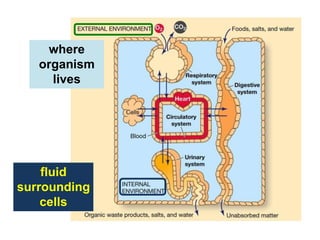
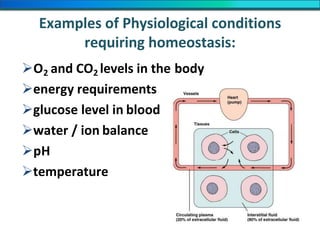
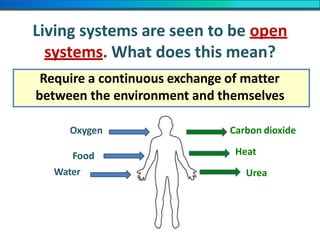
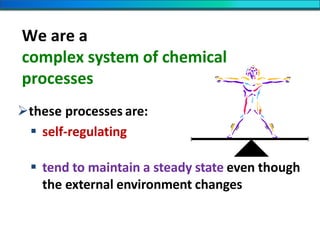
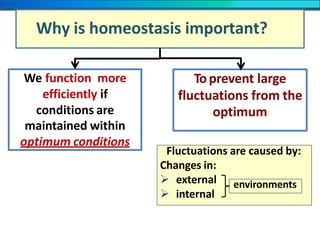
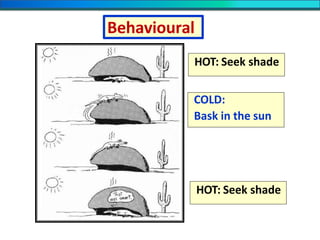
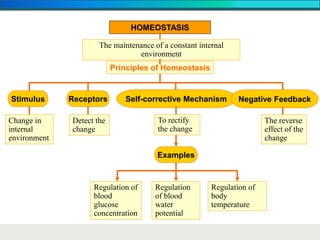
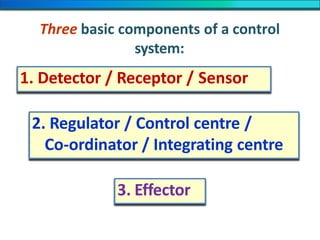
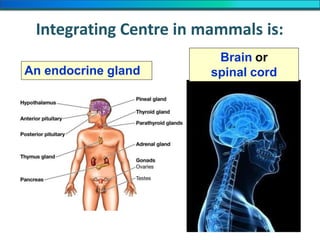
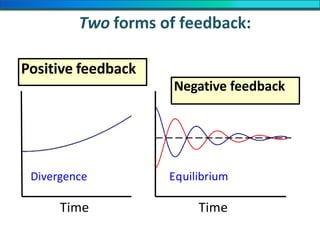
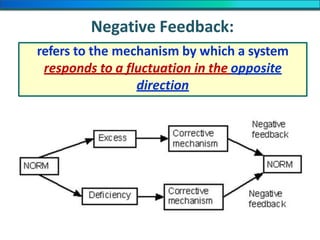
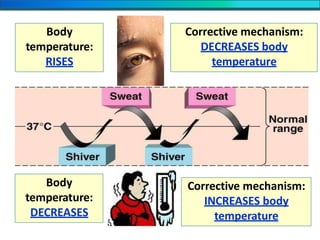
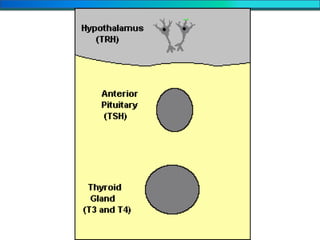
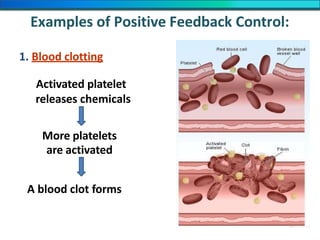
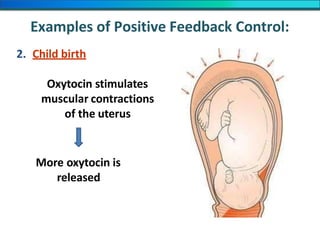
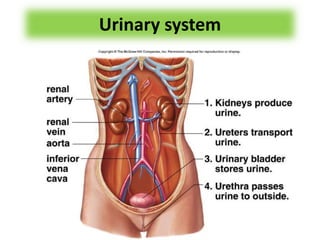
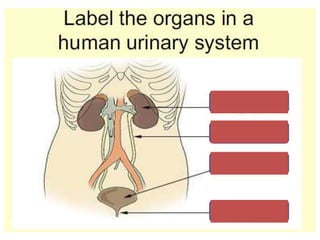
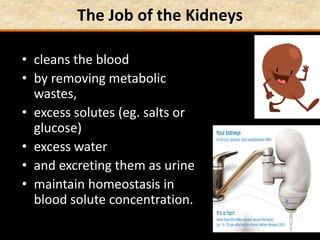
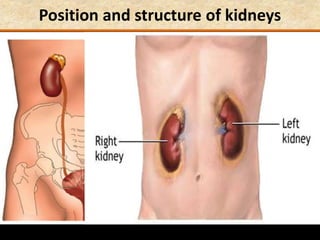
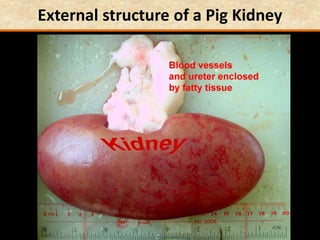
