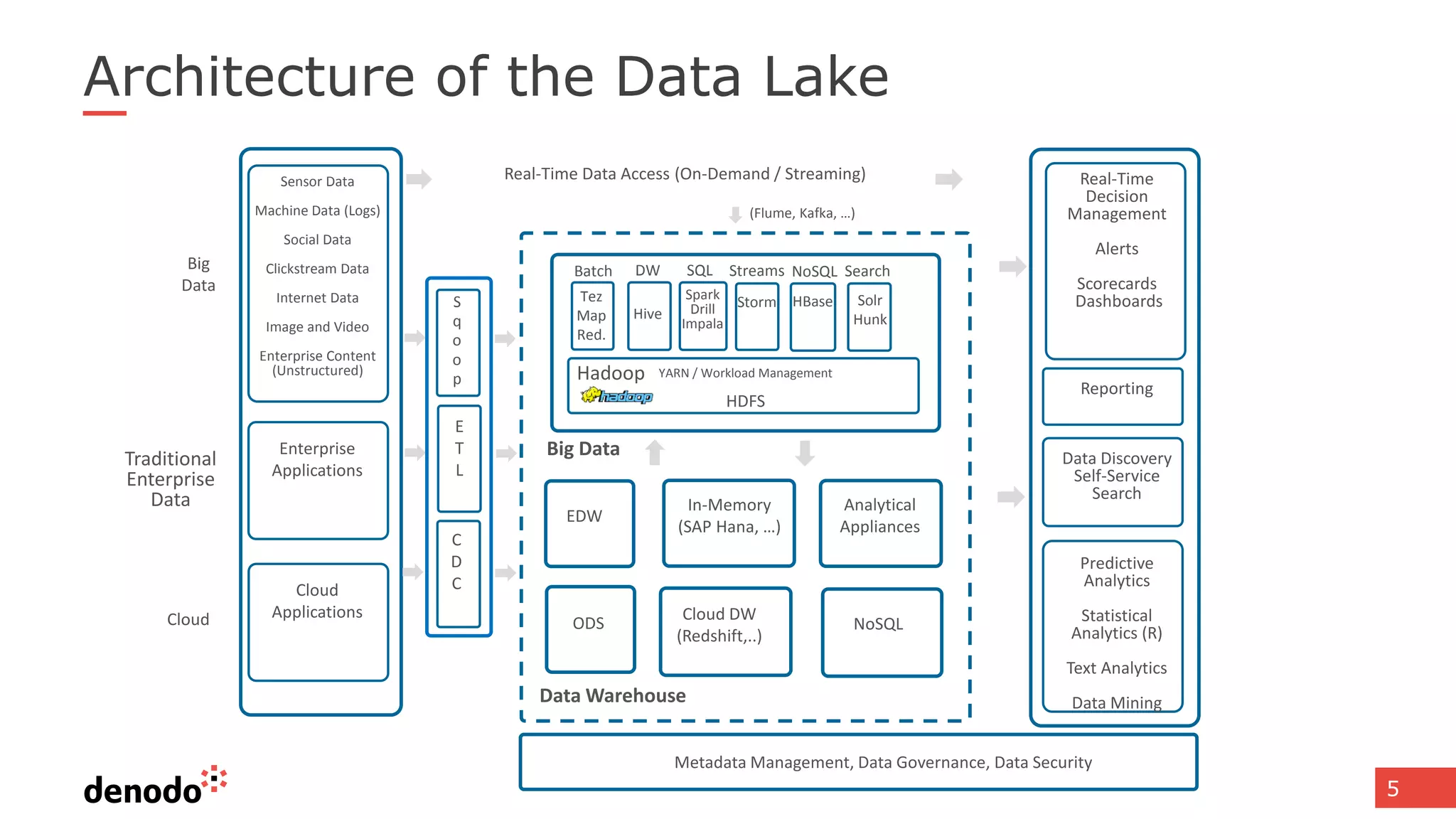
