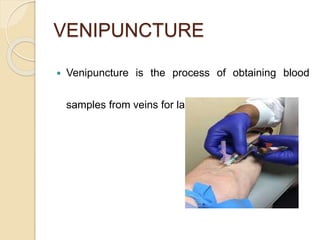
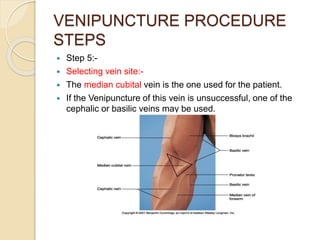
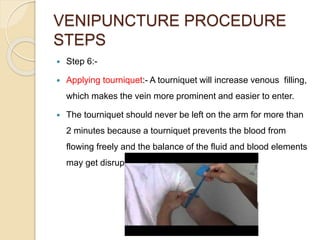
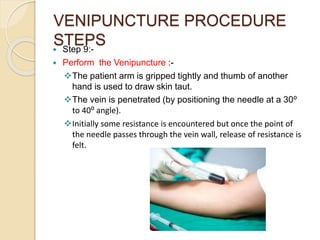
This document discusses the process of phlebotomy and blood specimen collection. Phlebotomy, also known as venipuncture, involves collecting a blood sample from veins using a needle. It describes the steps of the venipuncture procedure, which includes preparing materials, positioning the patient, selecting a vein, applying a tourniquet, cleansing the skin, inspecting needles/syringes, performing the puncture, and handling the collected blood samples appropriately based on testing requirements. Performing venipuncture properly is important for obtaining quality lab test results.