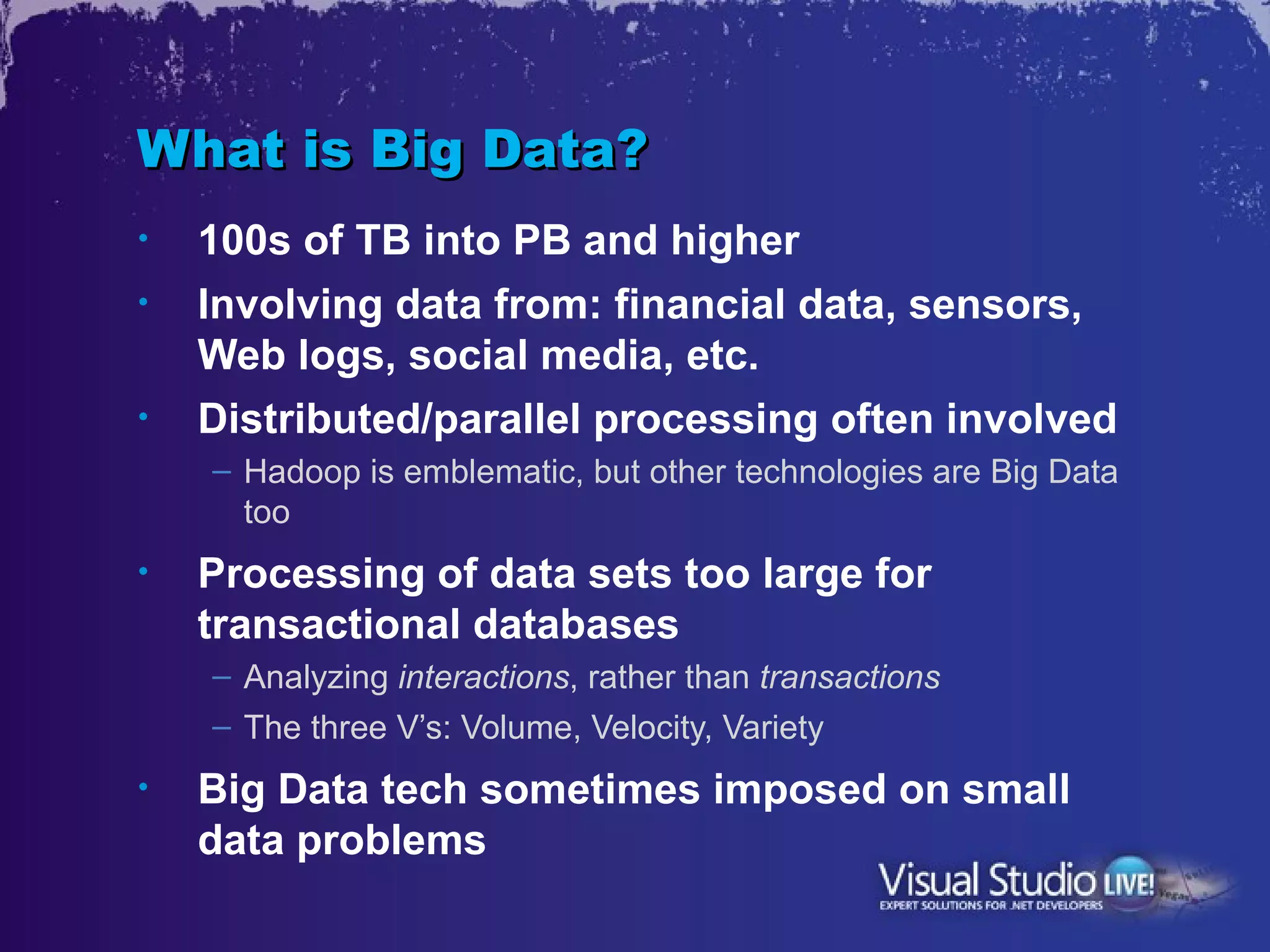
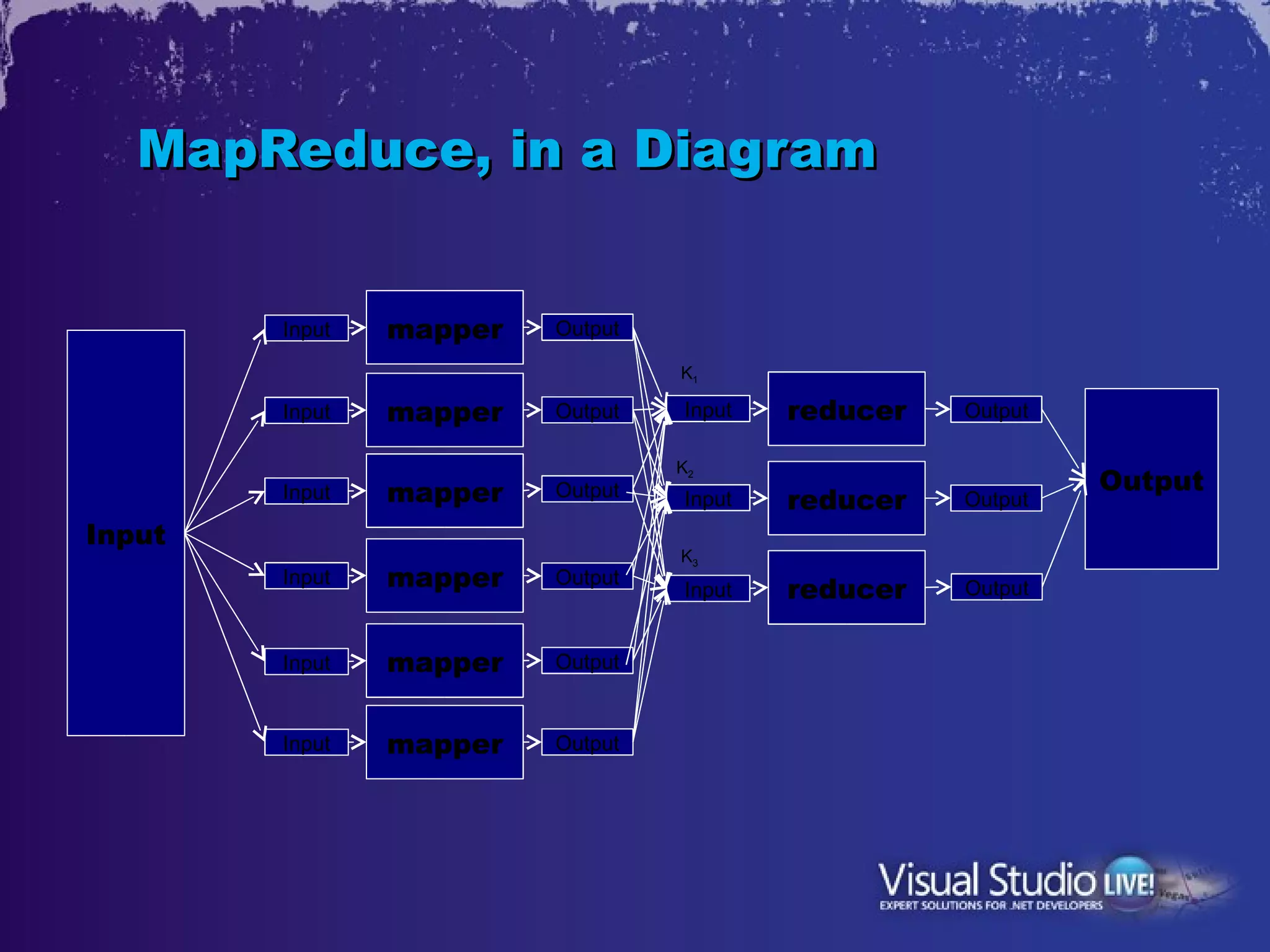
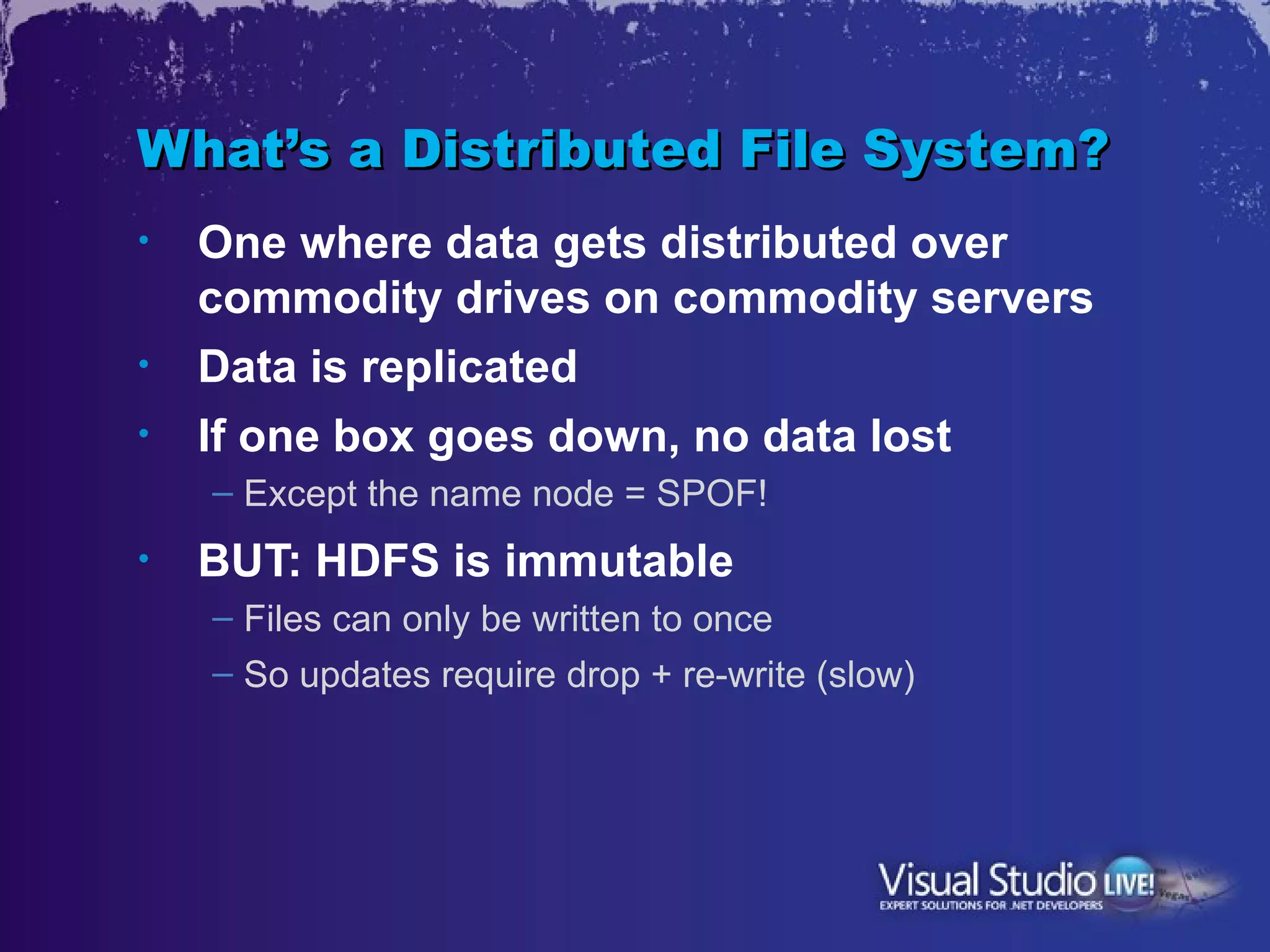
This document discusses Microsoft's efforts to make big data technologies like Hadoop more accessible through its products. It describes Hadoop, MapReduce, HDFS, and other big data concepts. It then outlines Microsoft's project to create a Hadoop distribution that runs on Windows Server and Windows Azure, including building an ODBC driver to allow tools like Excel to query Hadoop. This will help bring big data to more business users and integrate it with Microsoft's existing BI technologies.