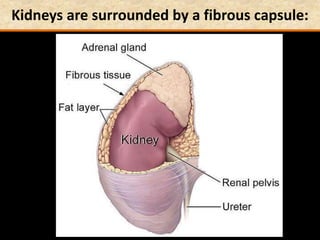
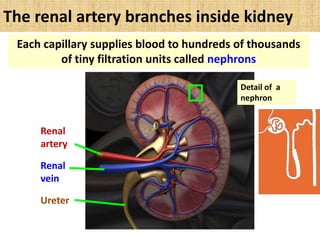
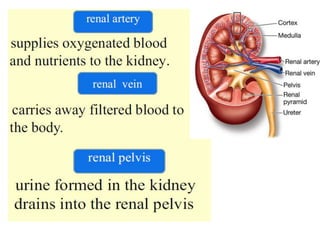
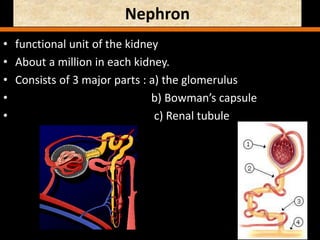
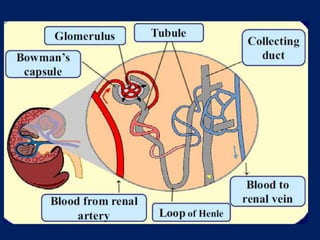
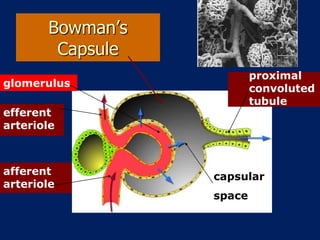
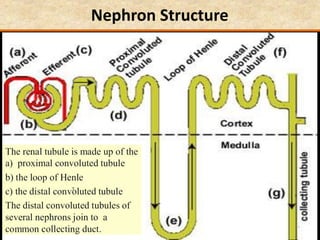
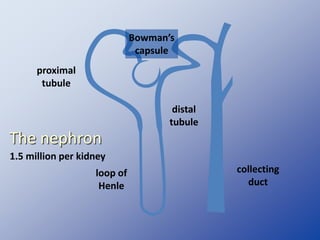
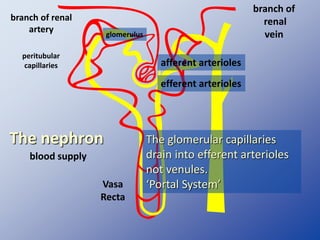
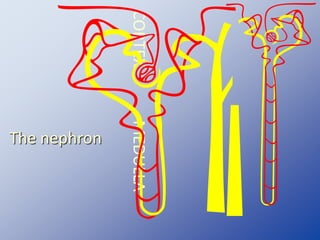
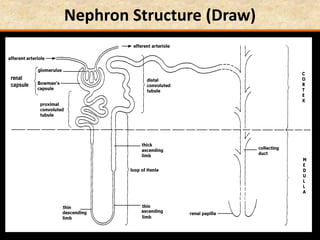
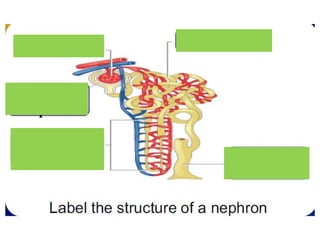
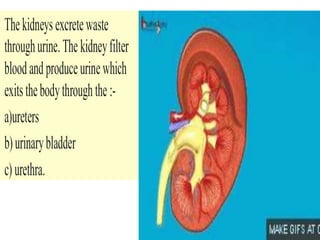
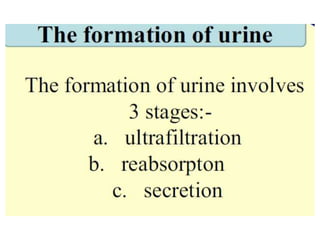
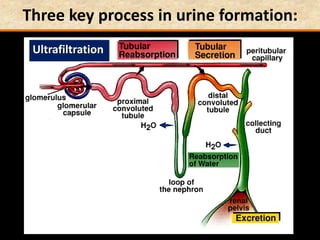
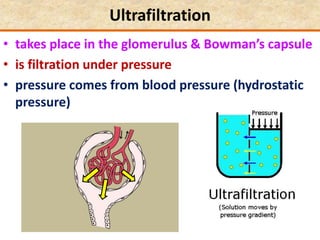
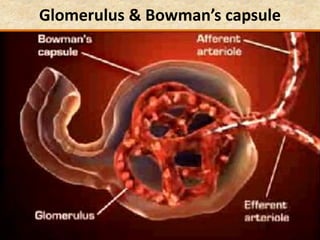
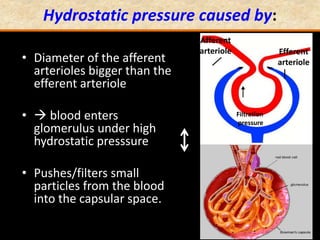
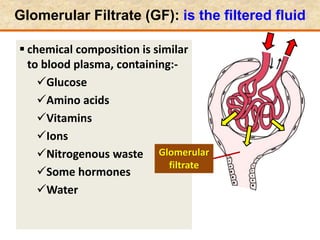
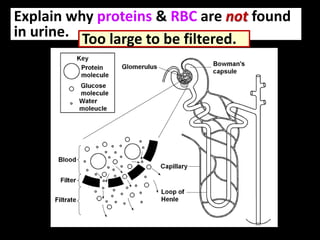
