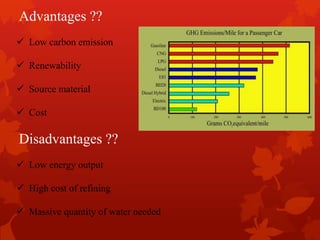
This document describes the manufacturing process for biodiesel from waste cooking oil. It involves a 4-step process: 1) testing the free fatty acid content to determine the appropriate conversion process, 2) heating the oil to convert it to biodiesel using a methoxide catalyst, 3) separating the biodiesel and glycerol layers, and 4) washing the biodiesel to remove impurities until the pH is neutral. The biodiesel is then tested for viscosity, copper corrosion, and flash point to ensure it meets standards before being implemented as an alternative fuel to address increasing crude oil prices and need for renewable fuels.