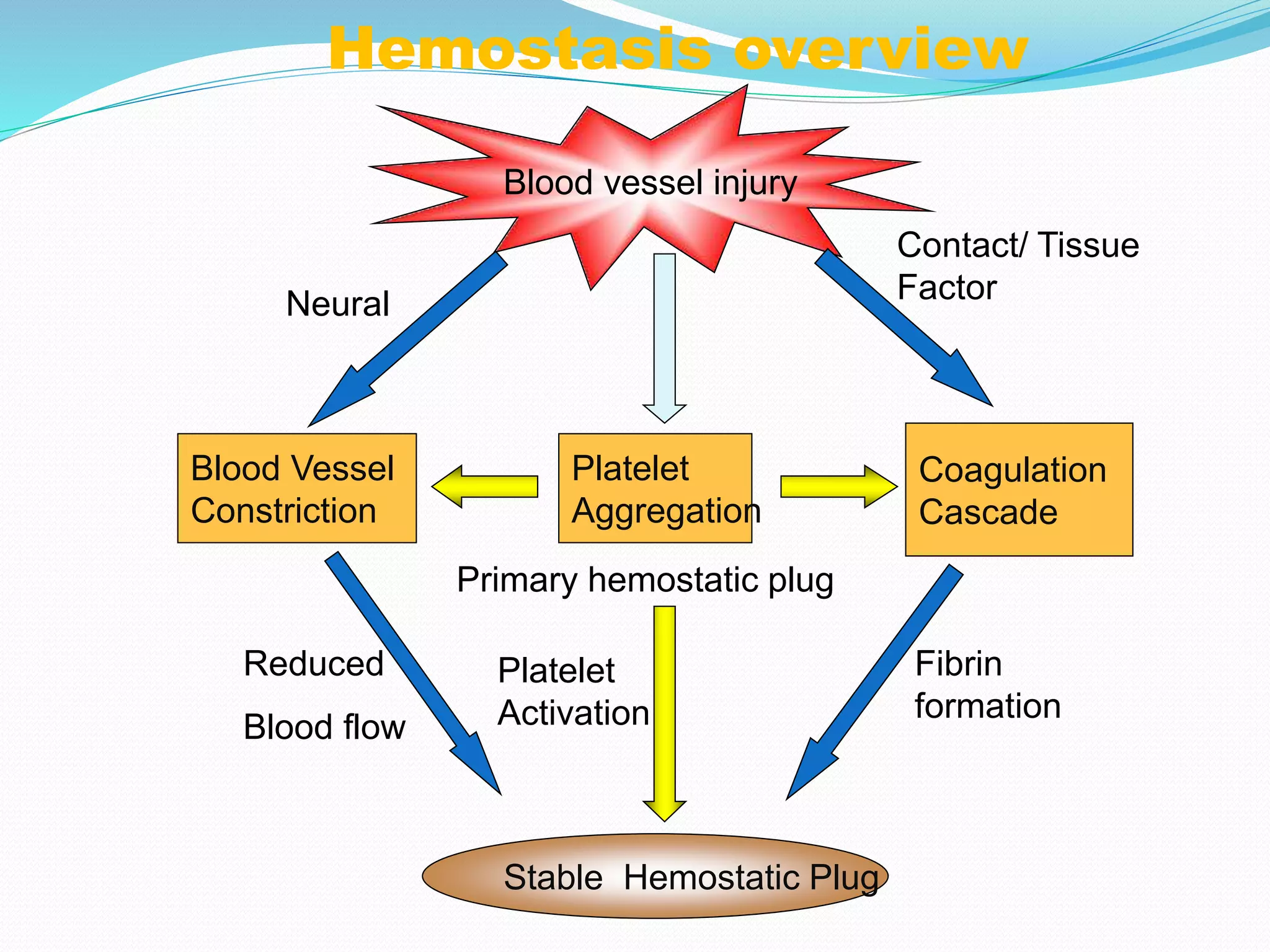
The document summarizes normal hemostasis and various bleeding disorders. It describes the three stages of normal coagulation as primary hemostasis involving platelets, secondary hemostasis involving clotting factors, and tertiary hemostasis involving fibrin formation and resolution. Causes of bleeding disorders include vessel wall abnormalities, platelet deficiencies or dysfunctions, and clotting factor derangements. Specific disorders discussed include immune thrombocytopenic purpura, hemophilia, von Willebrand disease, and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Tests used to evaluate bleeding disorders and clinical manifestations of different disorders are also summarized.