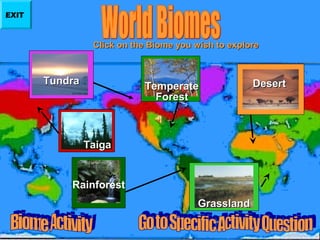
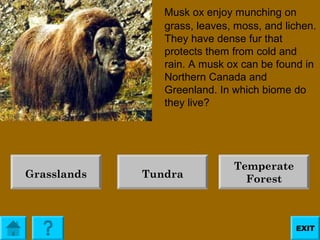
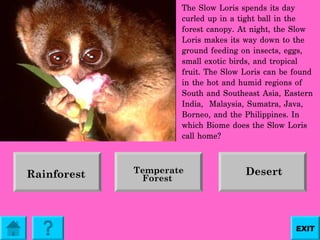
The document provides information about teaching biology standard 5.2 which involves inferring the types of organisms native to specific biomes. It explains that each biome contains a great deal of information and some biomes share similar plant and animal life, making this standard challenging to teach. It then defines what a biome is and provides examples of the major biomes - tundra, desert, grassland, taiga, temperate forest, and rainforest - including characteristics, plants, and animals commonly found in each one. Users can click on individual biomes for more details.