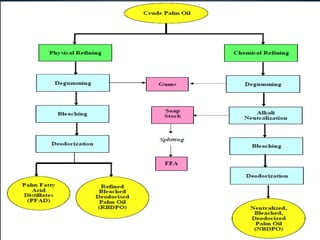
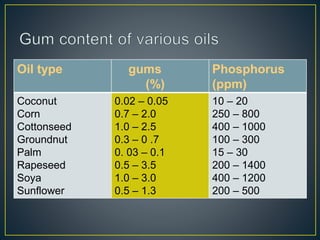
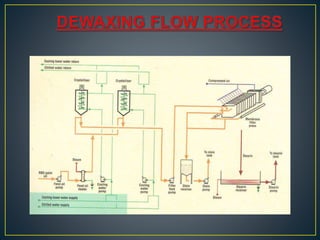
This document summarizes the key steps in refining crude vegetable oils. It discusses (1) degumming to remove gums and phosphorus through water degumming, (2) bleaching to reduce coloring pigments using bleaching earth, and (3) deodorization to remove odors and free fatty acids through vacuum distillation. The overall goal of the refining process is to produce an edible oil that is light in color and free of impurities, odors, and contaminants with an extended shelf life.