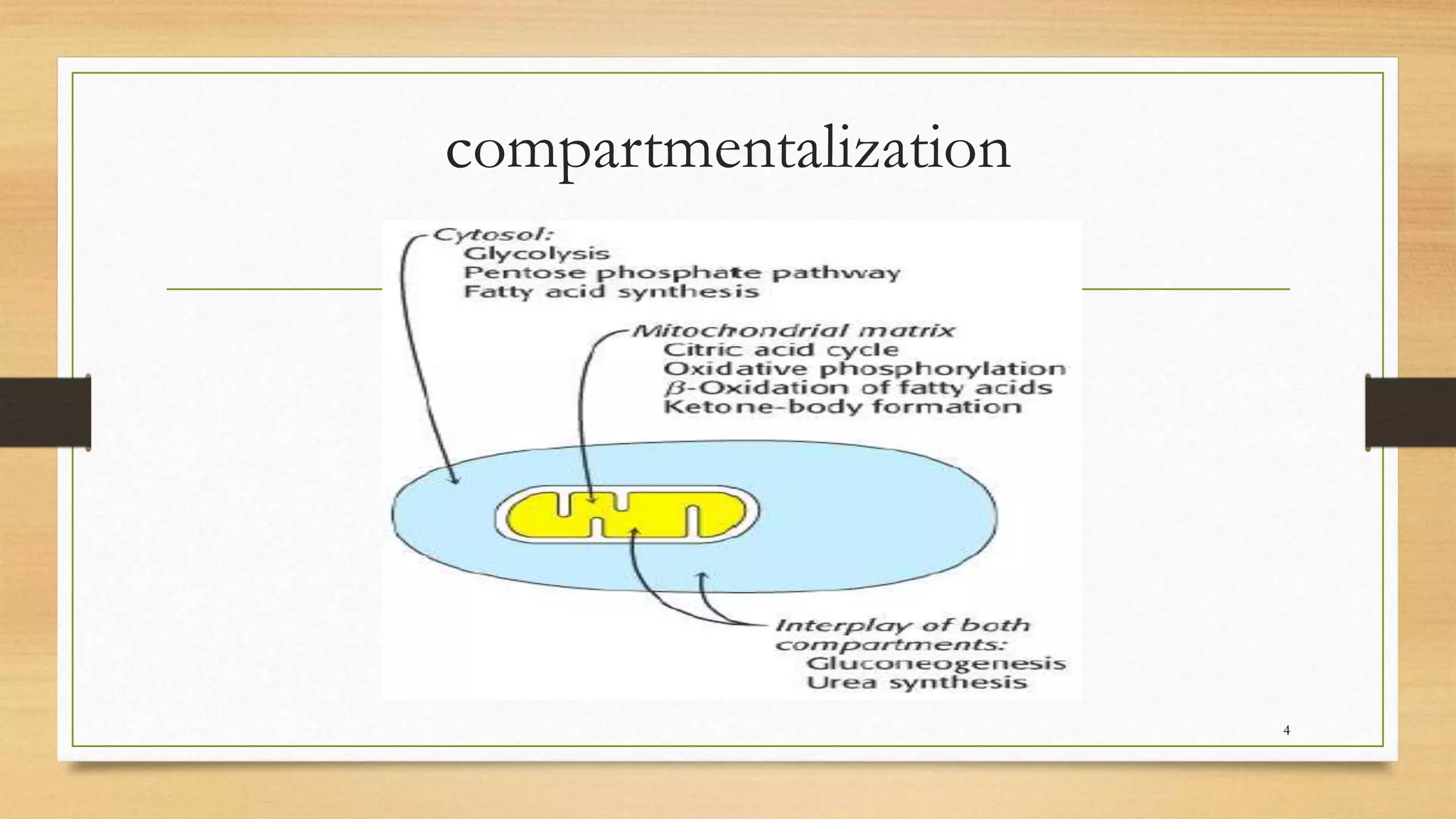
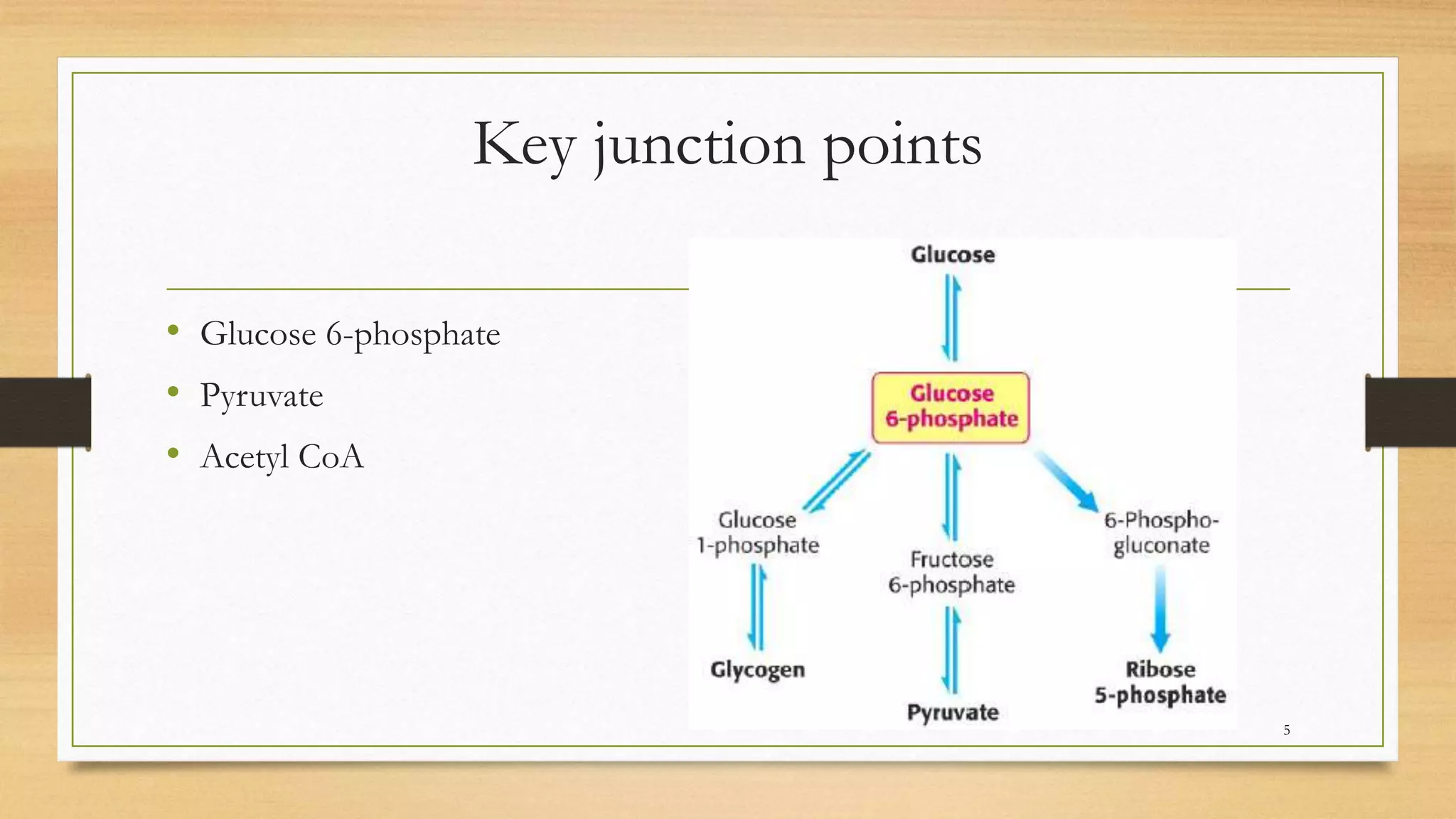
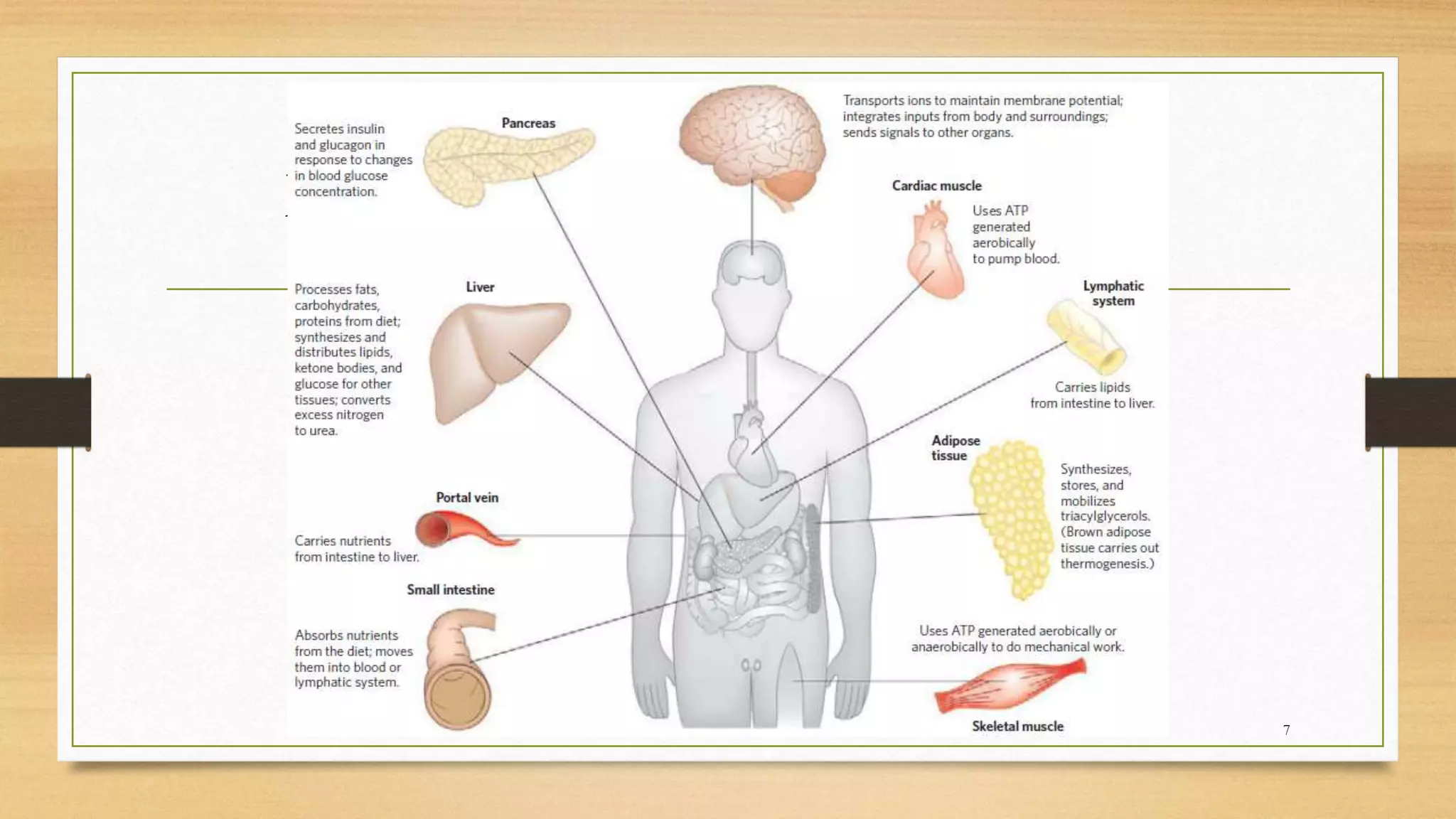
