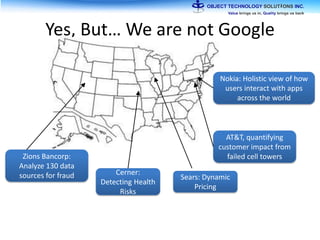
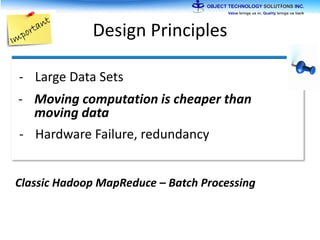
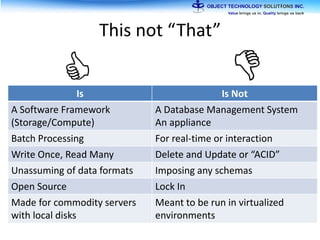
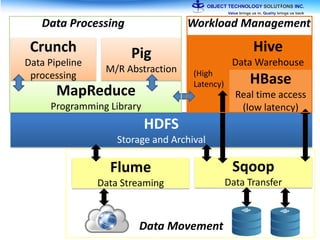
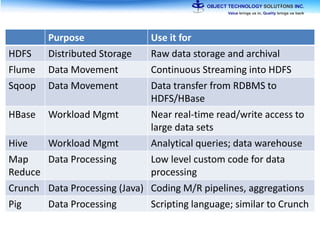
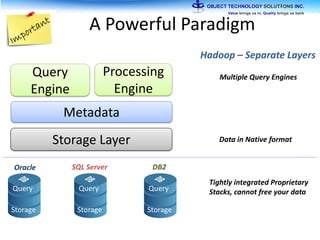
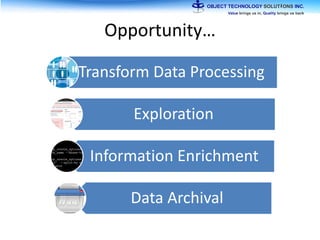
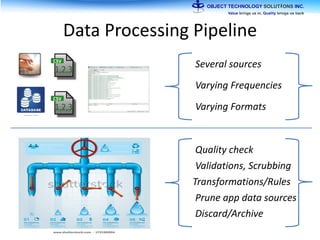
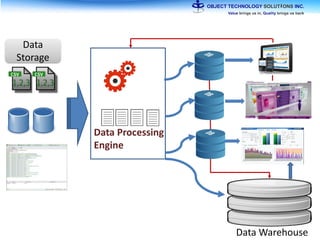
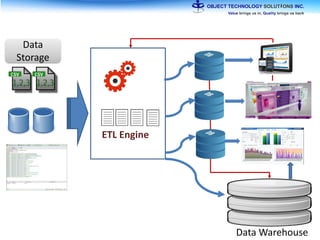
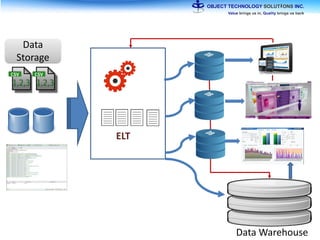
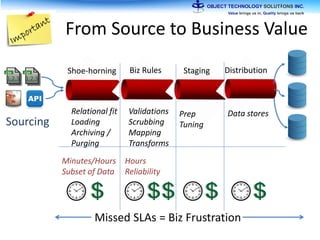
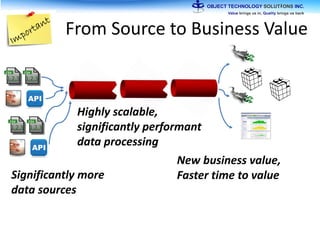
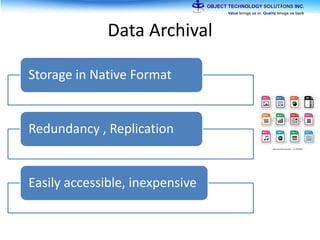
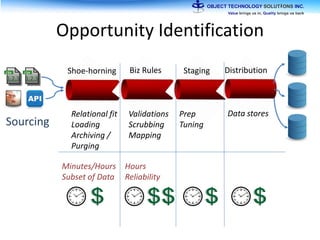
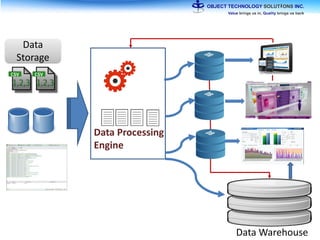
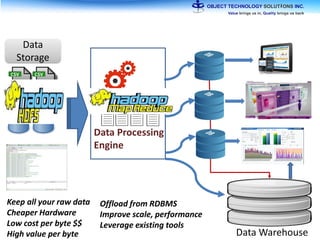
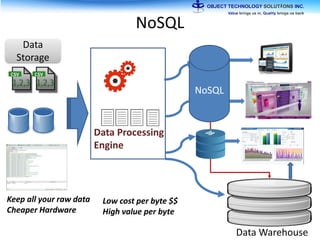
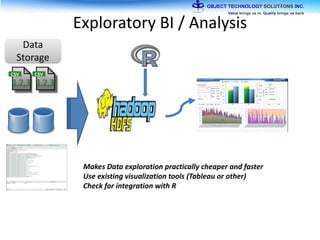
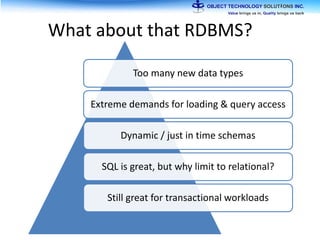
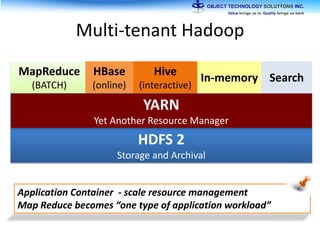
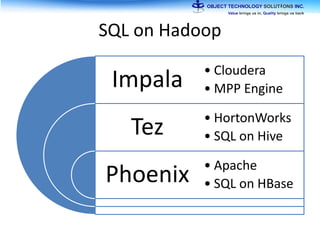
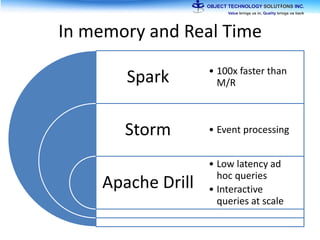
The document discusses the evolution and practical adoption of big data technologies, emphasizing their capabilities in processing and handling large scale datasets. It highlights real-world applications from various industries, and the importance of understanding data architecture for successful implementation. The text also touches on the future of big data with advancements such as SQL on Hadoop and the use of distributed computing frameworks.