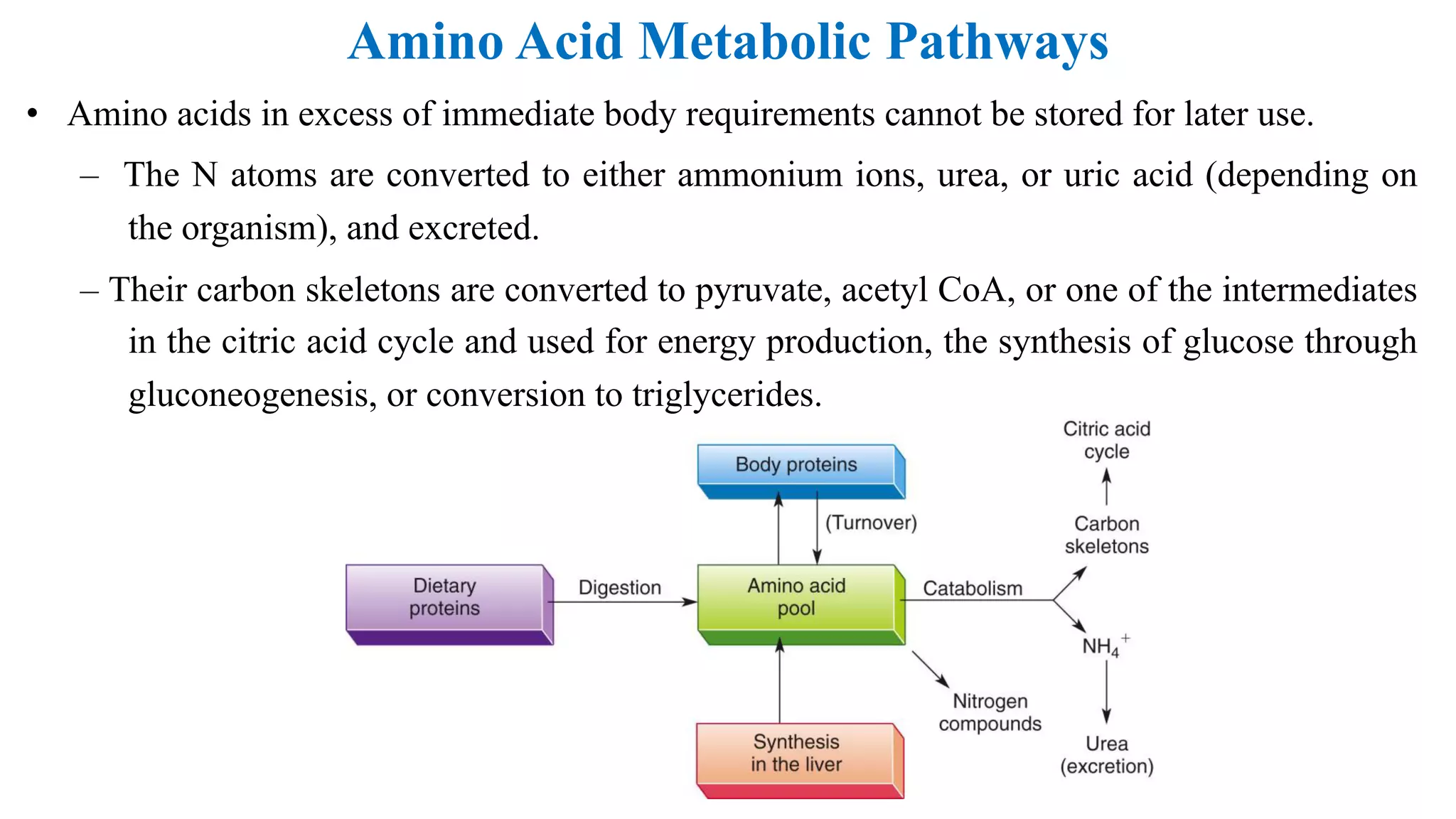
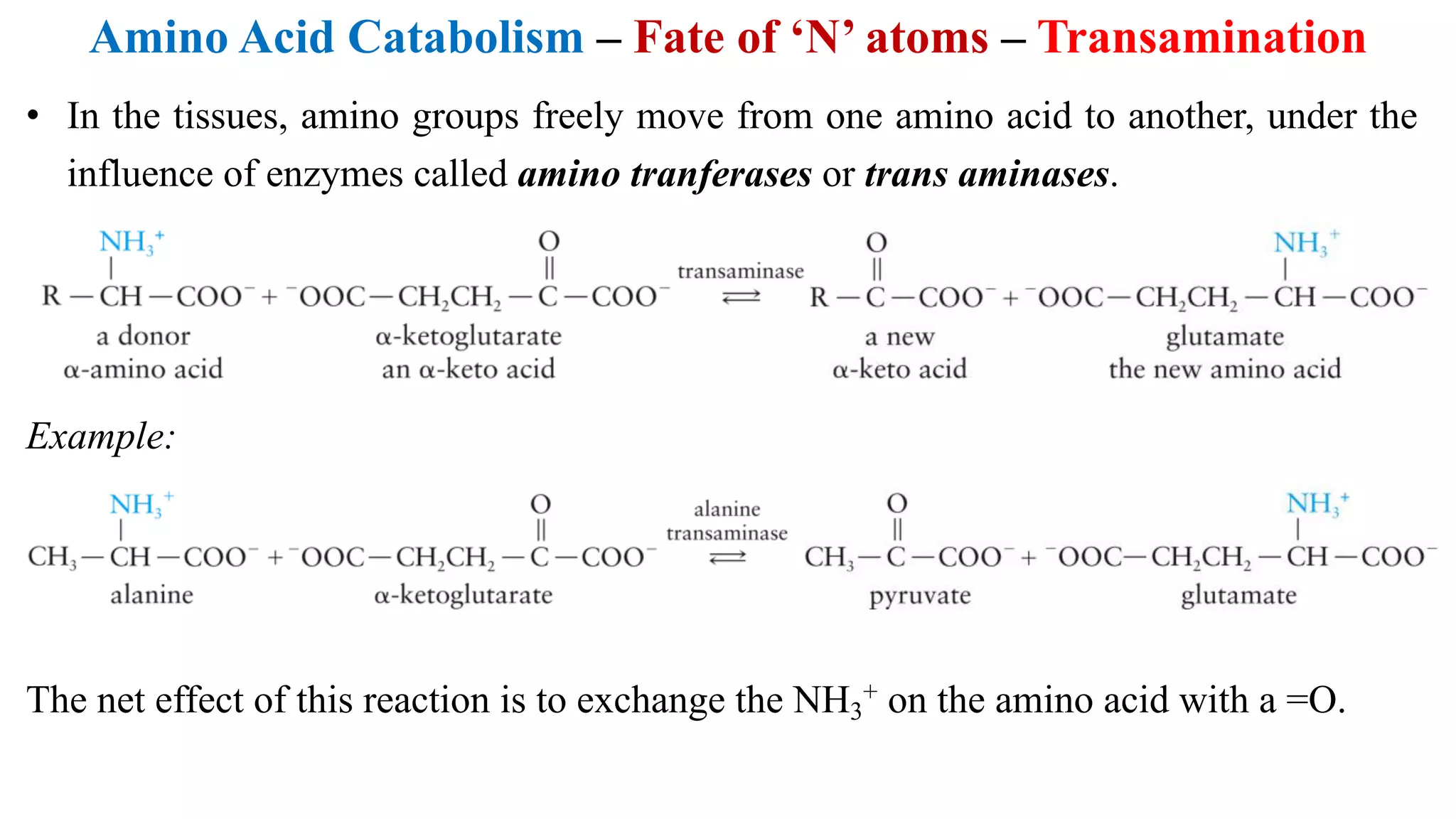
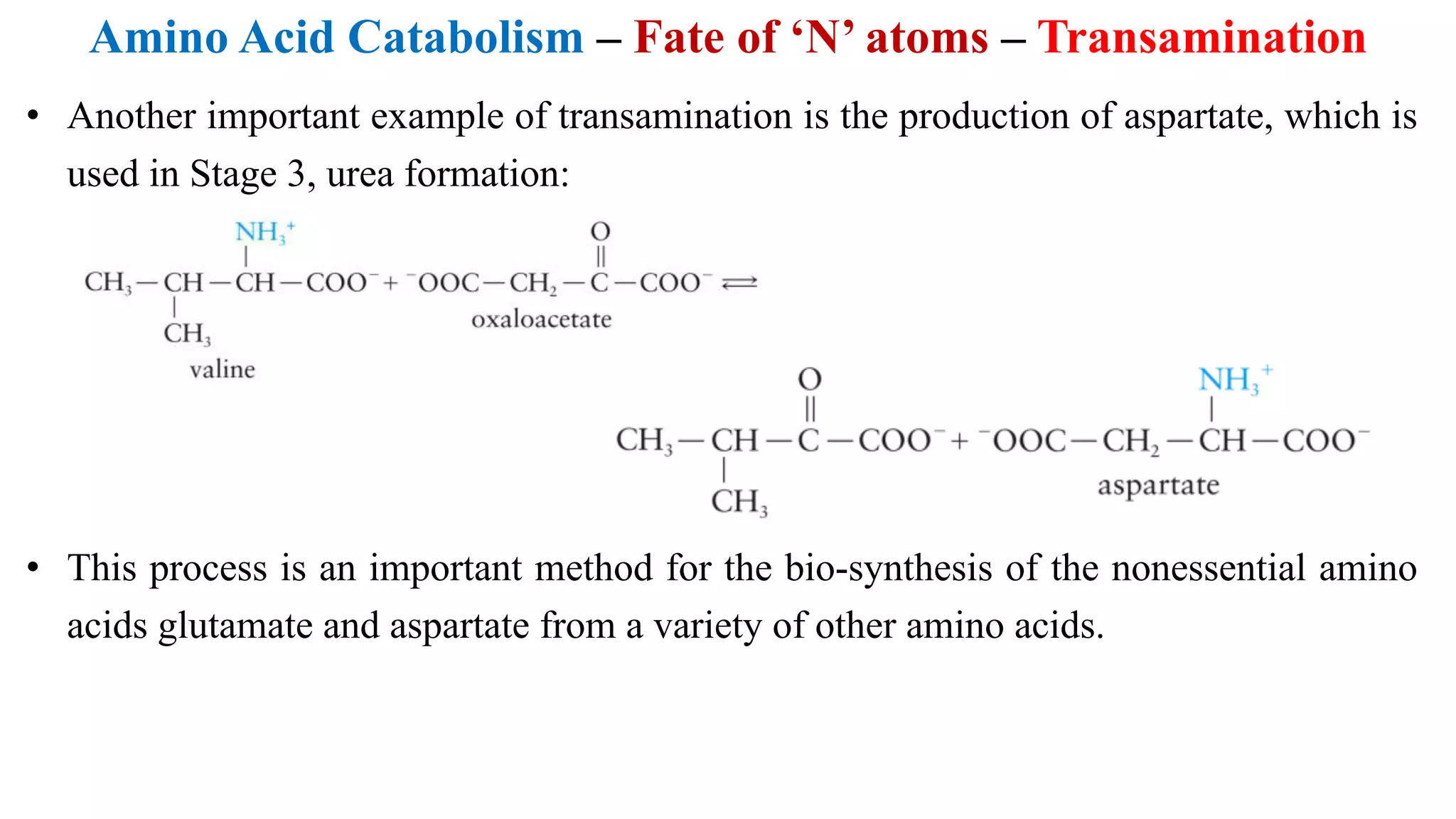
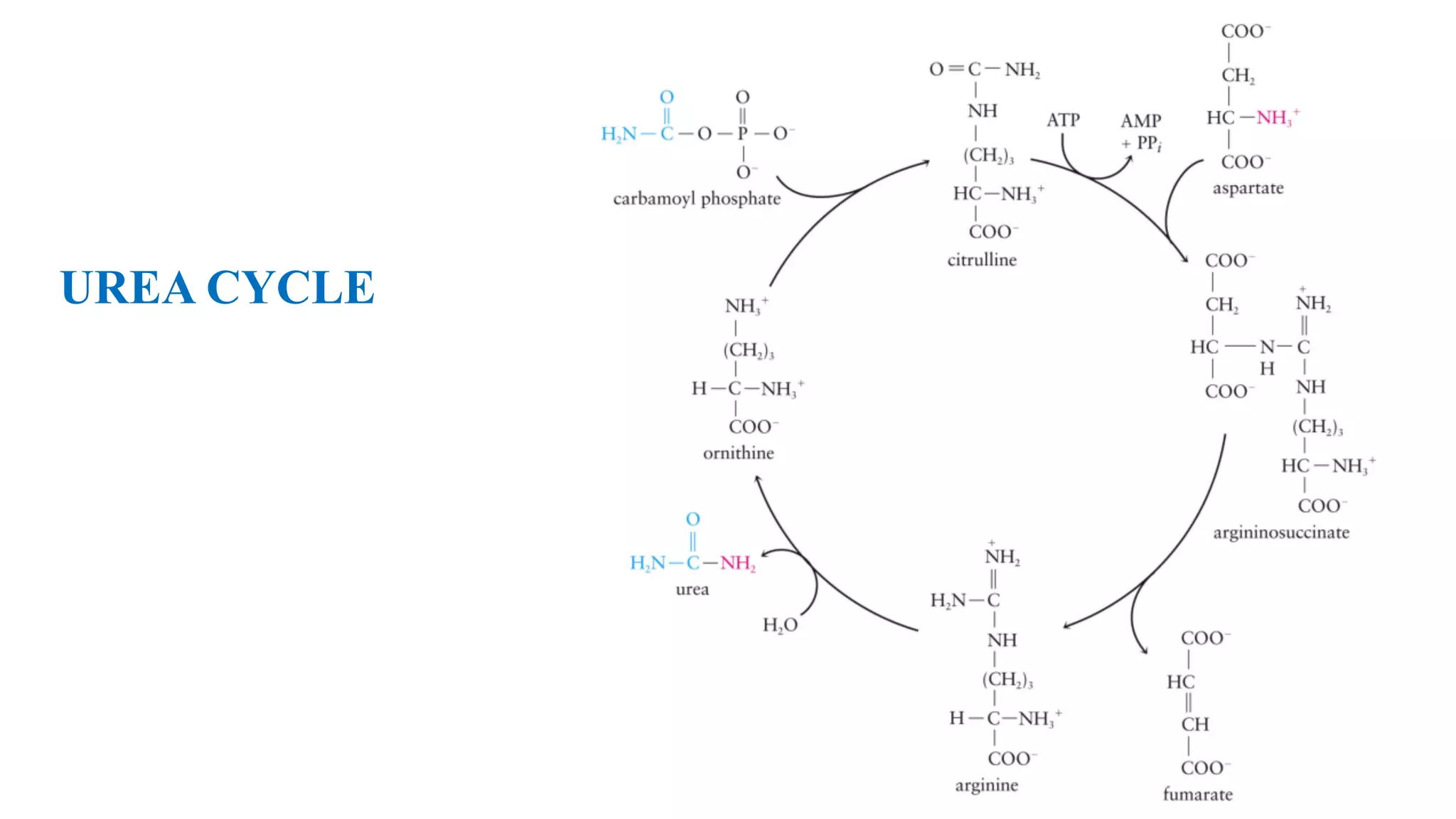
Amino acids can be used for energy production or as building blocks for proteins. Excess amino acids are broken down and their nitrogen is converted to urea via transamination, deamination, and the urea cycle to be excreted. Their carbon skeletons can be used for energy, gluconeogenesis, or triglyceride synthesis. Ten non-essential amino acids can be synthesized from intermediates in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle through various pathways.