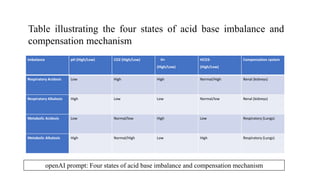
This document provides an overview of acid-base balance and the four main types of acid-base imbalances: respiratory acidosis, respiratory alkalosis, metabolic acidosis, and metabolic alkalosis. It describes the causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches for each type of imbalance. The key aspects of maintaining acid-base balance are regulating hydrogen ion concentration and buffering systems to keep arterial blood pH between 7.35-7.45. When the lungs or kidneys fail to regulate carbon dioxide or acid-base levels correctly, metabolic or respiratory acidosis and alkalosis can result.