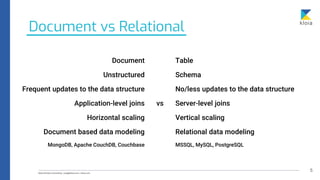
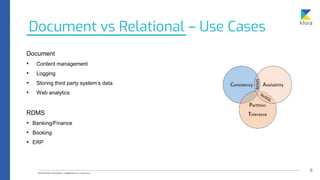
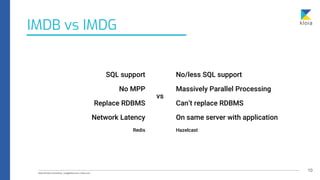
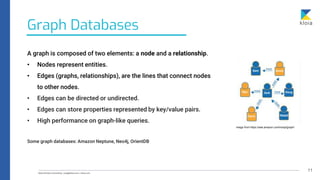
The document discusses the importance of database awareness in relation to system performance, scalability, and cost, emphasizing the need to understand both database and system functionality. It covers various types of databases, including document, relational, row-based, and column-based, detailing their use cases and characteristics. Additionally, it explores specific database technologies and compares features like event stores, time-series databases, Solr vs Elasticsearch, and in-memory databases.