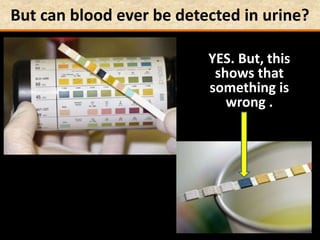
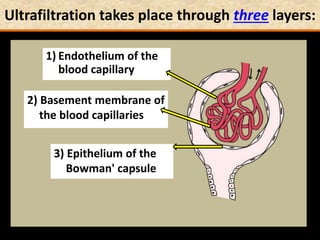
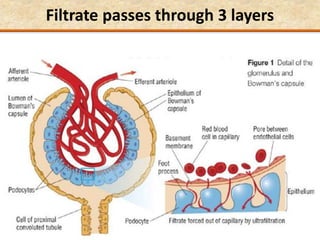
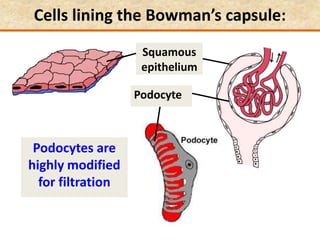
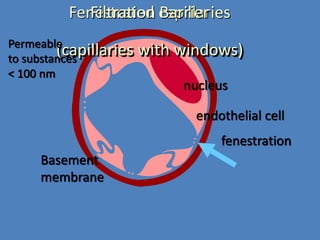
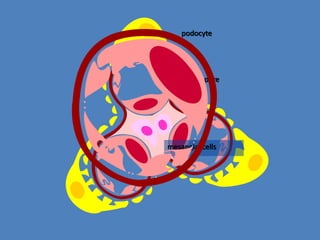
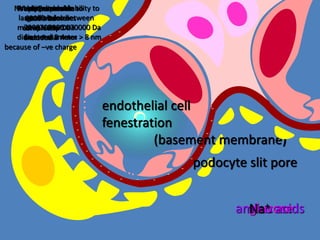
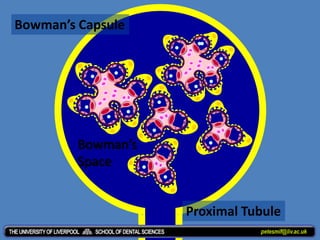
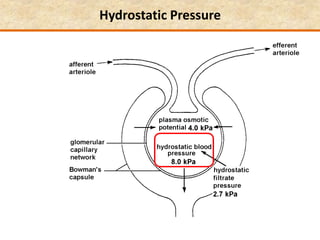
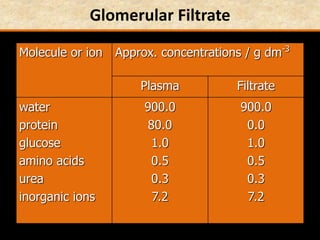
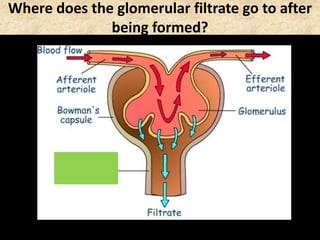
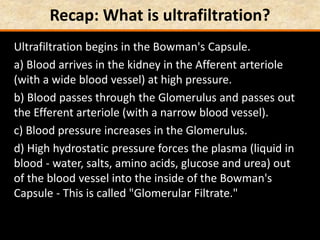
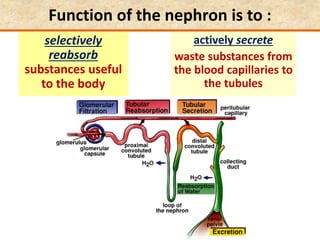
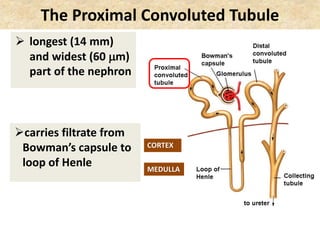
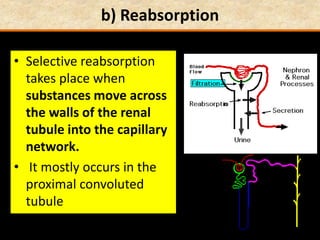
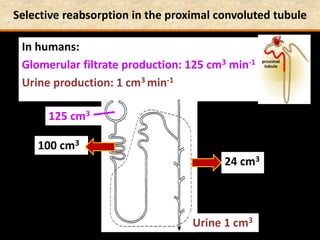
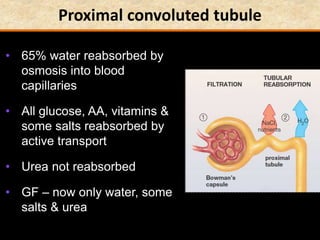
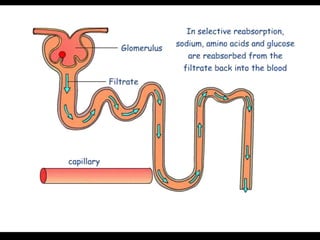
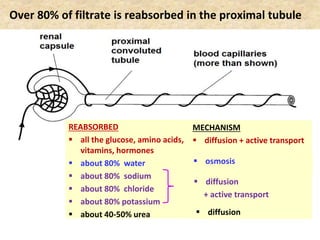
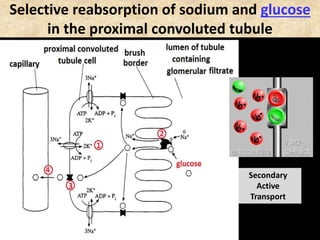
