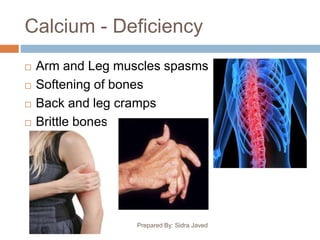
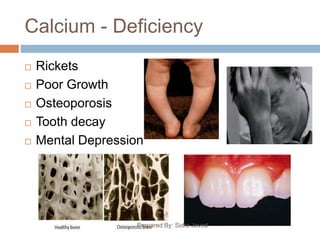
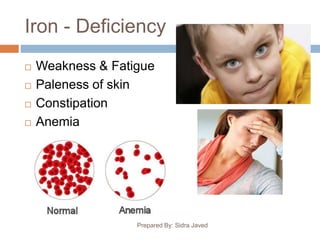
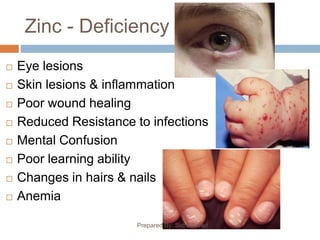
This document discusses several important minerals for human health including calcium, iron, phosphorus, and zinc. It provides information on their sources, roles in the body, deficiency symptoms, and significance. Specifically, it notes that calcium is essential for bone growth and health and is found in dairy products. Iron deficiency can cause anemia and fatigue and is obtained from meat, eggs, and leafy greens. Phosphorus is vital for bone structure and cell processes and is present in dairy, while zinc supports immune function and healing and is found in seafood, nuts and dairy. The document emphasizes the wide-ranging effects of mineral deficiencies on physical and mental well-being.