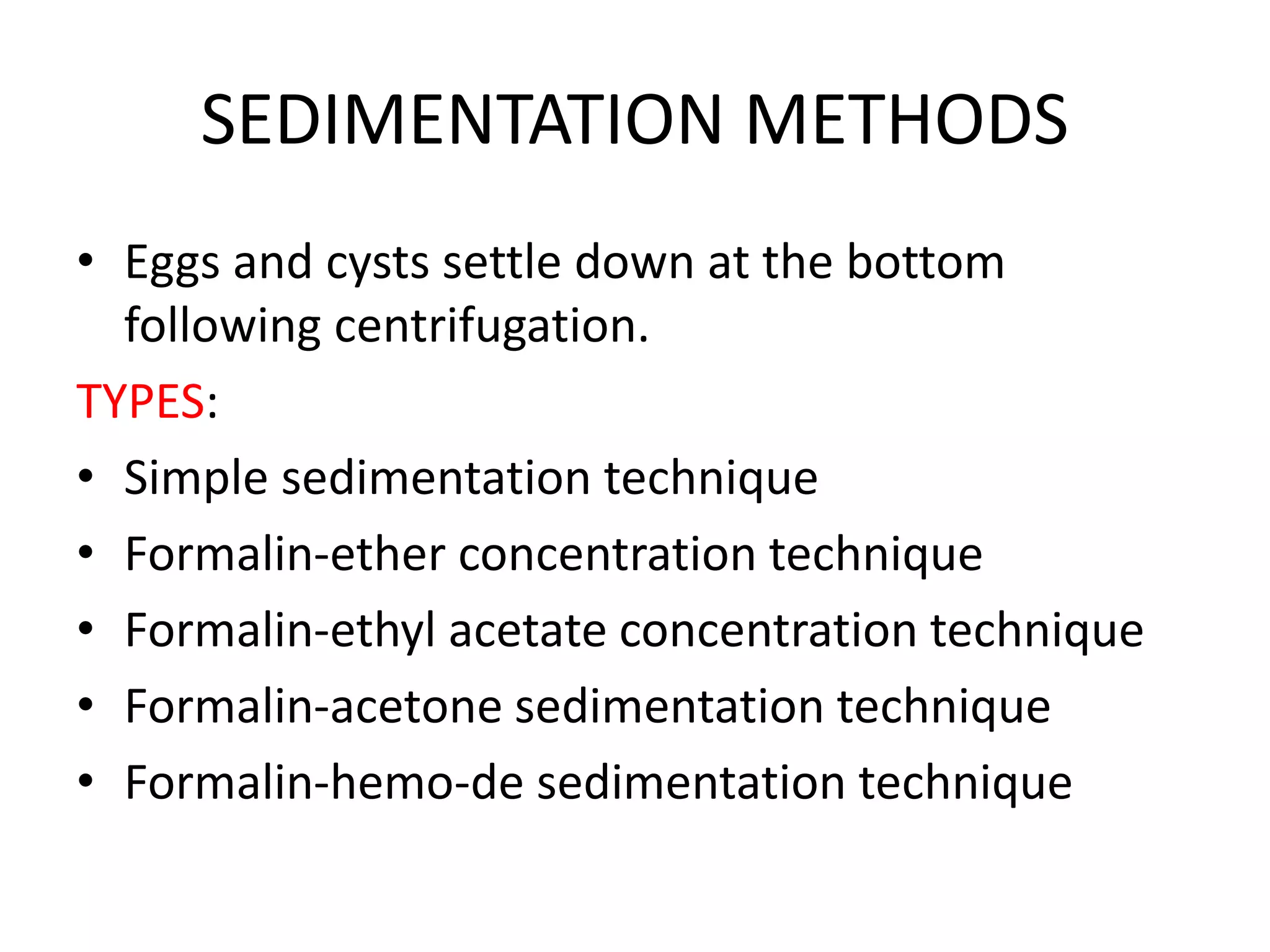
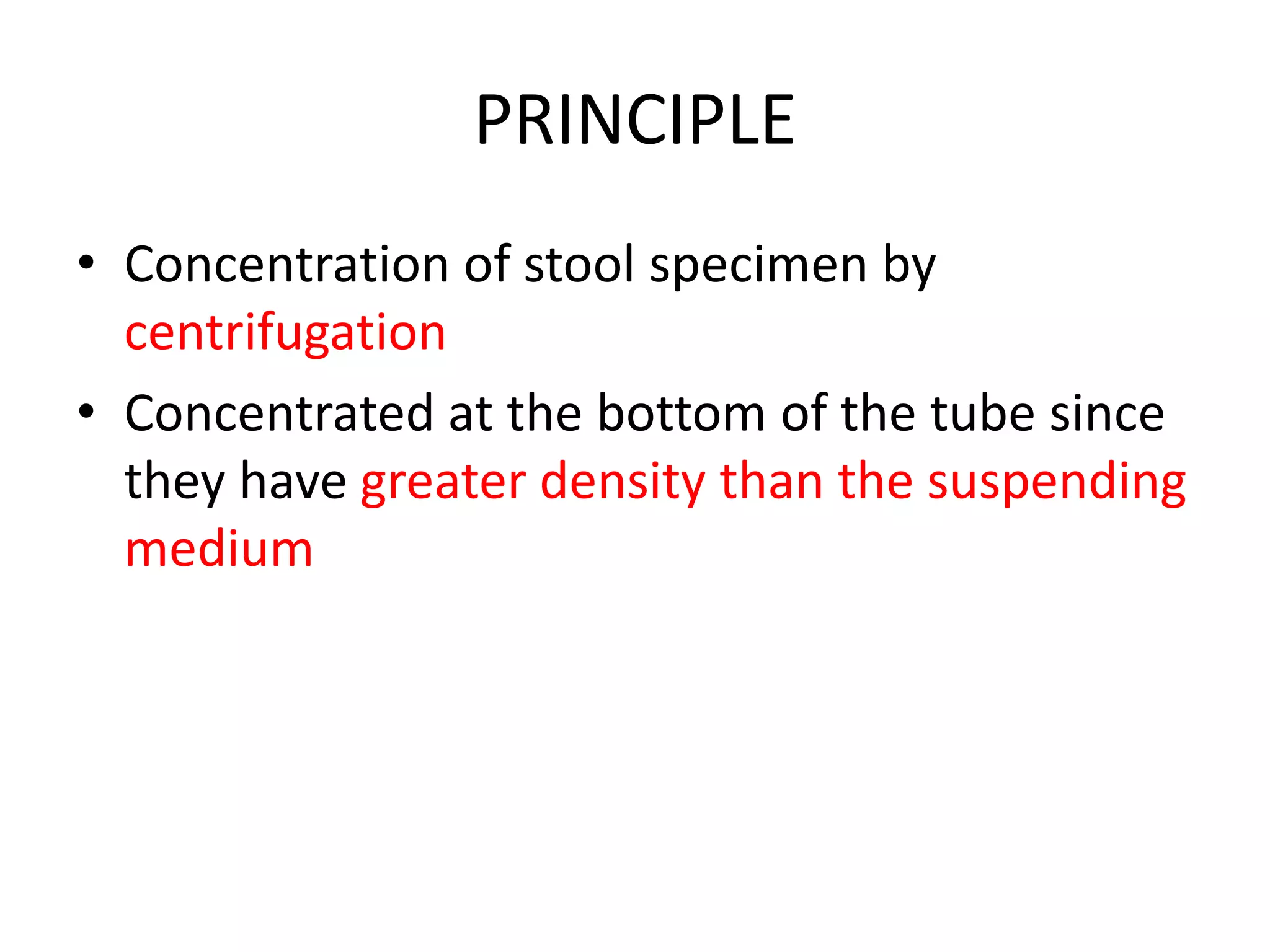
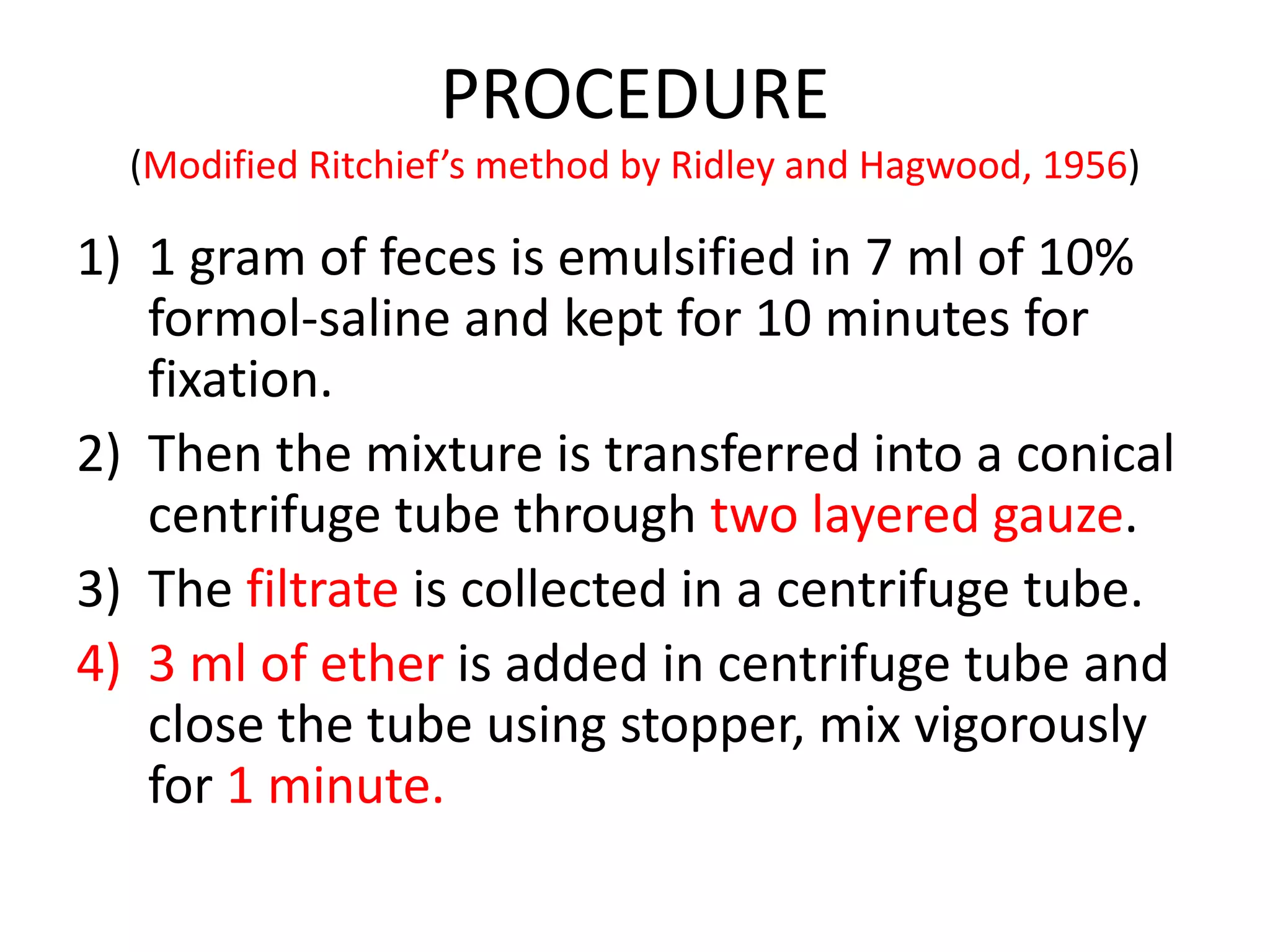
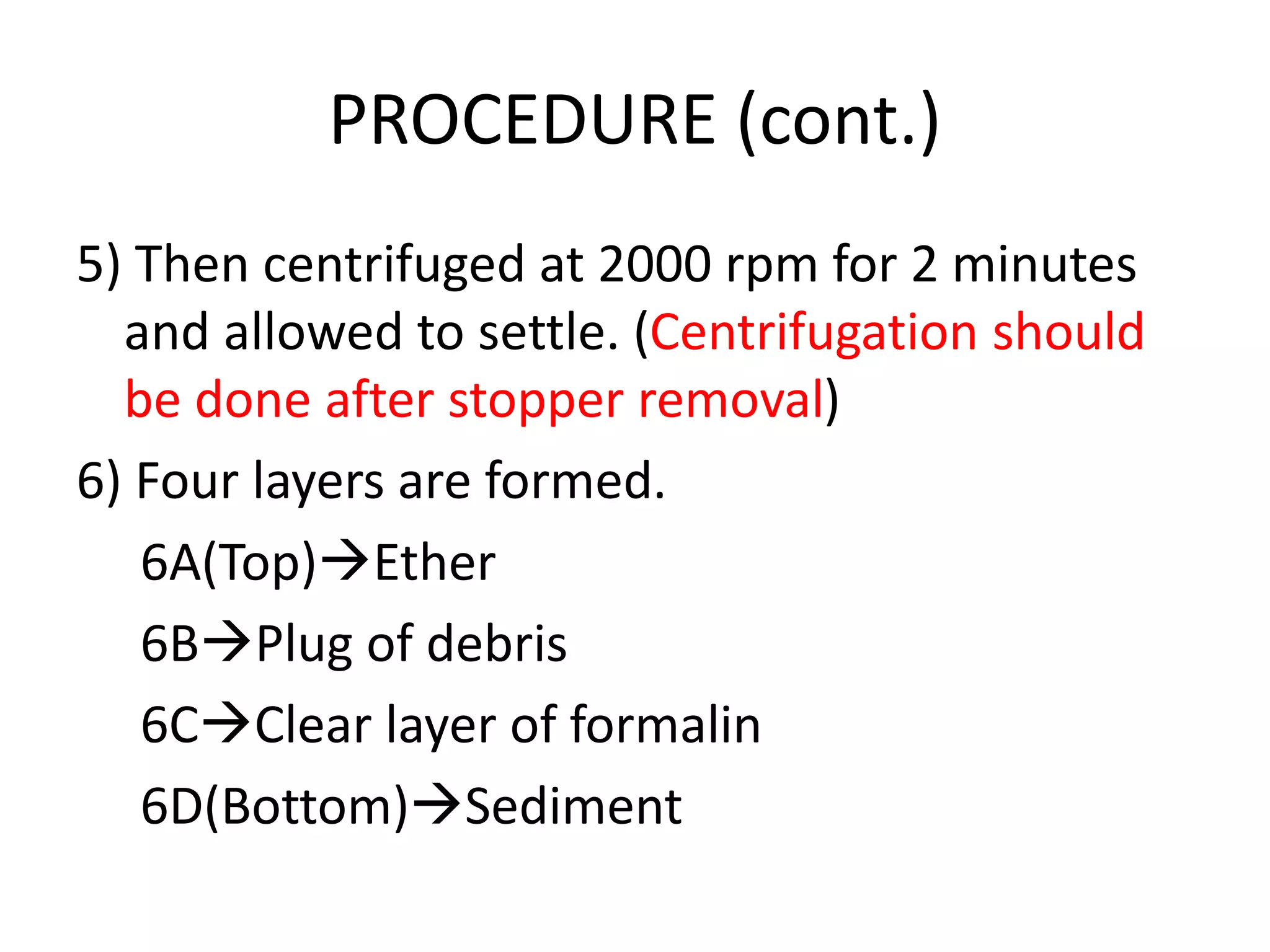
