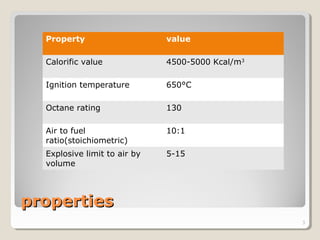
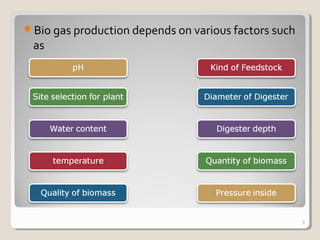
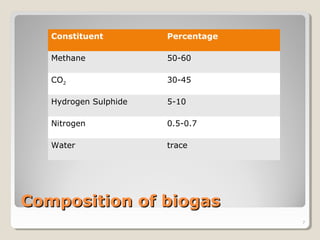
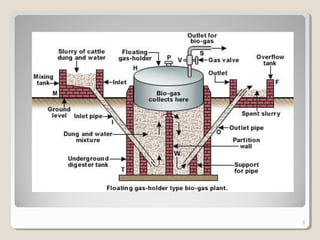
Biogas is a mixture of methane and other gases produced from the decomposition of organic materials in an oxygen-free environment. It is a renewable energy source that is produced through the fermentation of biomass such as leaves, animal waste, and other agricultural waste in an enclosed biogas plant. Biogas is around 50-60% methane, 30-45% carbon dioxide, and 5-10% hydrogen sulfide. It has a calorific value of 4500-5000 Kcal/m3 and an ignition temperature of 650°C. Approximately 67 m3 of biogas can be produced from 1 ton of biomass feedstock. Biogas has various applications such as cooking, power generation, and fuel for automobiles