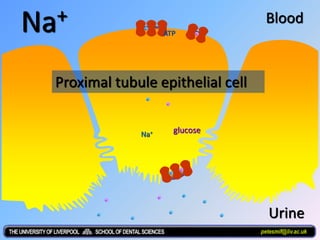
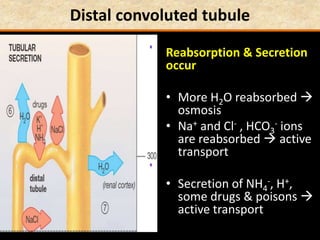
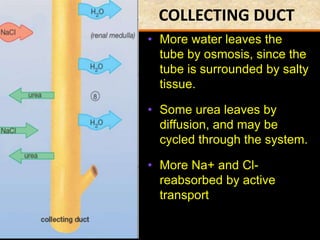
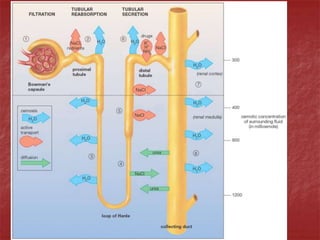
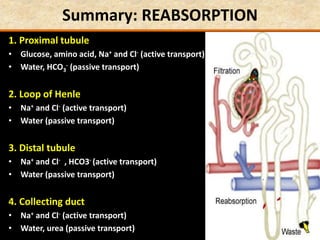
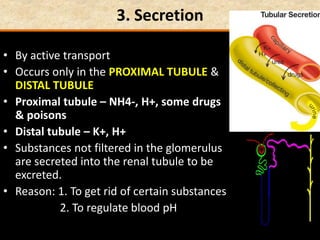
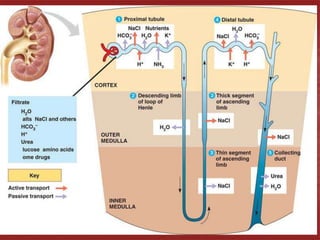
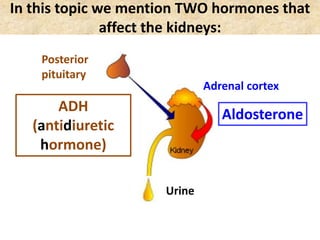
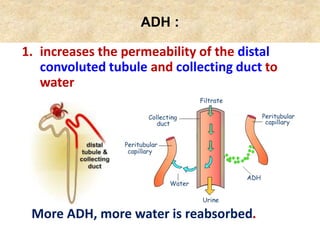
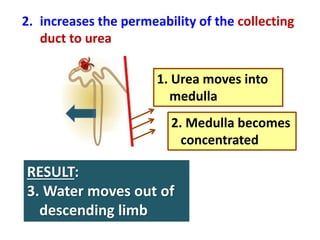
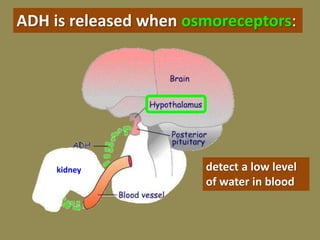
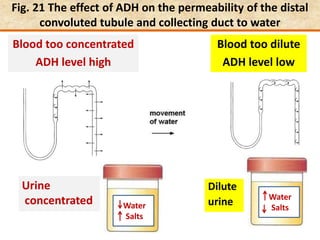
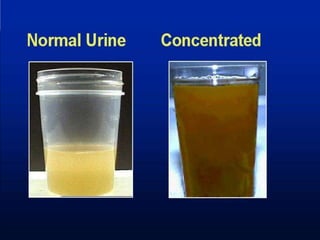
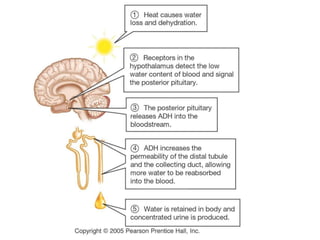
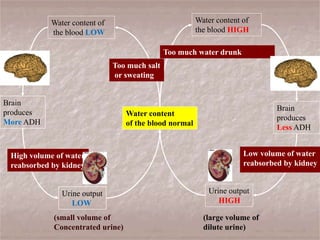
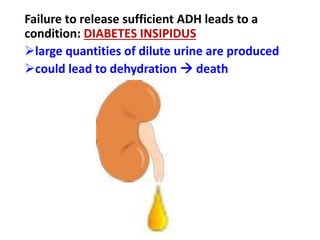
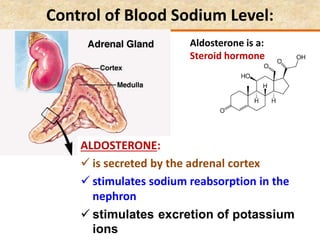
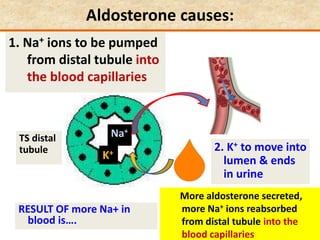
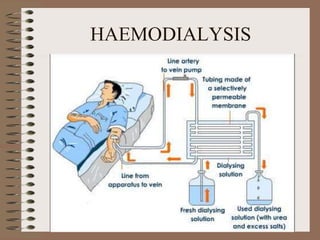
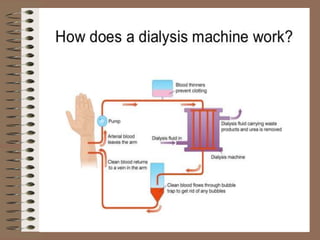