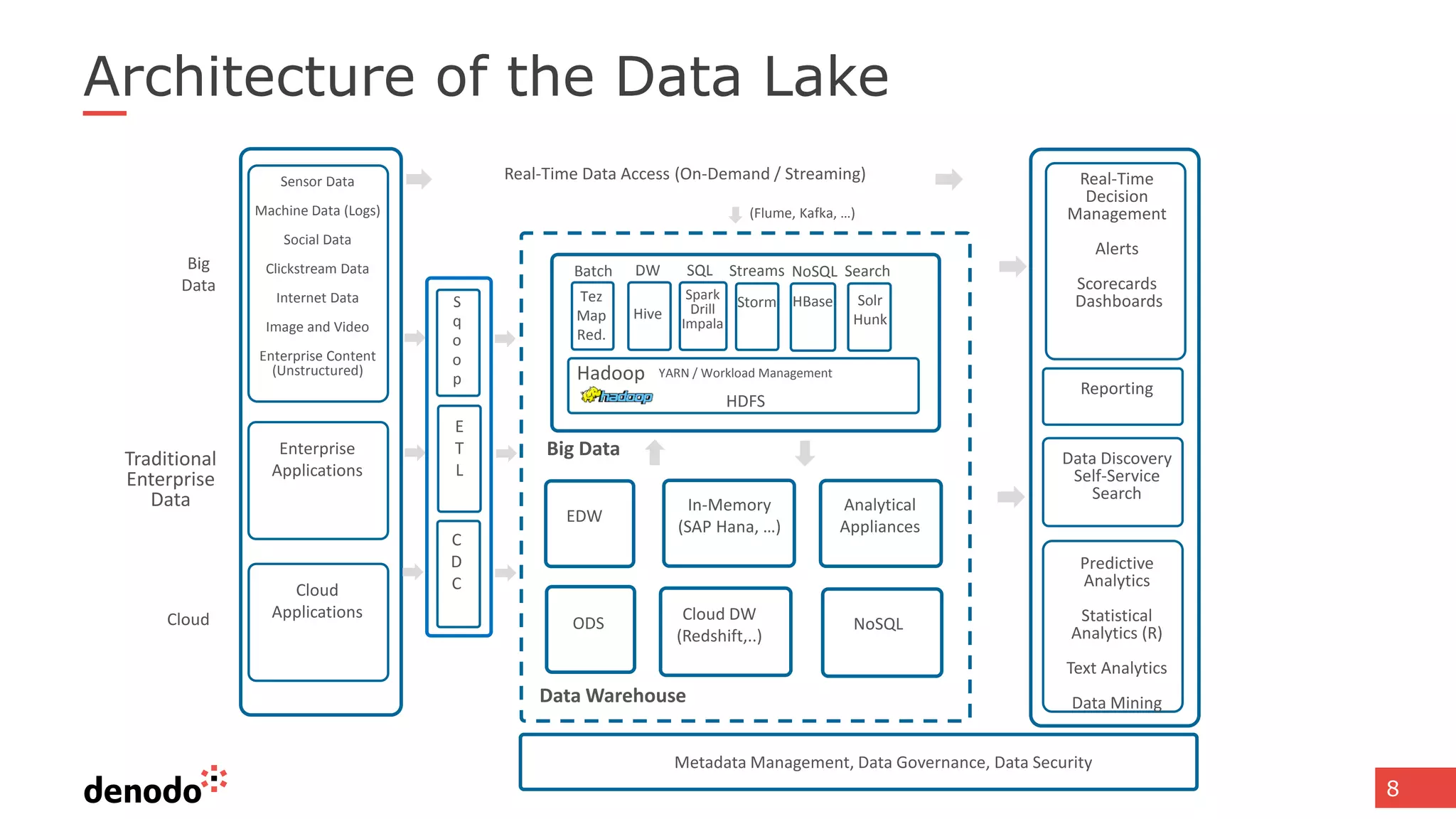
