The document discusses the integration of Big Data and SQL Server, covering foundational concepts such as the 3 V's (Volume, Velocity, Variety) and the role of Apache Hadoop in managing Big Data. It emphasizes the distinction between Big Data and traditional data warehousing, highlighting that Big Data primarily involves batch processing for large files while in-memory analytics can be used for real-time insights. It also presents various tools and methodologies for handling data, including MapReduce, Sqoop, and the use of NoSQL databases in a Big Data analytics context.





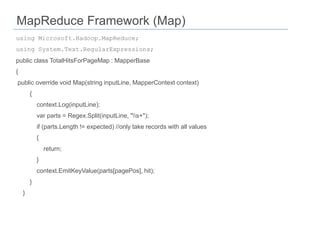

![using Microsoft.Hadoop.MapReduce;
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
public class TotalHitsForPageMap : MapperBase
{
public override void Map(string inputLine, MapperContext context)
{
context.Log(inputLine);
var parts = Regex.Split(inputLine, "s+");
if (parts.Length != expected) //only take records with all values
{
return;
}
context.EmitKeyValue(parts[pagePos], hit);
}
}
MapReduce Framework (Map)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phillycodecampmay2013-markkromer-bigdatasqlserver-130509002302-phpapp02/85/Philly-Code-Camp-2013-Mark-Kromer-Big-Data-with-SQL-Server-8-320.jpg)