The document discusses homeostasis and the role of the kidneys in maintaining homeostasis. It begins by defining homeostasis as the maintenance of relatively stable internal conditions in the body despite changes in the external environment. It then describes the three main components of homeostasis - receptors that detect changes, control centers that regulate responses, and effectors that cause the responses. As an example, it explains how negative feedback loops work to regulate factors like body temperature and hormone levels. The document then focuses on the kidneys and urine formation. It describes the parts of the nephron, how ultrafiltration in the glomerulus produces an initial filtrate, and how subsequent reabsorption and secretion in the nephron tubules allow the kidneys to regulate


![Homeostasis:
Greek: ‘homoios’ = similar
‘stasis’ = standing still
Homeostasis is the
maintenance of a relatively
stable internal environment
The ‘internal’ environment is
the:
tissue fluid [interstitial fluid]
plasma](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-160602125821/85/COORDINATION-RESPONSE-PART-3-HOMEOSTATIS-URINE-FORMATION-4-320.jpg)
















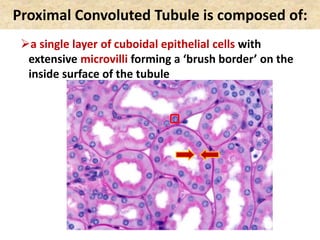
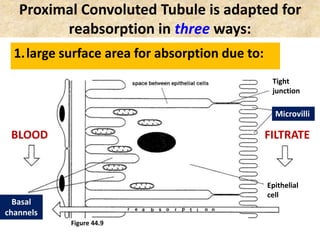
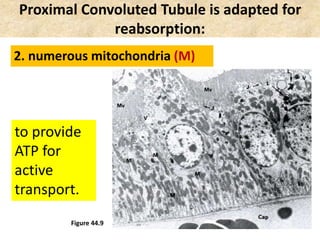
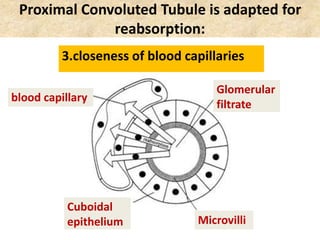

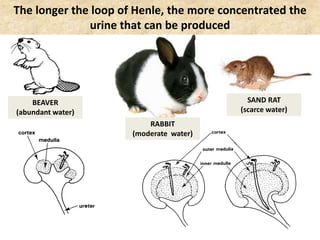
![Birds & Mammals are the only vertebrates:
which can produce a urine which is more
concentrated than the blood
[hypertonic]
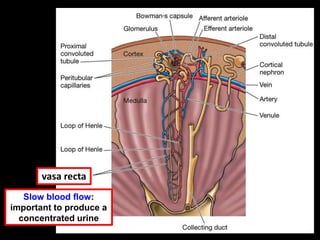
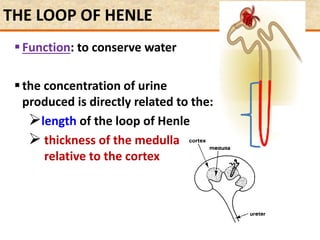
with loops of Henle
