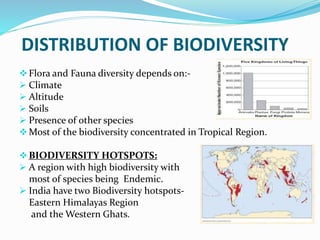
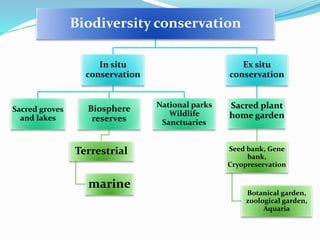
This document discusses biodiversity, including its definition, types, distribution, benefits, threats, and conservation. It notes that biodiversity represents the variety of life on Earth and is essential for human survival. There are three types of biodiversity: genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity. Most biodiversity is concentrated in tropical regions and biodiversity hotspots. While biodiversity provides many benefits, it faces threats from habitat loss, overexploitation, pollution, and climate change. Conservation efforts include both in situ and ex situ strategies to protect biodiversity for current and future generations.