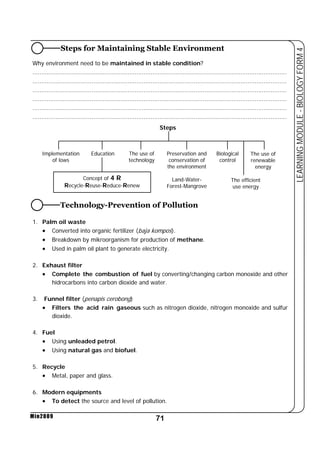
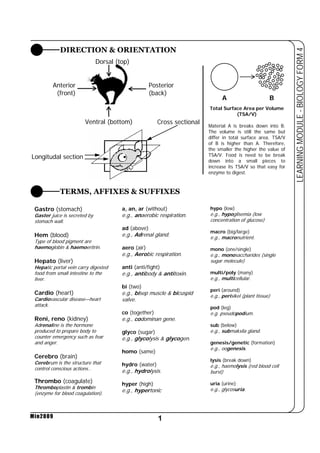
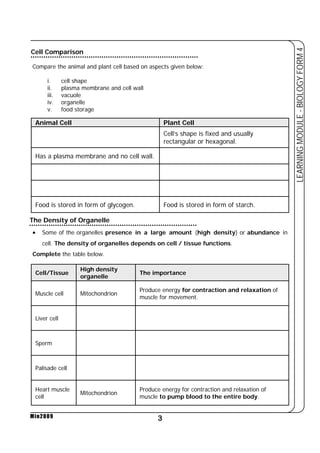
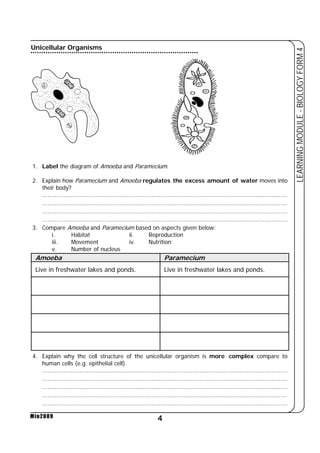
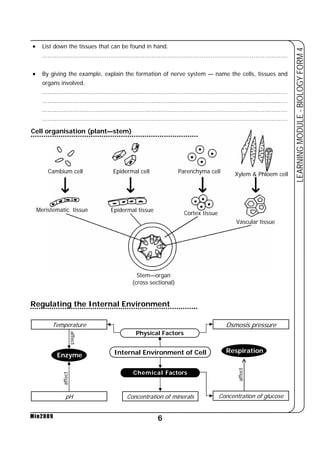
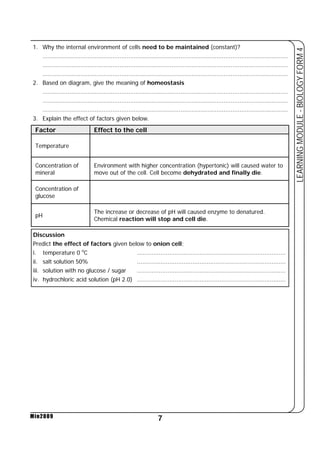
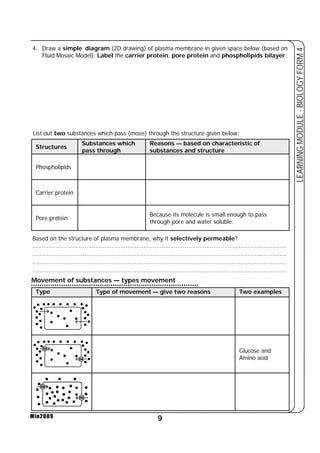
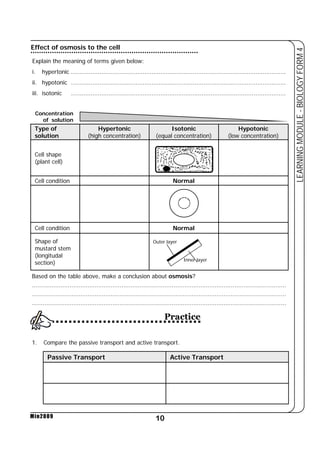
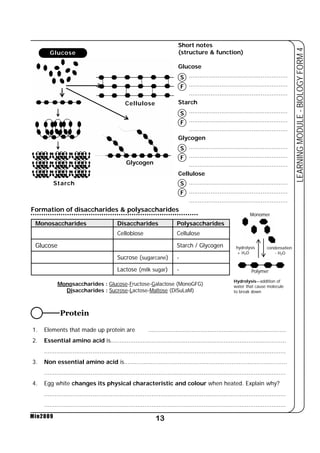
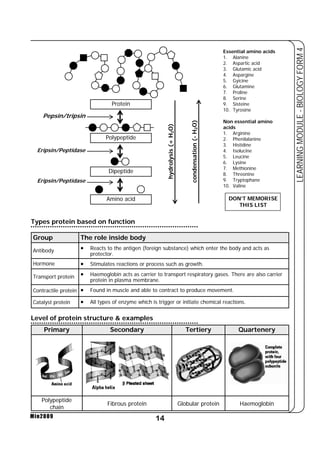
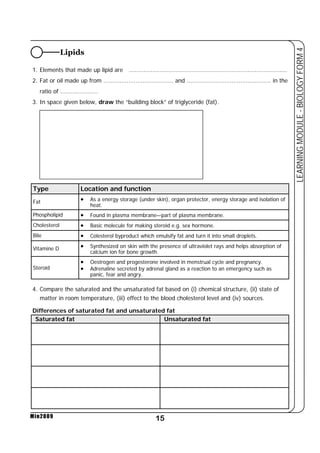