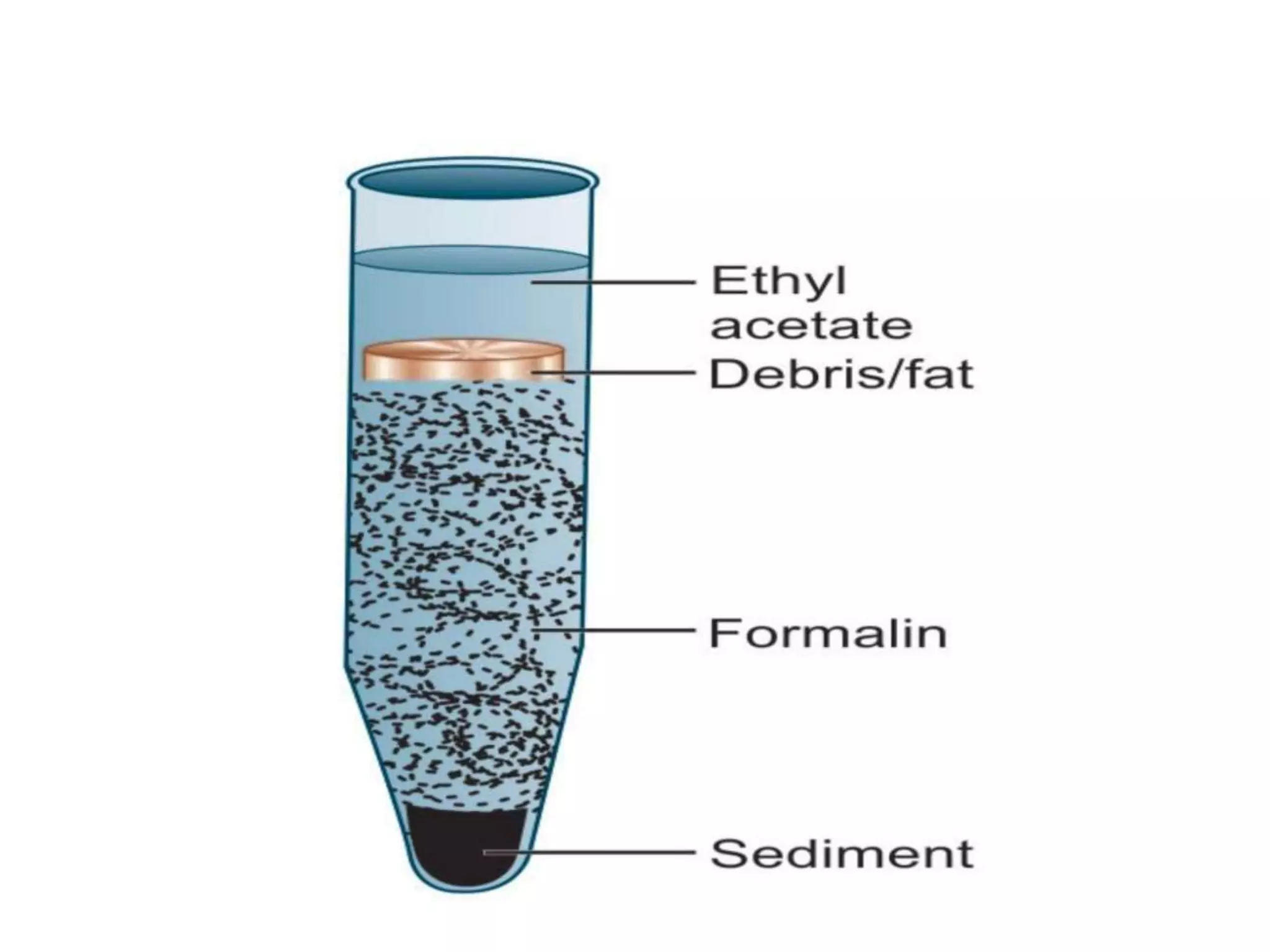
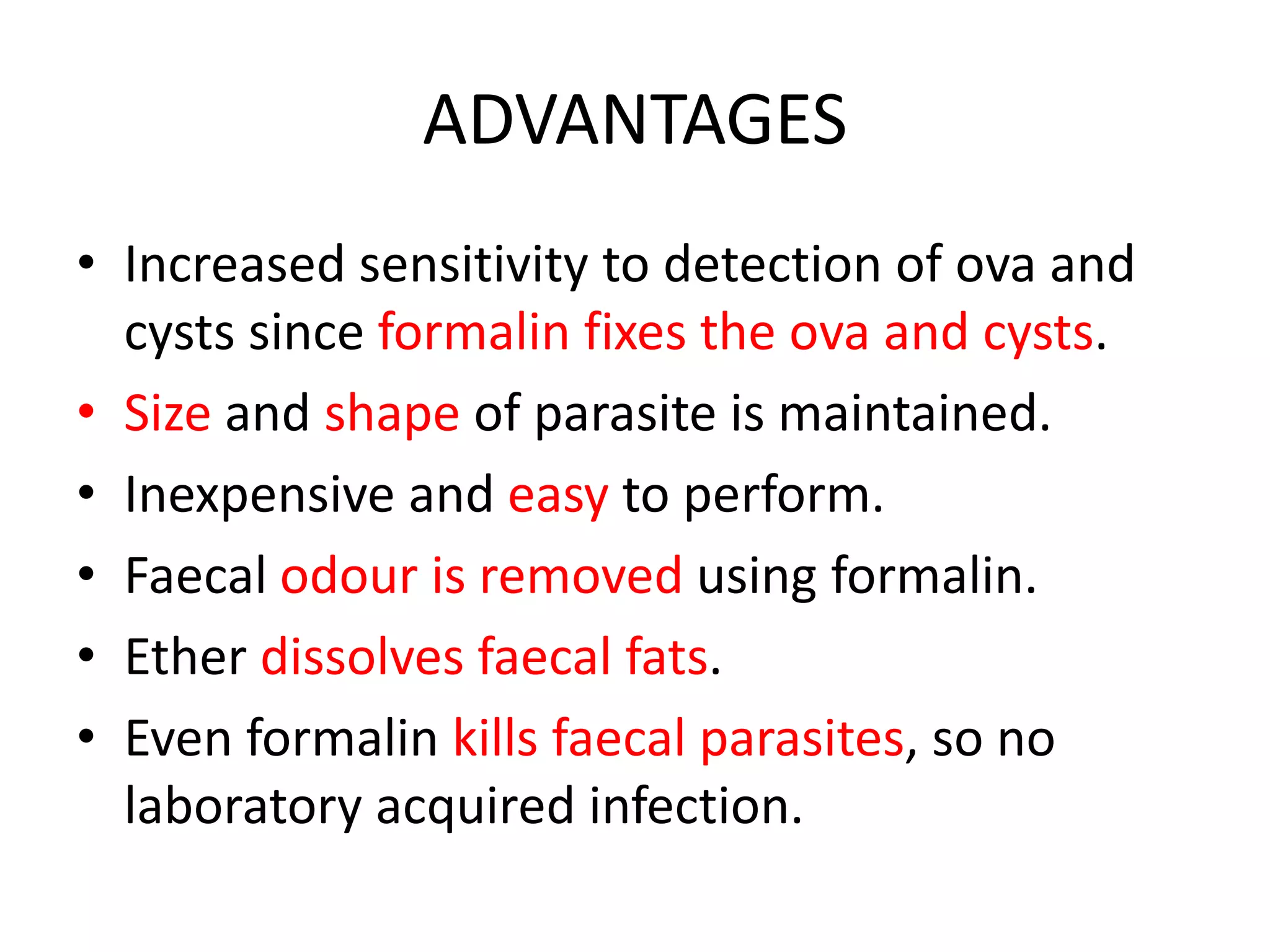
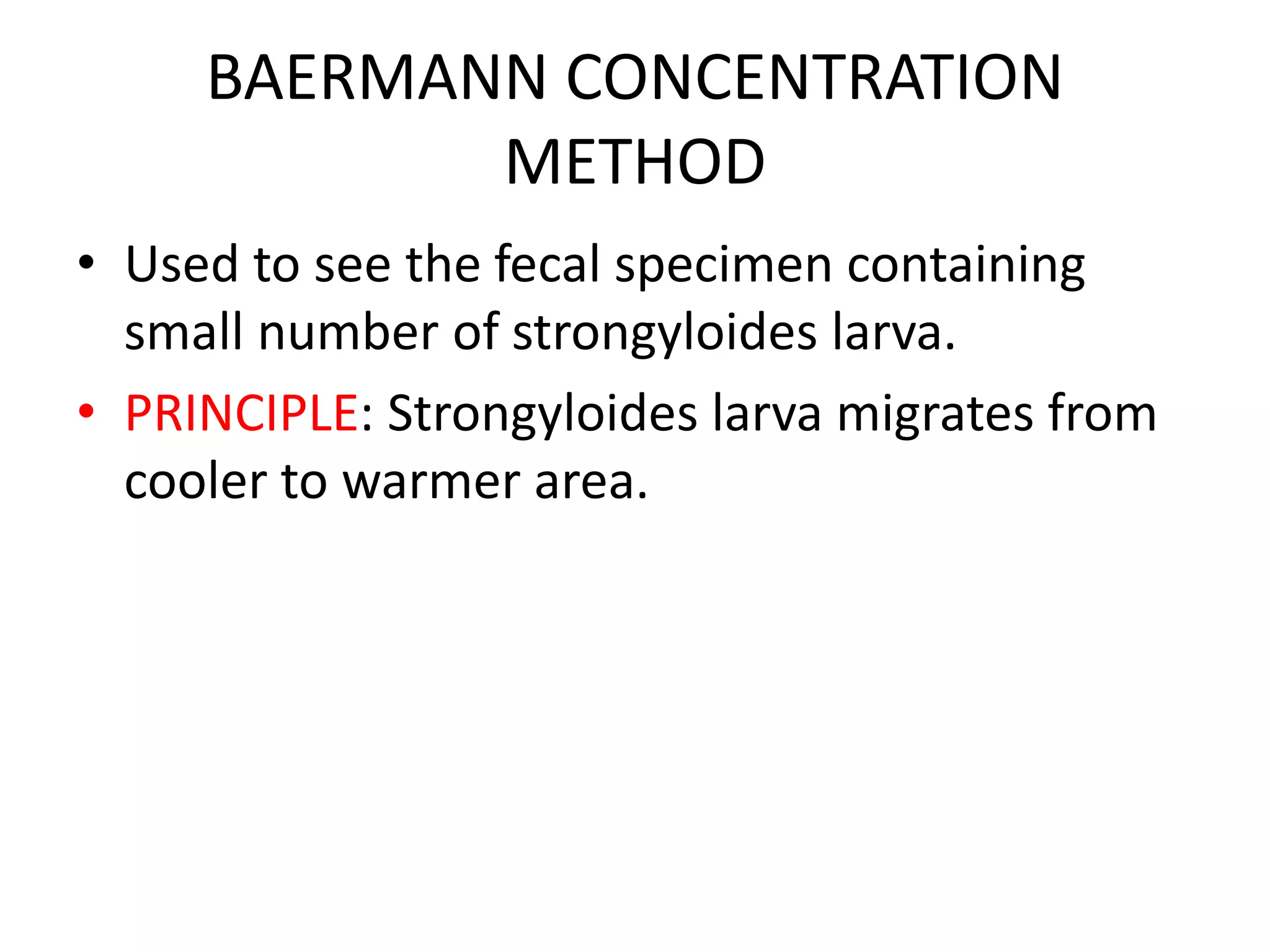
