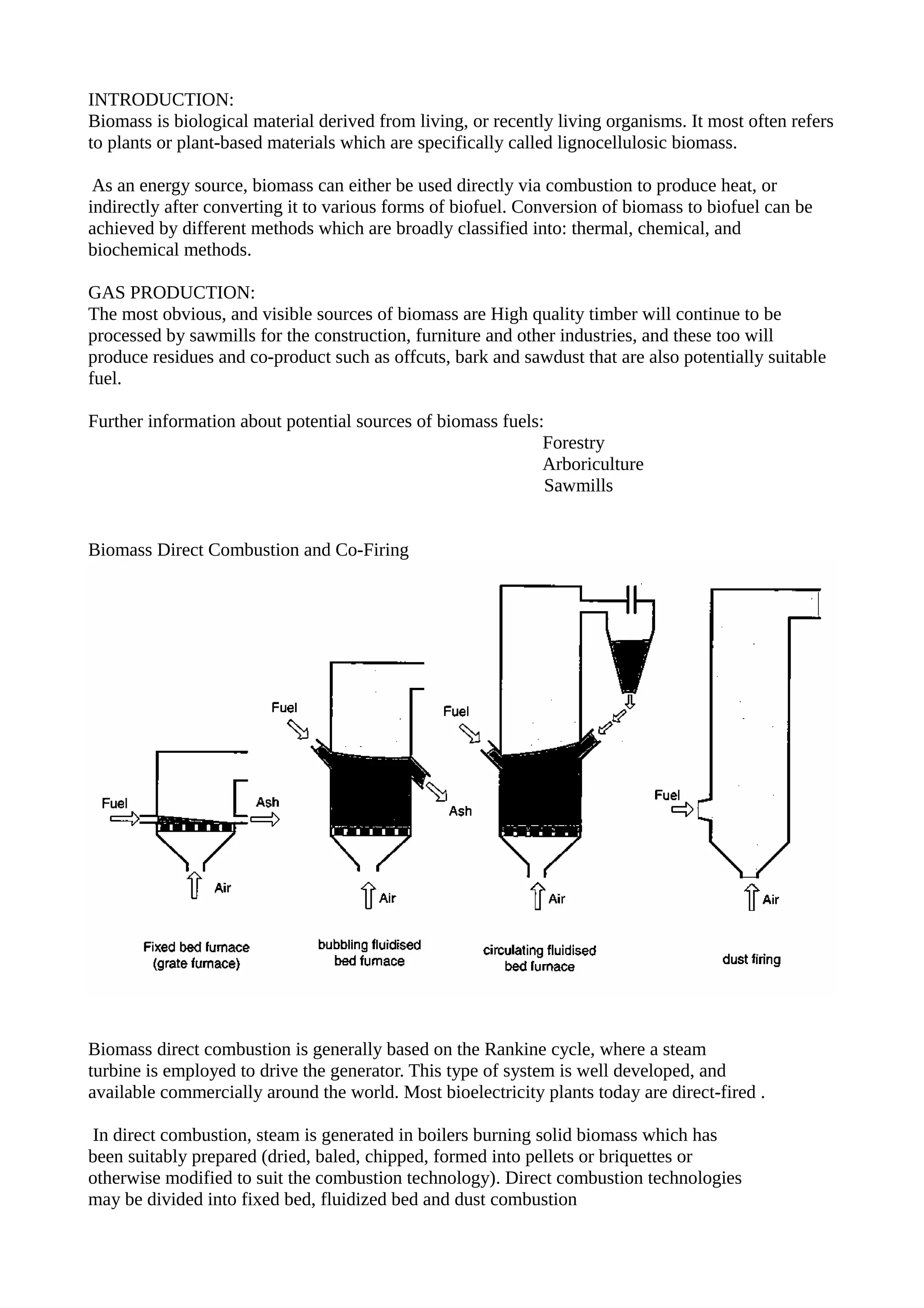
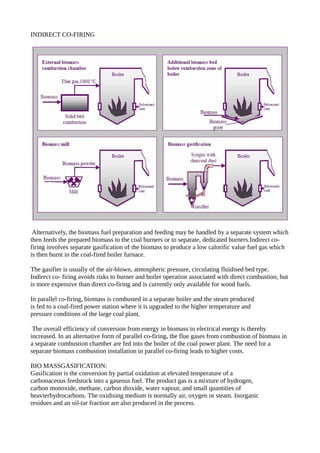
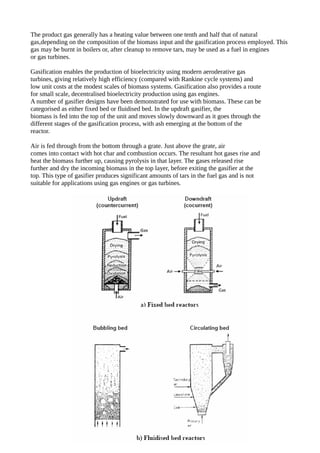
Biomass, primarily from plants, serves as a renewable energy source that can be utilized directly for heat or converted into biofuels through methods like thermal, chemical, and biochemical processes. Various technologies for biomass conversion include direct combustion, co-firing with fossil fuels, and gasification, each with unique advantages and operational considerations. In the U.S., biopower plants harness around 60 million tons of biomass annually to generate significant electricity, supporting both grid-connected and modular systems for local power generation.