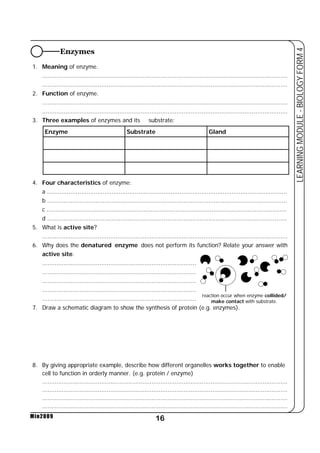
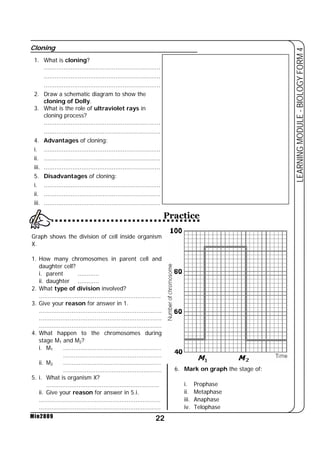
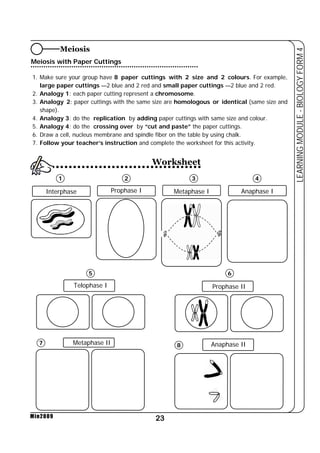
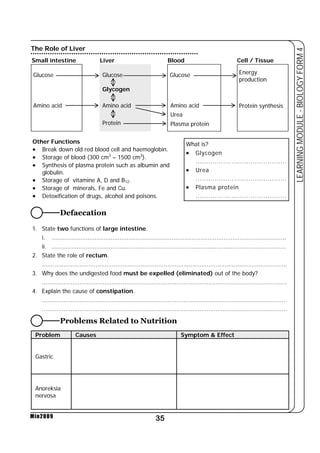
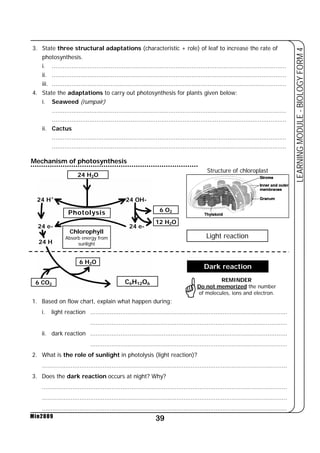
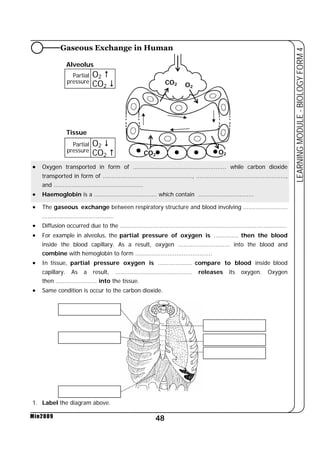
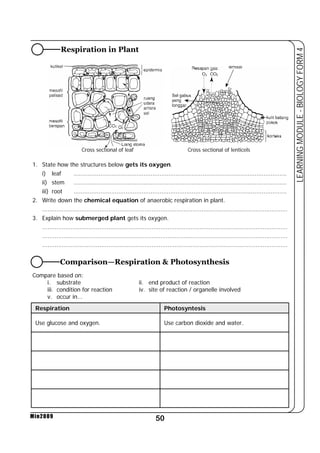
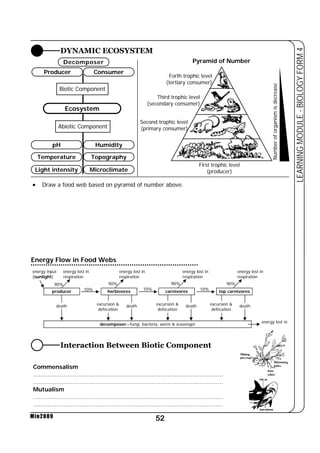
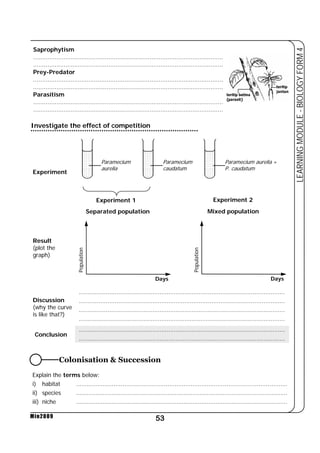
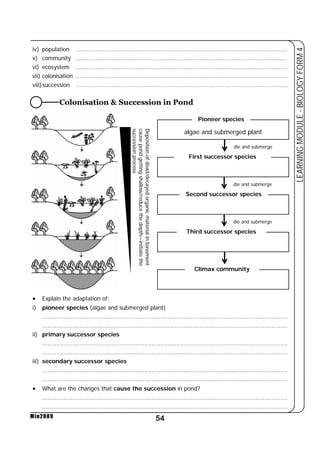
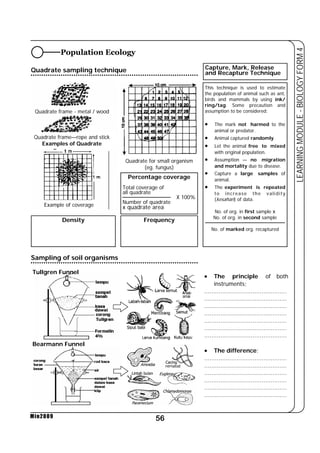