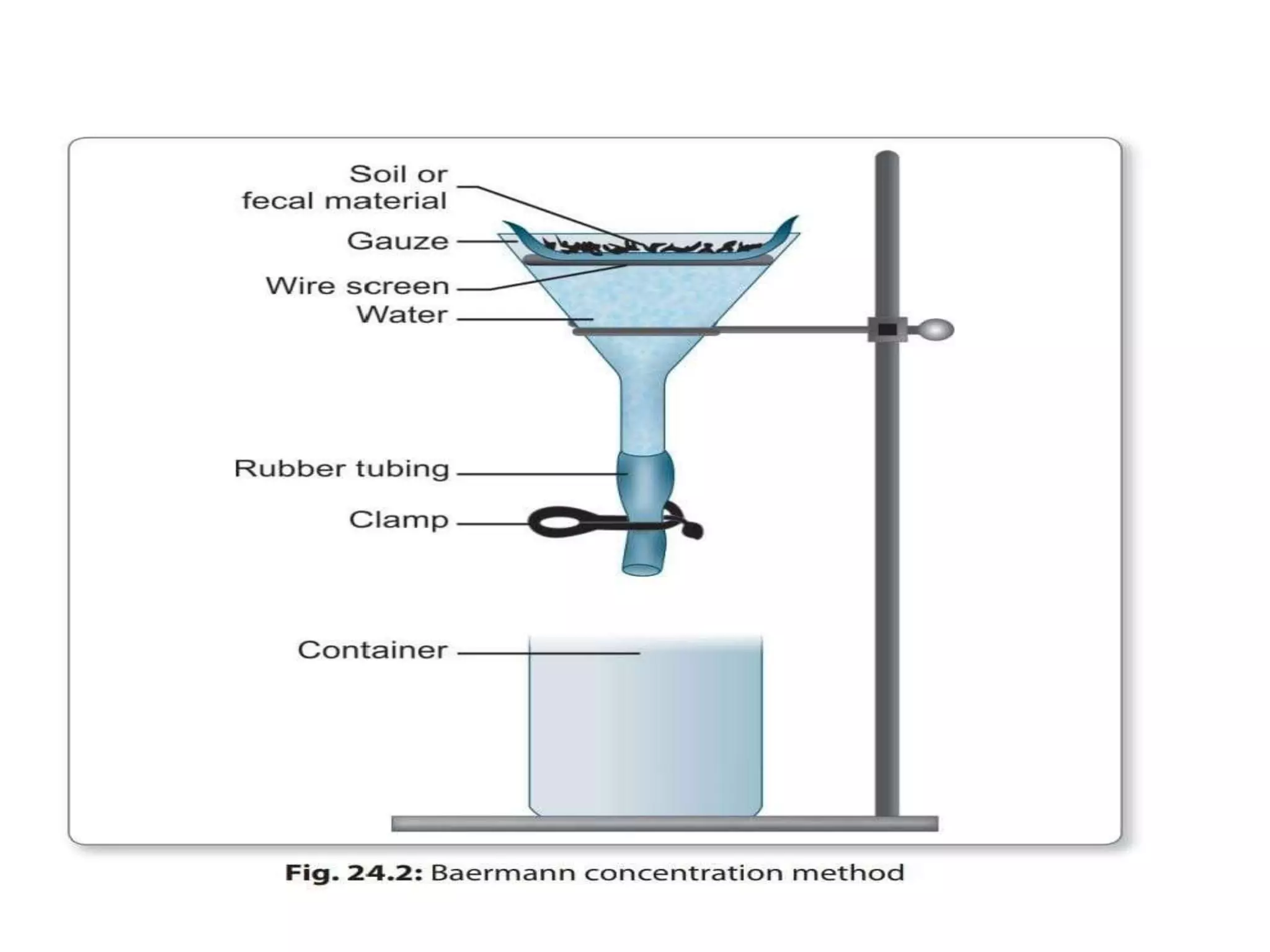
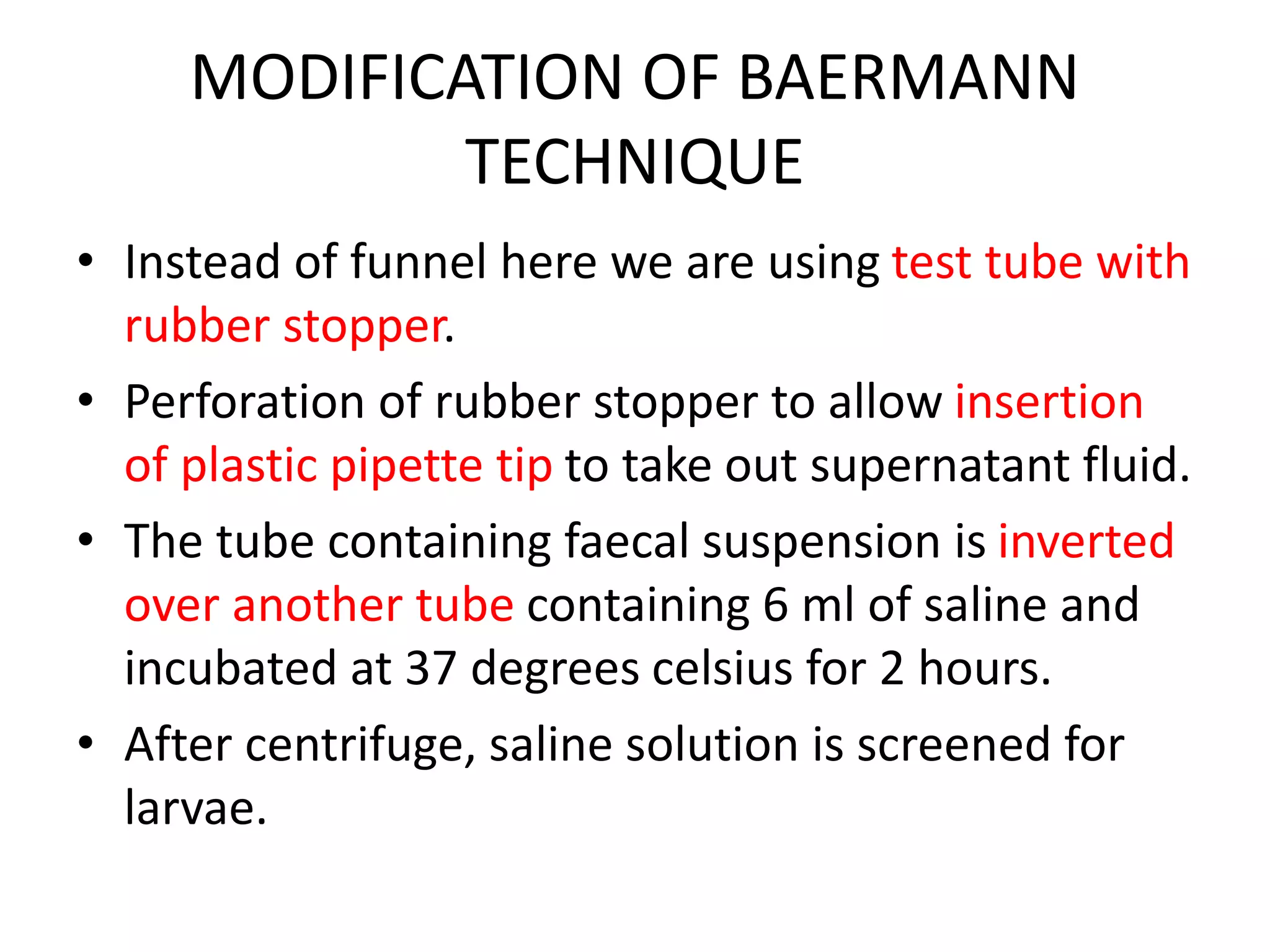
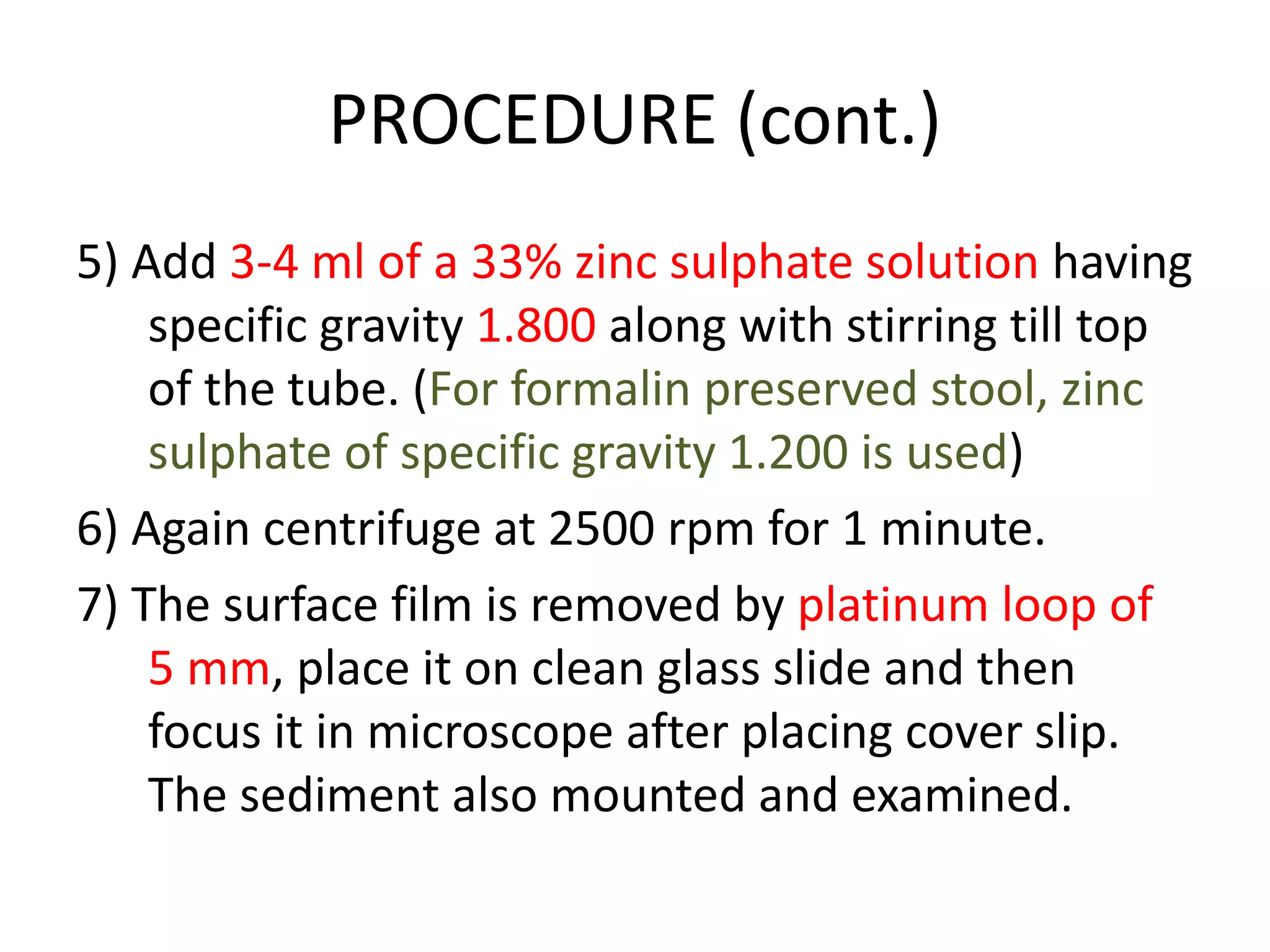
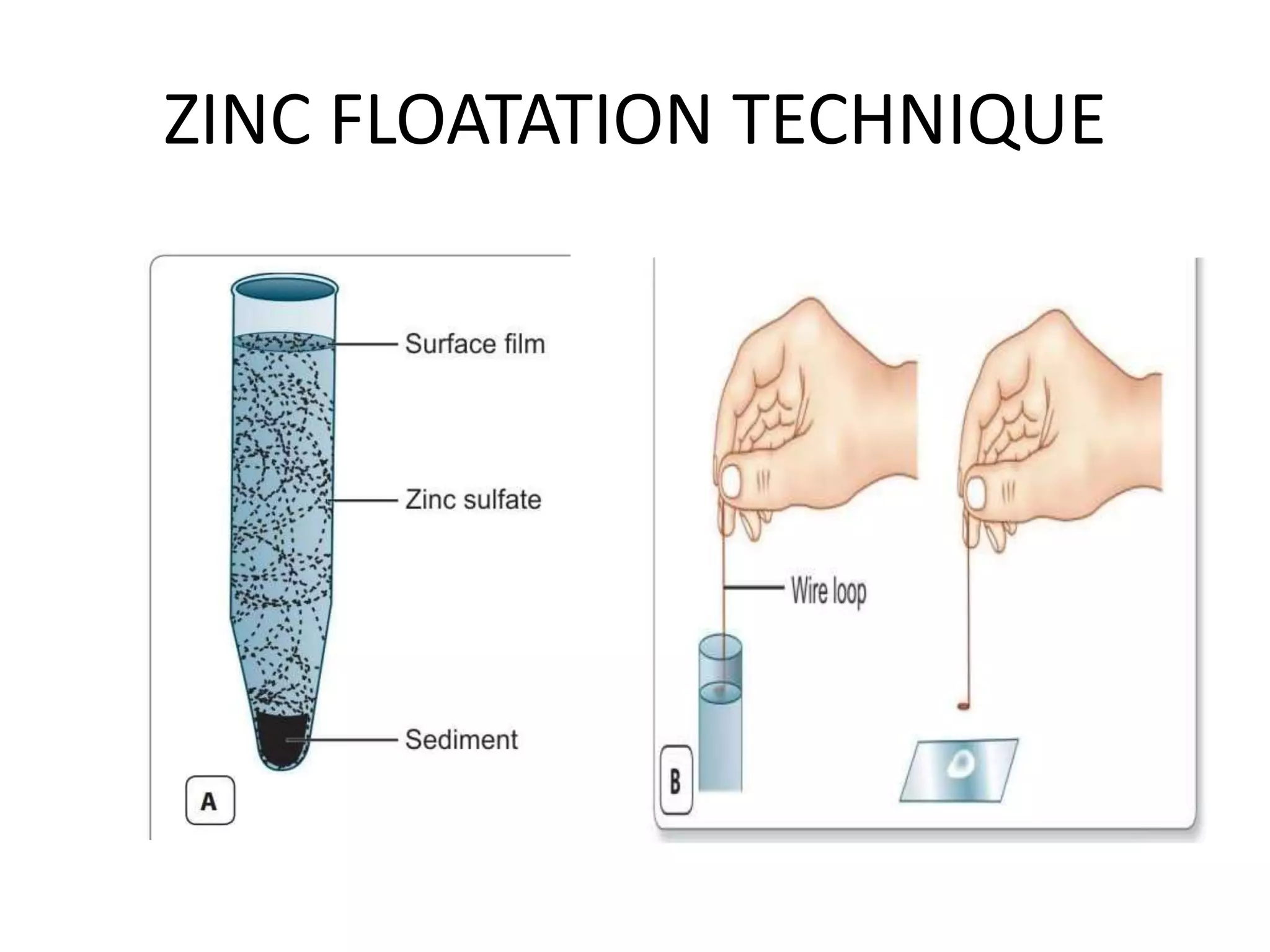
This document describes various stool concentration techniques used to detect parasites that may be present at low levels. It discusses when concentration is needed, such as for low parasite loads, epidemiological analysis, or assessing prognosis. The key concentration methods covered are sedimentation, floatation, and modifications of specific techniques like Formalin-ether sedimentation and Zinc sulfate floatation. Sedimentation involves centrifugation to concentrate heavier parasites at the bottom of a tube, while floatation uses high density solutions to make parasites float for easier detection microscopically. Baermann and Sheather's sugar techniques are also summarized as specialized concentration methods.