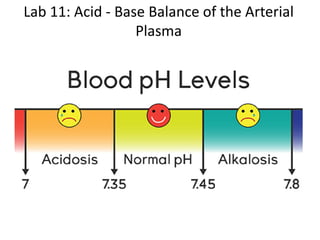
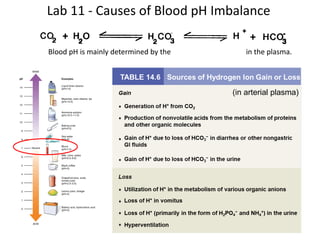
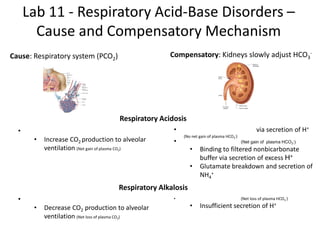
The document discusses acid-base balance in the arterial plasma and disorders that can disrupt this balance. It maintains that blood pH is important to regulate at 7.4 for metabolic processes. Respiratory and renal systems work to balance pH levels through carbonic acid buffering. Respiratory acidosis and alkalosis involve the lungs not eliminating carbon dioxide properly, while metabolic versions stem from other causes like lactic acid production. The lungs and kidneys each compensate differently, with the kidneys slowly adjusting bicarbonate and the lungs rapidly modulating carbon dioxide levels. Case studies are used to analyze how the body responds to initial pH changes through compensated steady states of related values over time.