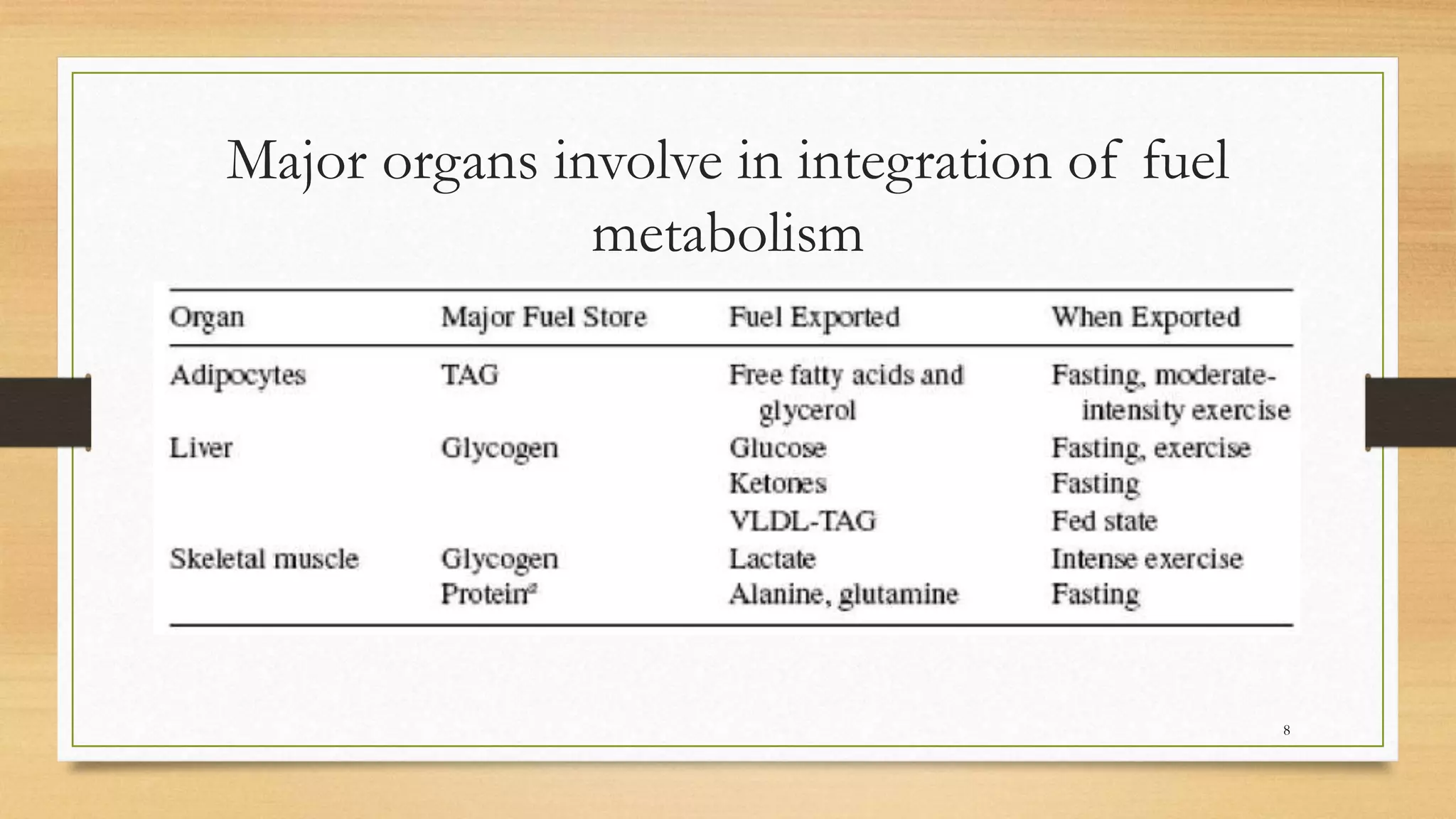
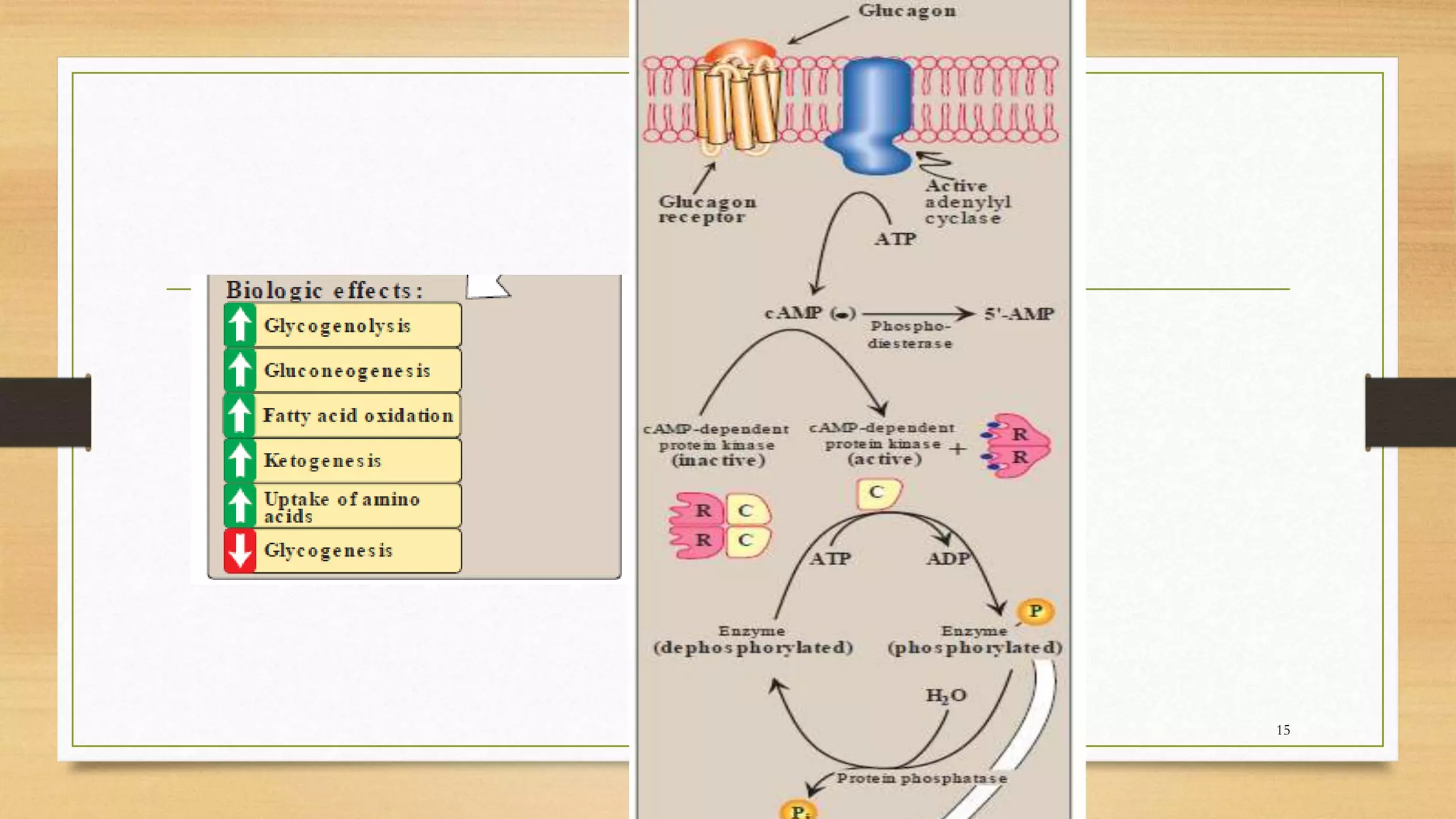
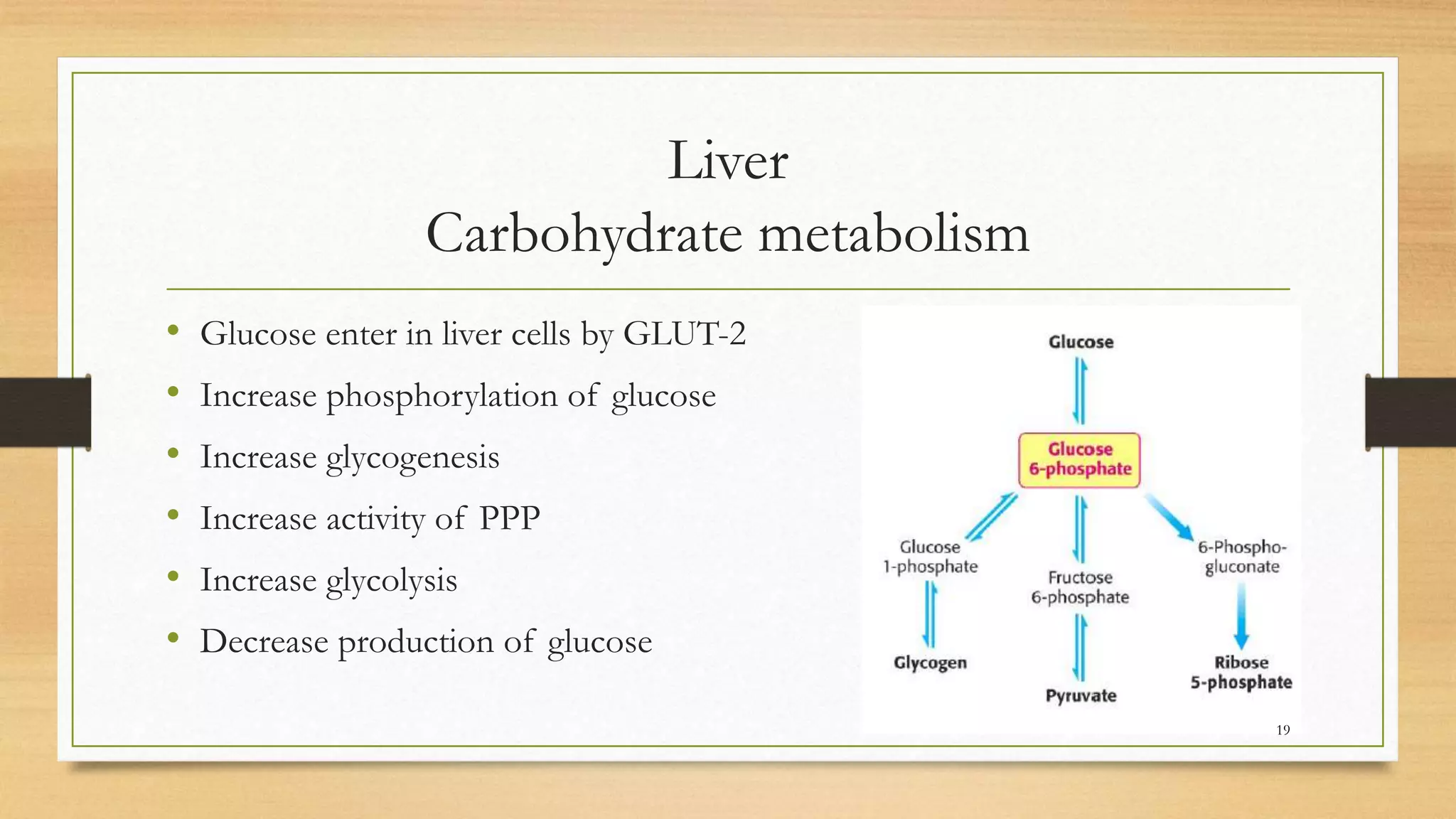
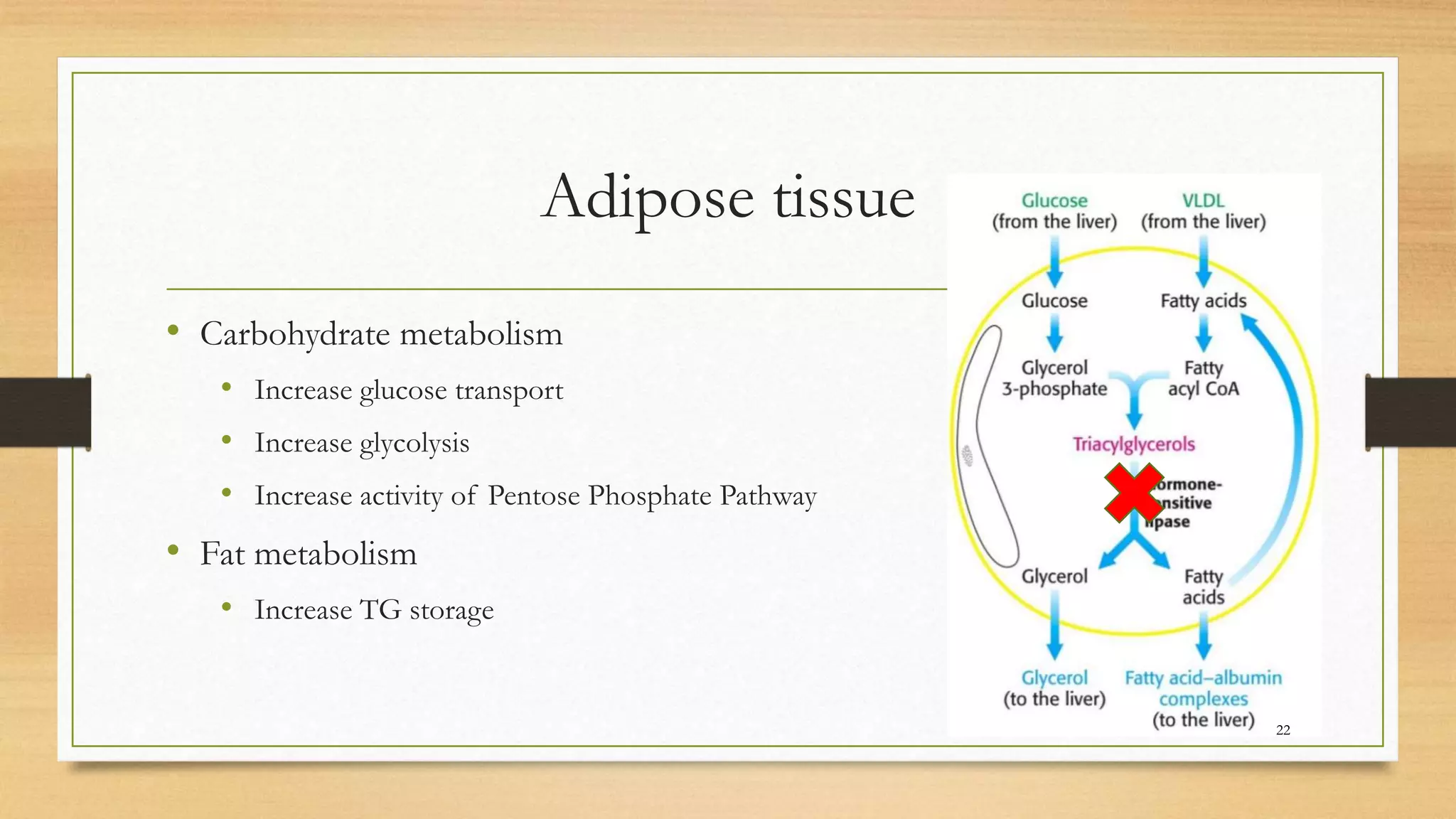