Loop of Henle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-160602125821/85/COORDINATION-RESPONSE-PART-3-HOMEOSTATIS-URINE-FORMATION-109-320.jpg)
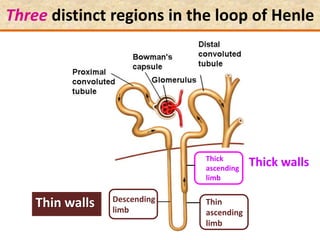
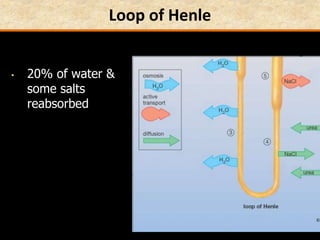
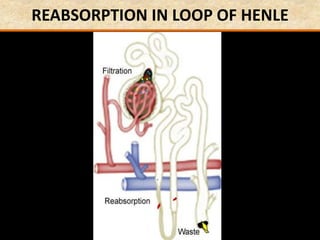
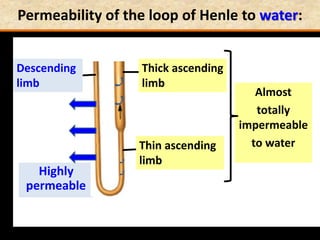
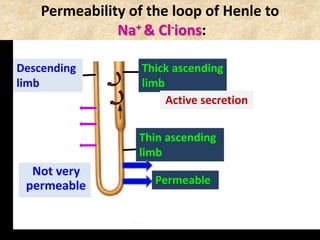
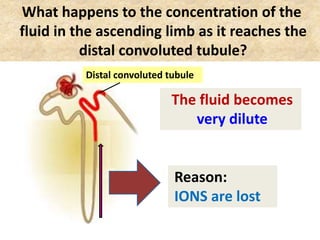
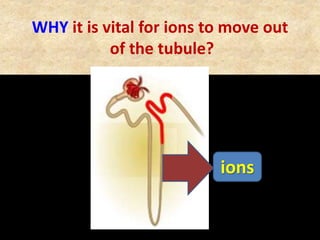
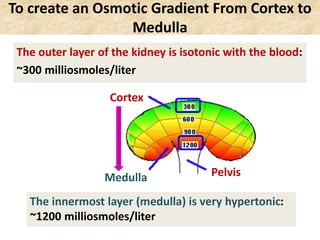
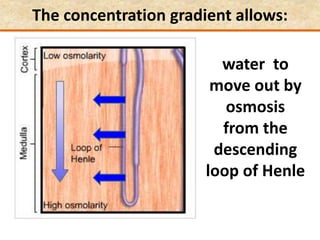
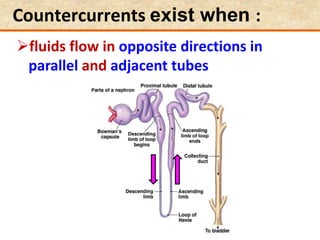
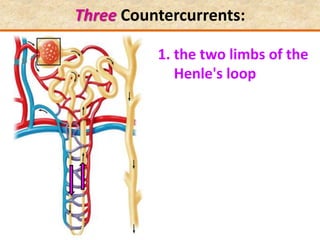
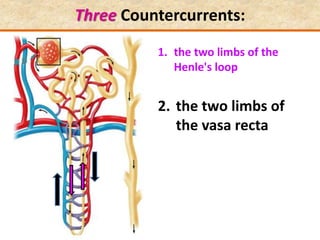
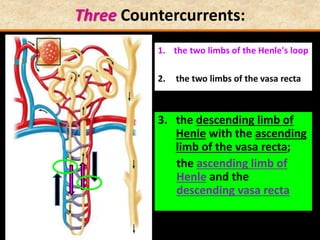
![Question: [SEP, 2009]
Briefly describe the role of each of the following in
osmoregulation in humans:
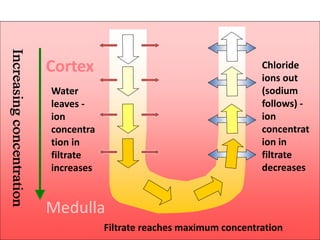