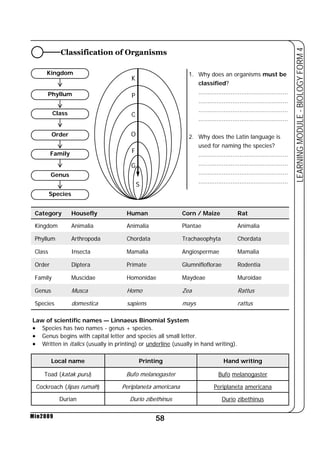
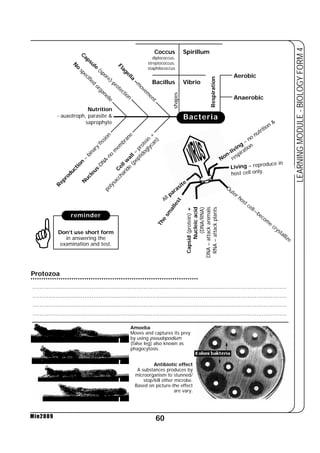
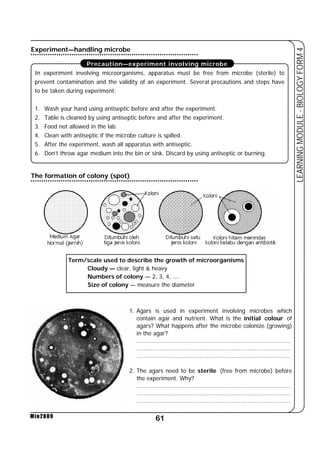
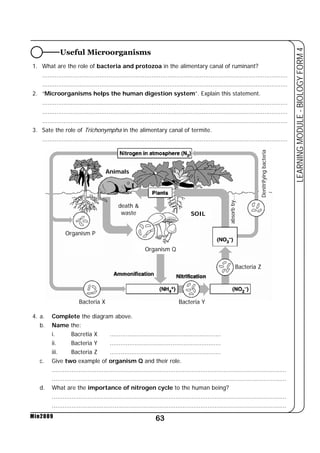
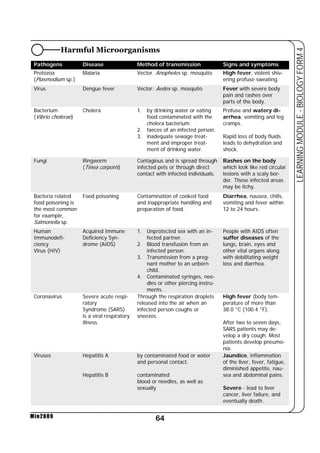
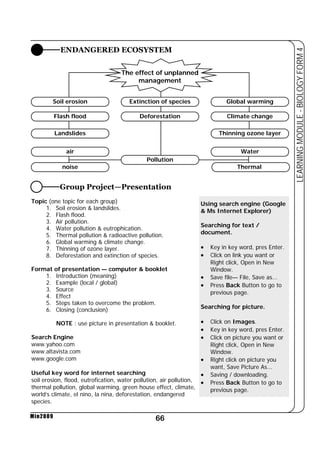
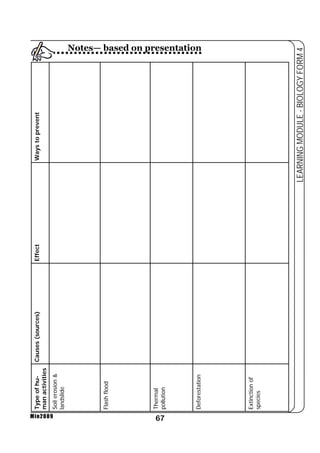
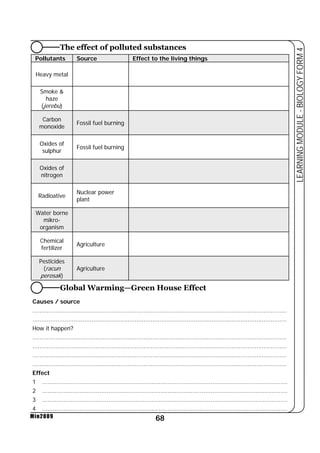
This document provides a learning module on biology for Form 4 students. It includes information on cell structure and organization, movement of substances into and out of cells, and the basic chemical components of living things like carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Diagrams and tables are included to illustrate topics like organelle functions, osmosis, and the structures of biological molecules. The module aims to explain key concepts in biology and provide students with definitions, examples, and practice questions to enhance their understanding.



















