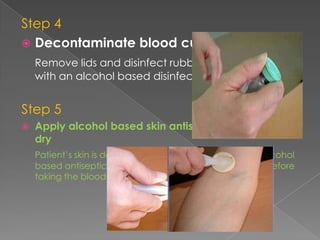
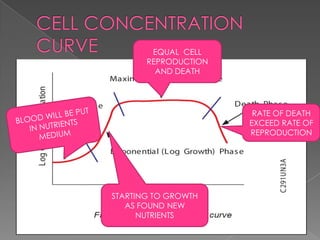
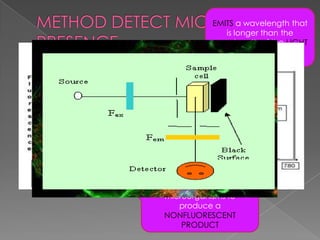
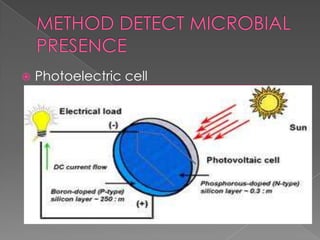
This document describes the process for collecting and analyzing blood cultures. Blood cultures involve injecting blood samples into bottles containing culture media to detect microorganisms. The process involves drawing blood via venipuncture, decontaminating bottle tops, applying antiseptic to the skin, inoculating bottles, mixing, labeling, and sending samples for analysis. Automated blood culture analyzers use techniques like fluorescence, colorimetry, or pressure changes to detect microorganism growth and provide results. Factors like adequate sample volume, contamination prevention, and analyzer features should be considered when purchasing a system.