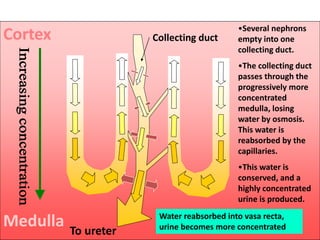
i) The descending limb of the Loop of Henle; (2)
Is permeable to water. Functions towards water
conservation.
ii) The ascending limb of the Loop of Henle; (2)
Is relatively impermeable to water but permeable to salts.
The tissue fluid inside the medulla becomes concentrated as
salts move out of the ascending limb. This causes water to be
drawn out of the descending limb.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-160602125821/85/COORDINATION-RESPONSE-PART-3-HOMEOSTATIS-URINE-FORMATION-127-320.jpg)













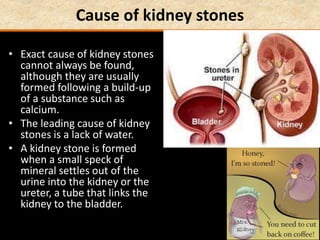
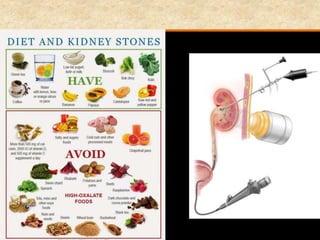


![Manneken Piss [Brussels, Belgium]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-160602125821/85/COORDINATION-RESPONSE-PART-3-HOMEOSTATIS-URINE-FORMATION-175-320.jpg)