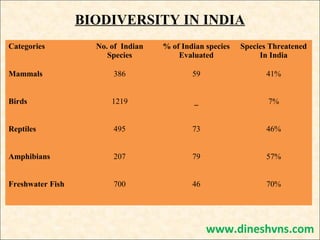
This document discusses biodiversity and its conservation. It begins with definitions of biodiversity and explains that it represents the variety of life on Earth. It then describes the three types of biodiversity: diversity of species, ecosystems, and genes. Key topics covered include the distribution of biodiversity globally and within India, benefits provided by biodiversity, threats to biodiversity like habitat loss, and approaches to conservation like protected areas and environmental education. International agreements to protect biodiversity are also summarized, along with recent biodiversity-related events.