![2. Why does the unicellular organism such as yeast and bacteria are able to survive only
by performing anaerobic respiration? [only produce small amount of energy]
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
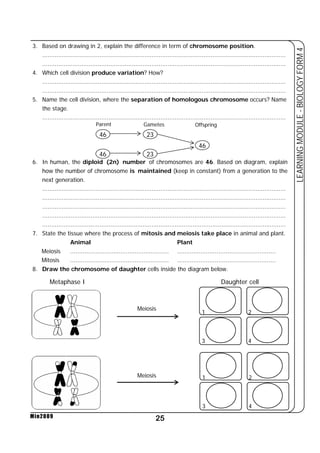
......................................................................................................................................
3. During flood, most of plant will die. Explain why? [based on respiration]
......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................
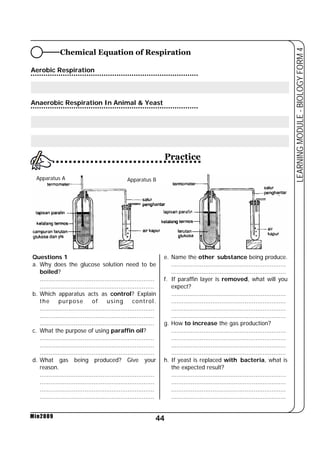
4. Compare between aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration based on:
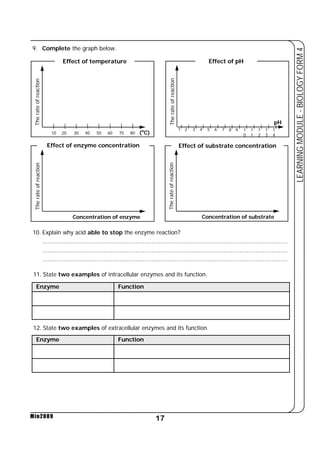
i) Substrate used
ii) Product of reaction
iii) The amount ATP produced
iv) Site of reaction.
Aerobic Respiration Anaerobic Respiration
Substrate used is glucose Substrate used is glucose
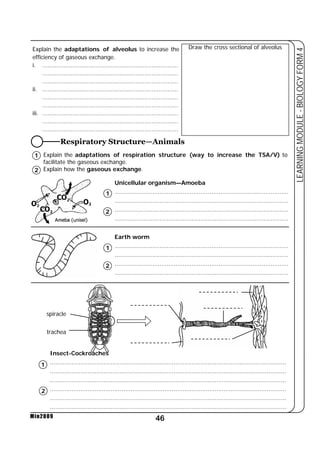
Respiratory Structure—Human
45
LEARNING MODULE - BIOLOGY FORM 4
• Role of cartilage rings?
................................................
................................................
................................................
• Function of epiglottis?
................................................
................................................
................................................
• Function of diaphragm?
................................................
................................................
................................................
Min2009
epiglottis
larynx
lung](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learningmodulebiologyform4-141213085437-conversion-gate01/85/Learning-module-biology-form-4-46-320.jpg)








![Ways to prevent thinning of ozone layer
1 .........................................................................................................................................
2 .........................................................................................................................................
3 .........................................................................................................................................
4 .........................................................................................................................................
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD)
Definition
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
Relationship with dissolved oxygen level
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
Eksperiment-measuring BOD value
• Blue methylene will decolorises in a sort time due to low
level of dissolved oxygen where the oxygen usage by
microbe is high.
• This means the BOD value is high.
• The increase usage of oxygen will reduce the oxygen level
and increase the BOD value. [O2 È — BOD Ç]
The effect of high BOD value to aquatic organism.
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
70
LEARNING MODULE - BIOLOGY FORM 4
Min2009
Eutrophication occur due to the sudden increase of algae population
and increased the BOD value (low level of dissolved oxygen).
Explain that phenomena. [algae is producing oxygen trough photosynthesis]
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
Why the presence of organic waste or fertilizer will increase the BOD value?
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................................](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learningmodulebiologyform4-141213085437-conversion-gate01/85/Learning-module-biology-form-4-71-320.jpg)