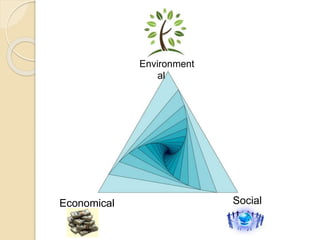
Green building refers to structures and processes that are environmentally responsible and efficient in their use of resources throughout the building's lifecycle. The goals of green building are to reduce, reuse, recycle, and refuse resources. Some key principles are optimizing the structure's efficiency, as well as energy, water, materials, and waste reduction. The benefits of green building include environmental protections, cost savings, and improved social outcomes like health and quality of life. Challenges include growing waste and costs, while impacts on natural resources include development of land and energy usage.