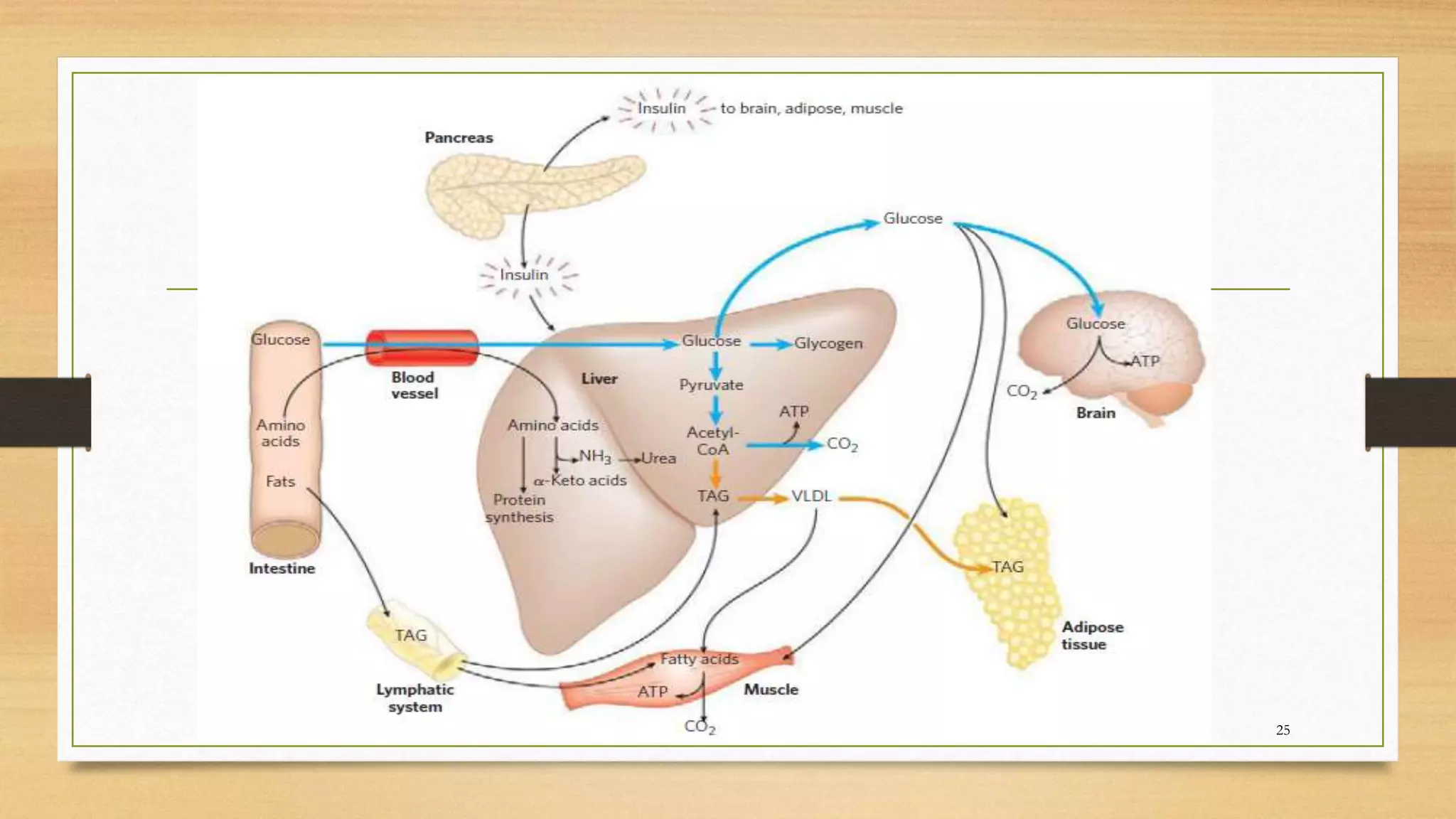
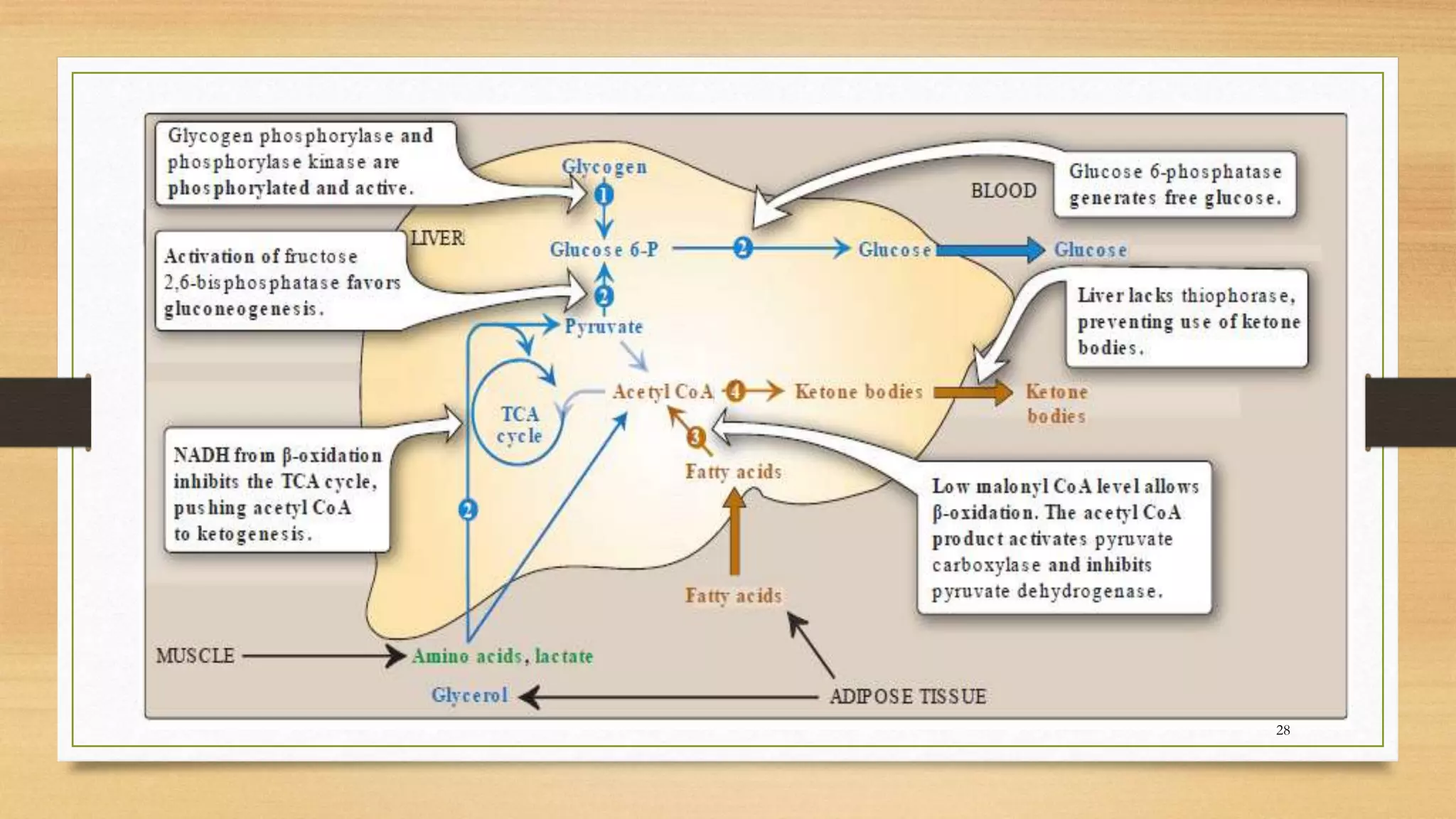
The integration of metabolism ensures a constant supply of fuel to all tissues. Metabolic pathways are controlled through four mechanisms: substrate availability, allosteric effectors, covalent modification of enzymes, and regulation of enzyme synthesis. During the absorptive state after a meal, elevated insulin and substrate availability promote anabolism through increased storage of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins in liver, adipose tissue, and skeletal muscle. In the fasting state, glucagon stimulates glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis, and ketogenesis in the liver to maintain blood glucose levels while fatty acids are oxidized in other tissues.