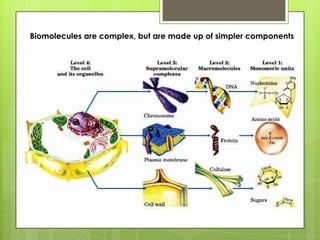
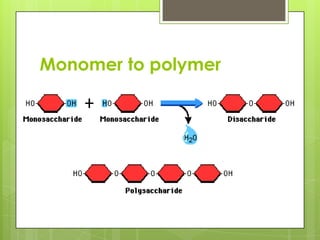
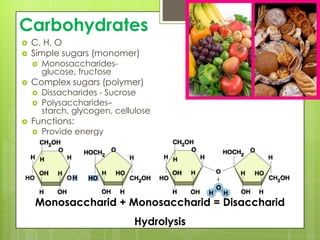
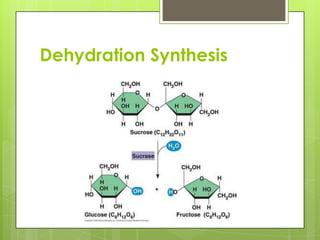
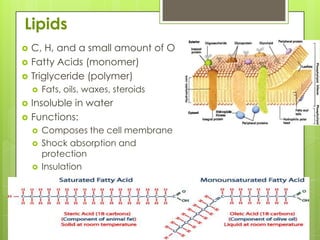
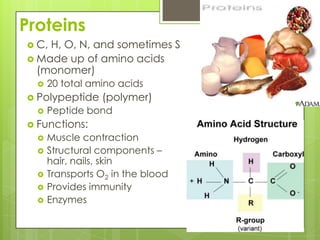
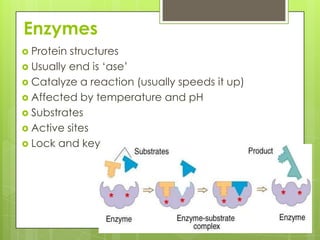
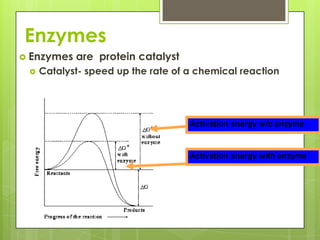
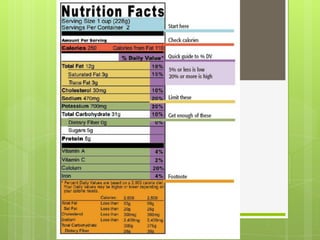
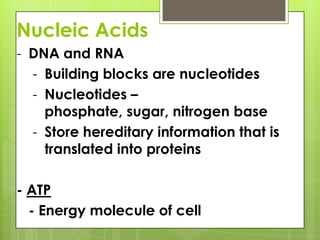
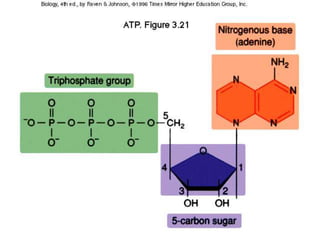
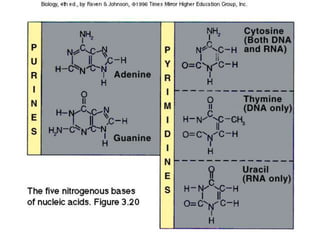
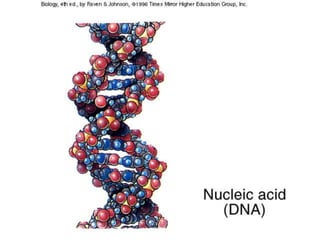
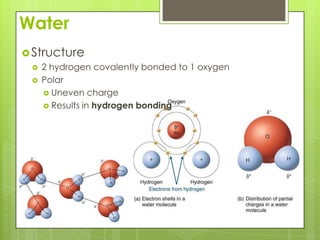
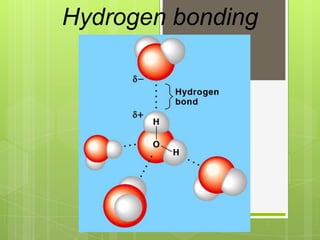
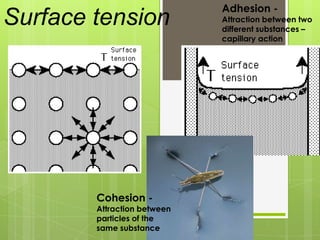
The document discusses the basic biomolecules that make up living things - carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids and water - including their monomers, polymers, functions, and dietary sources. It also covers enzymes, calories, metabolism, pH, and the states of water. The roles of these molecules and concepts are fundamental to biochemistry and human nutrition.