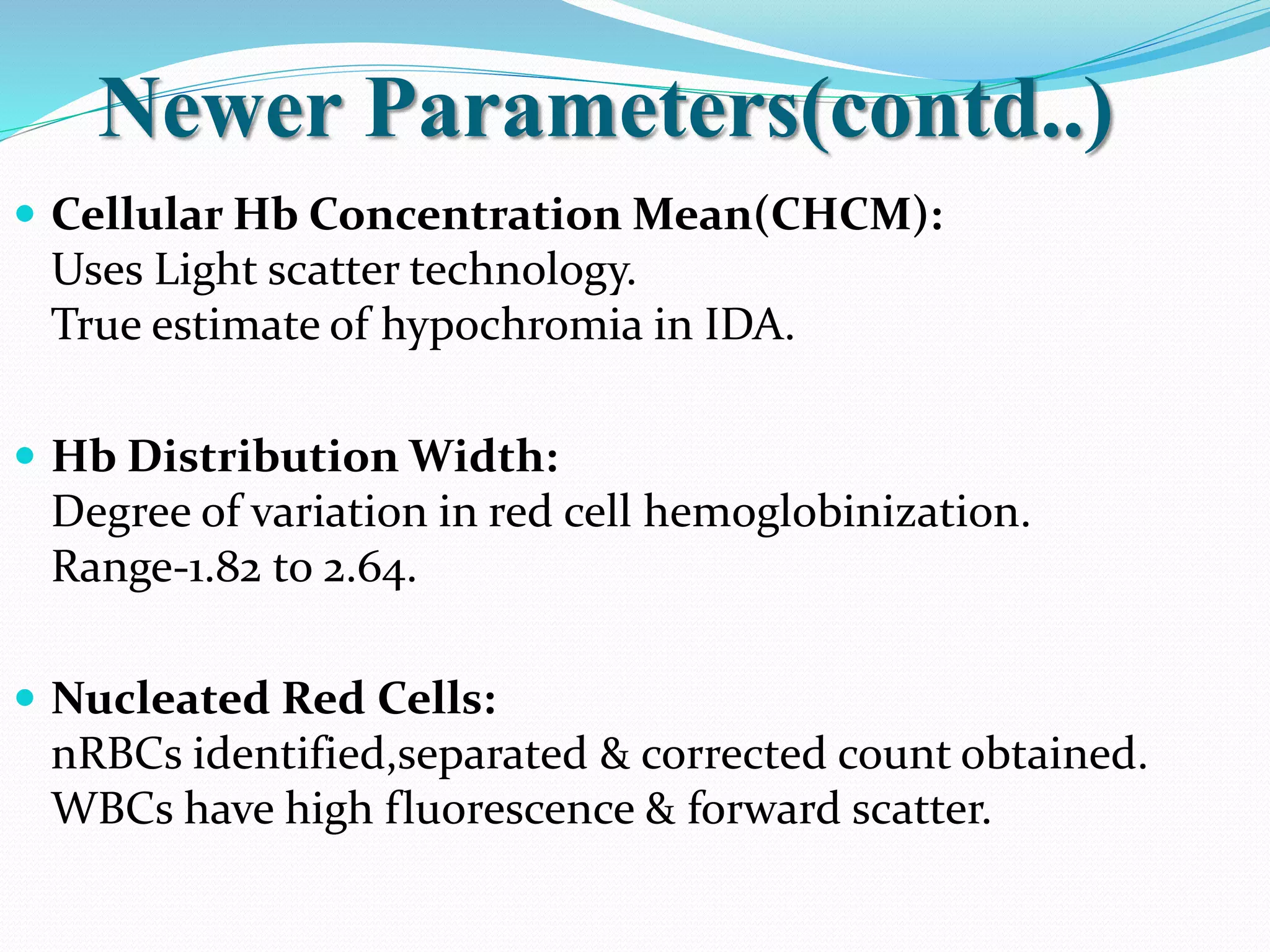
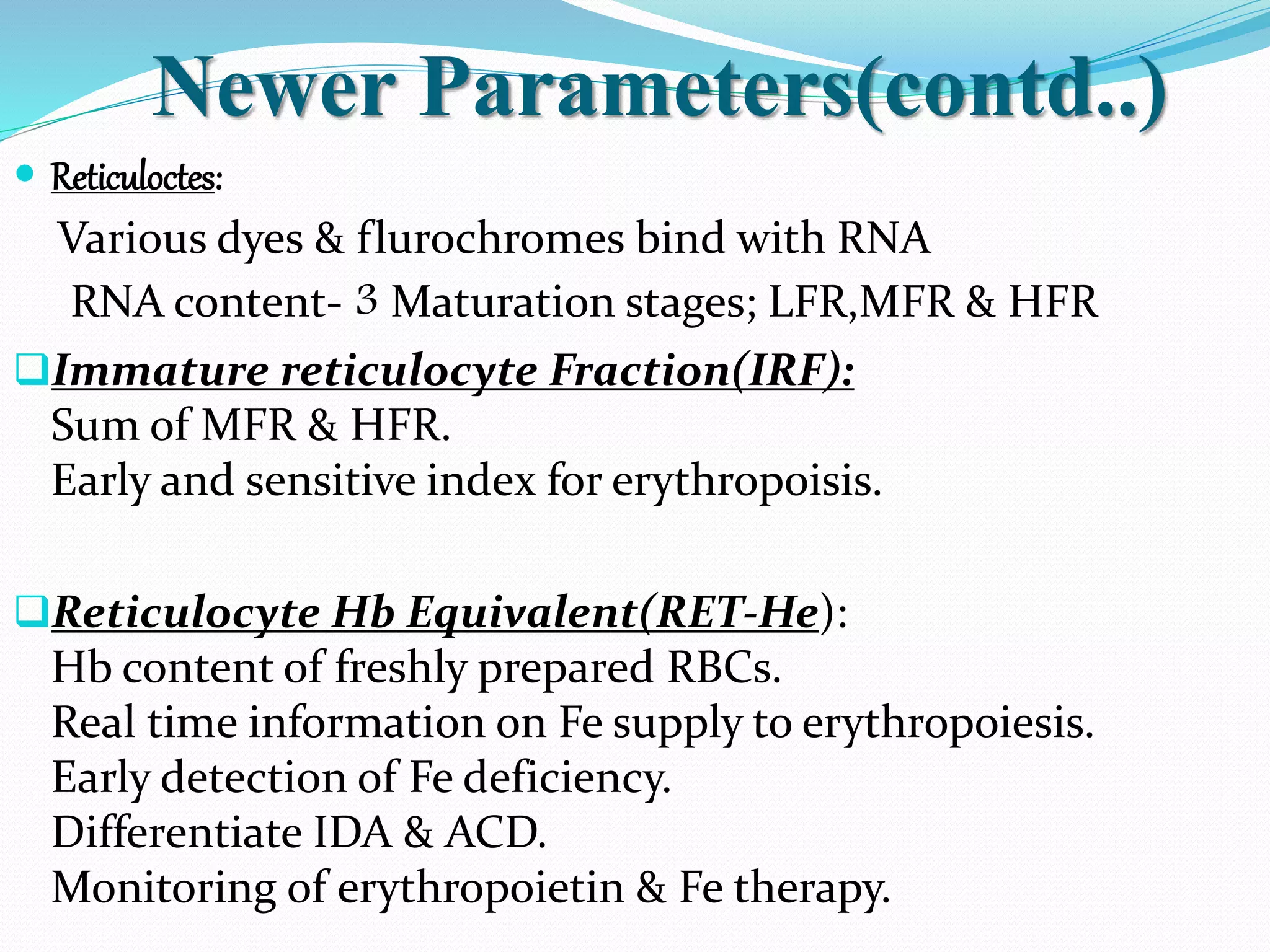
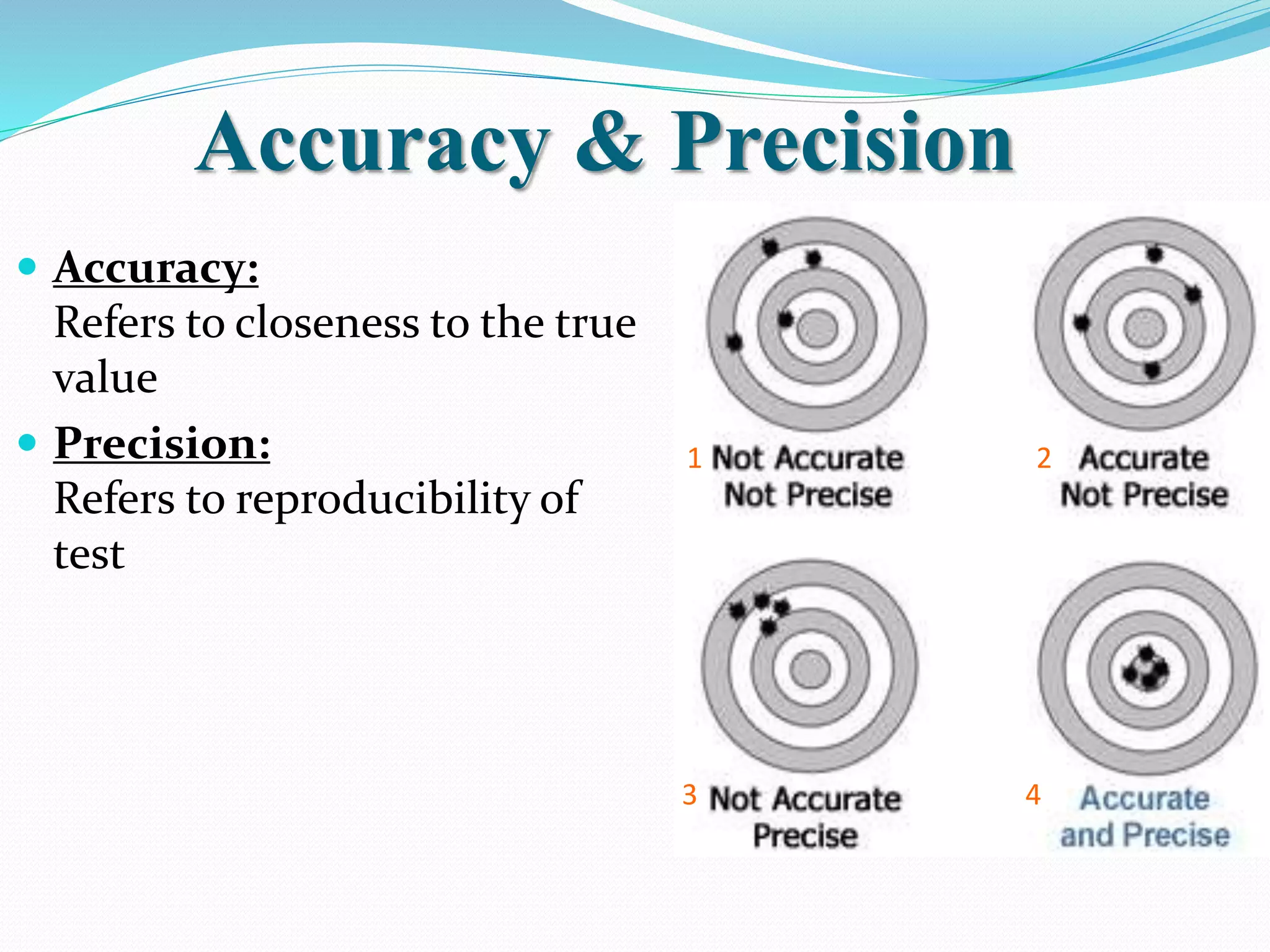
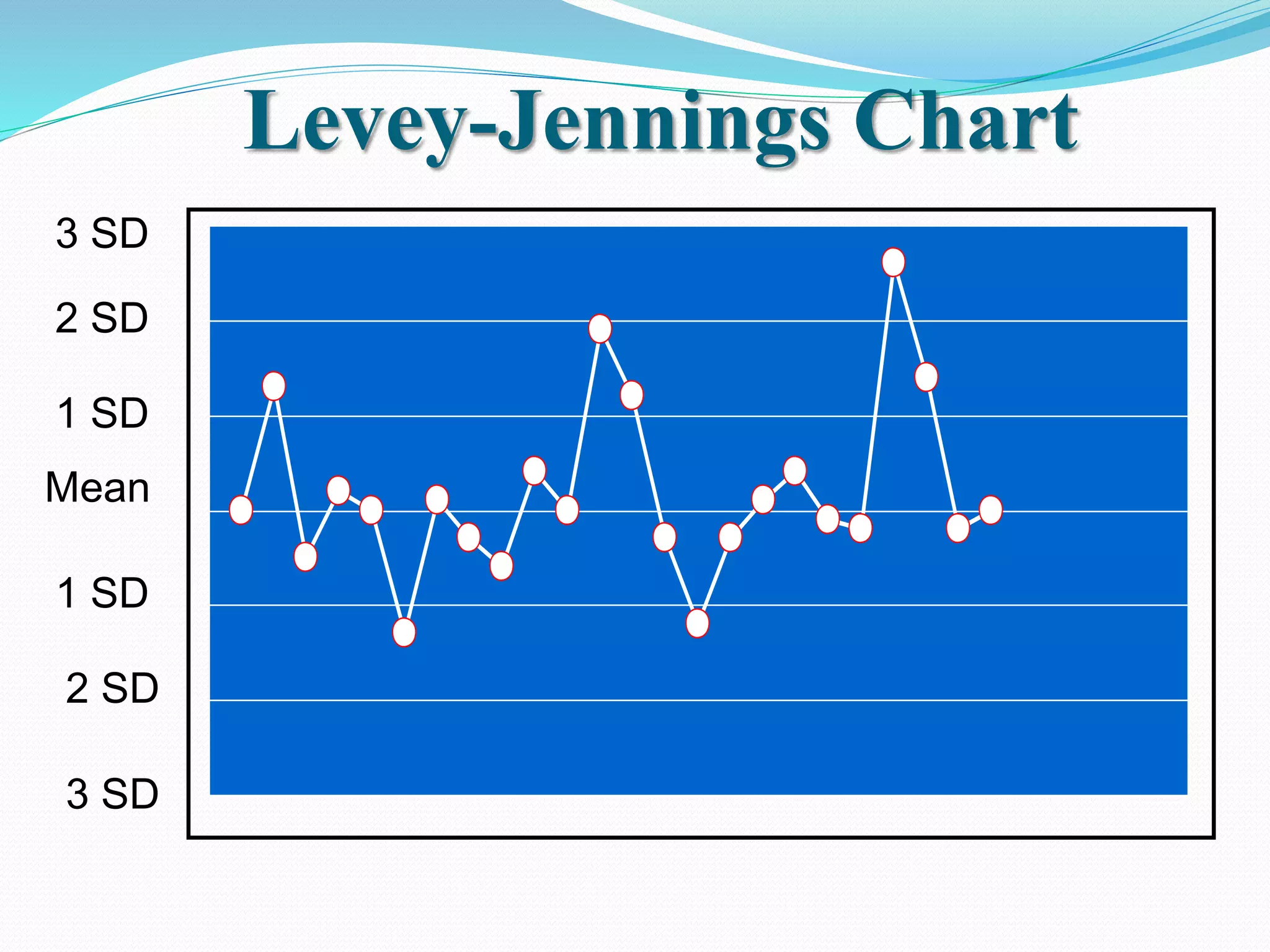
