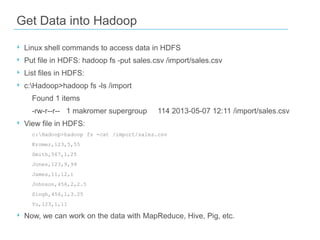
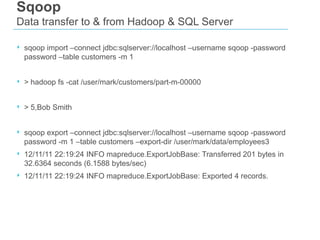
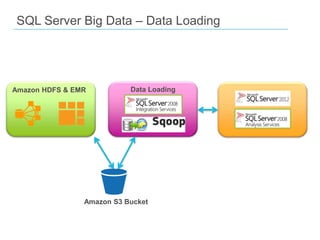
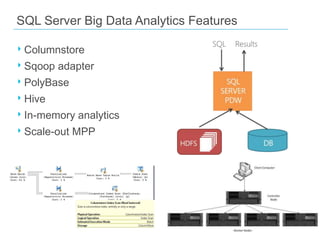
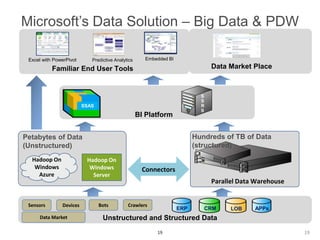
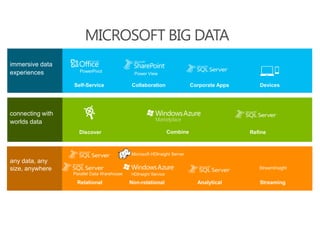
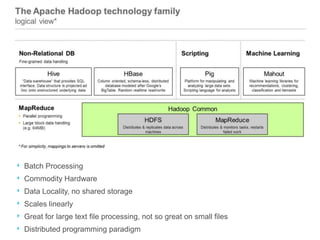
The document discusses the concept of big data, emphasizing its characteristics such as volume, velocity, and variety, as well as the big data ecosystem including Apache Hadoop and NoSQL databases. It details the integration of SQL Server with big data analytics, covering techniques for data processing, loading, and the use of various tools like Hive and Sqoop. Additionally, it explains the importance of adopting a big data approach for analytics to handle large volumes of unstructured data and the necessity of analytical tools for meaningful insights.







![MapReduce Framework (Map)
using Microsoft.Hadoop.MapReduce;
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
public class TotalHitsForPageMap : MapperBase
{
public override void Map(string inputLine, MapperContext context)
{
context.Log(inputLine);
var parts = Regex.Split(inputLine, "s+");
if (parts.Length != expected) //only take records with all values
{
return;
}
context.EmitKeyValue(parts[pagePos], hit);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdatarealworld-131023143617-phpapp02/85/Big-Data-in-the-Real-World-10-320.jpg)