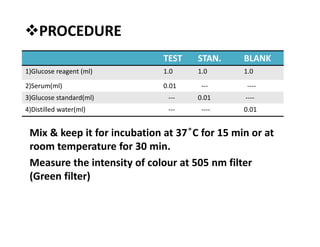
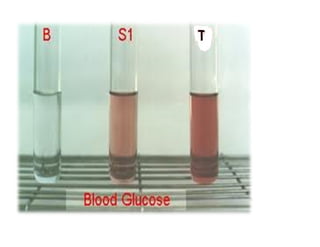
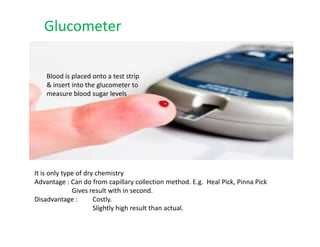
This document describes several methods for estimating glucose levels in blood, urine, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The most common enzymatic method uses glucose oxidase and peroxidase (GOD-POD) to produce a color change that can be measured to determine glucose concentration. Blood is typically collected in fluoride tubes to prevent glycolysis. Urine requires preservatives due to bacterial growth. CSF glucose is normally between 15-45 mg/dL and levels below normal may indicate bacterial infection or hypoglycemia.