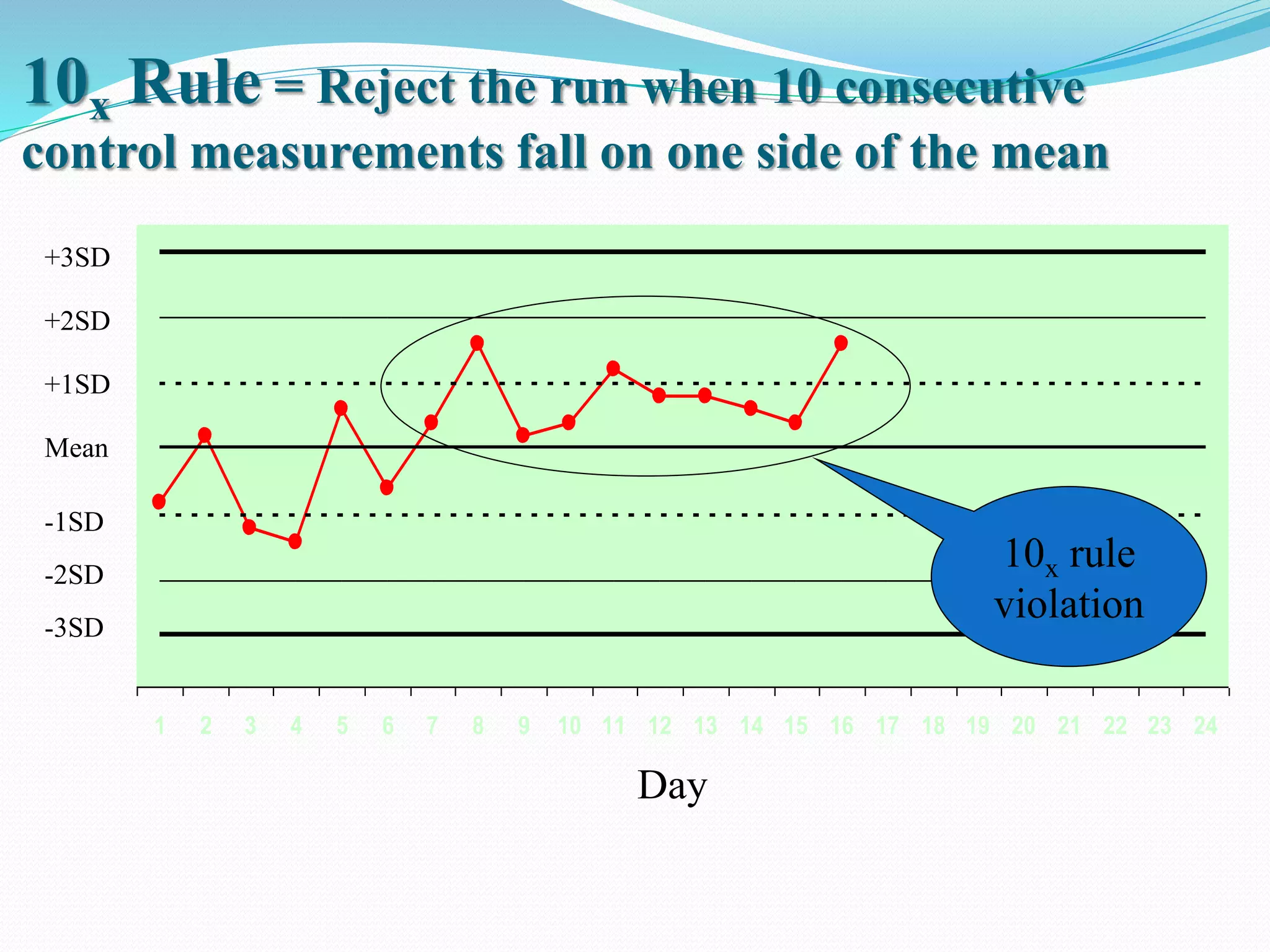
Automated hematology analyzers provide several advantages over manual methods including speed, accuracy, precision, and the ability to perform multiple tests on a single sample. They work using various principles such as electrical impedance, optical light scatter, and fluorescence to count and characterize red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Quality control measures like the use of controls analyzed daily and the application of rules like the Westgard rules help monitor the performance of these automated analyzers.