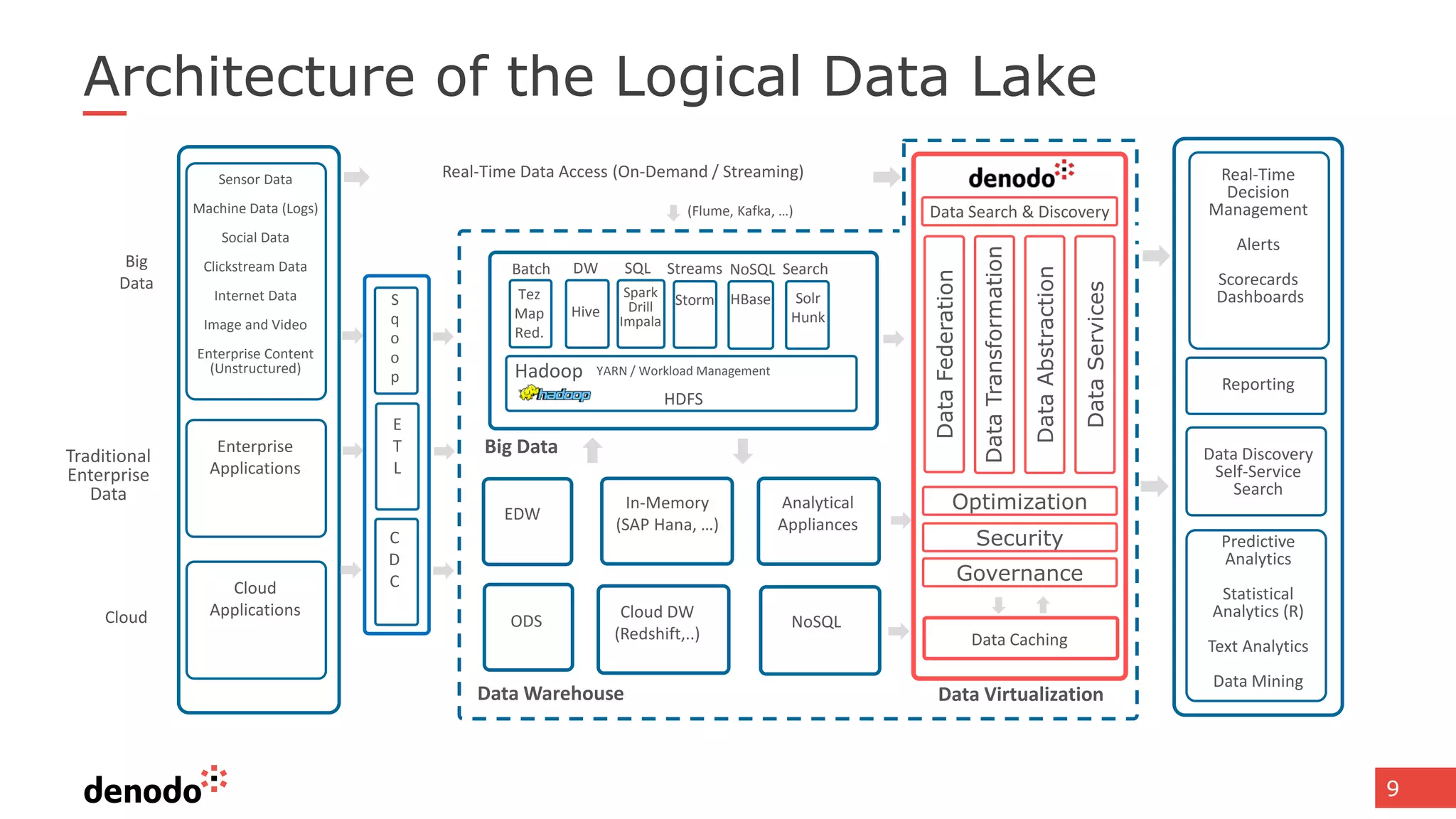
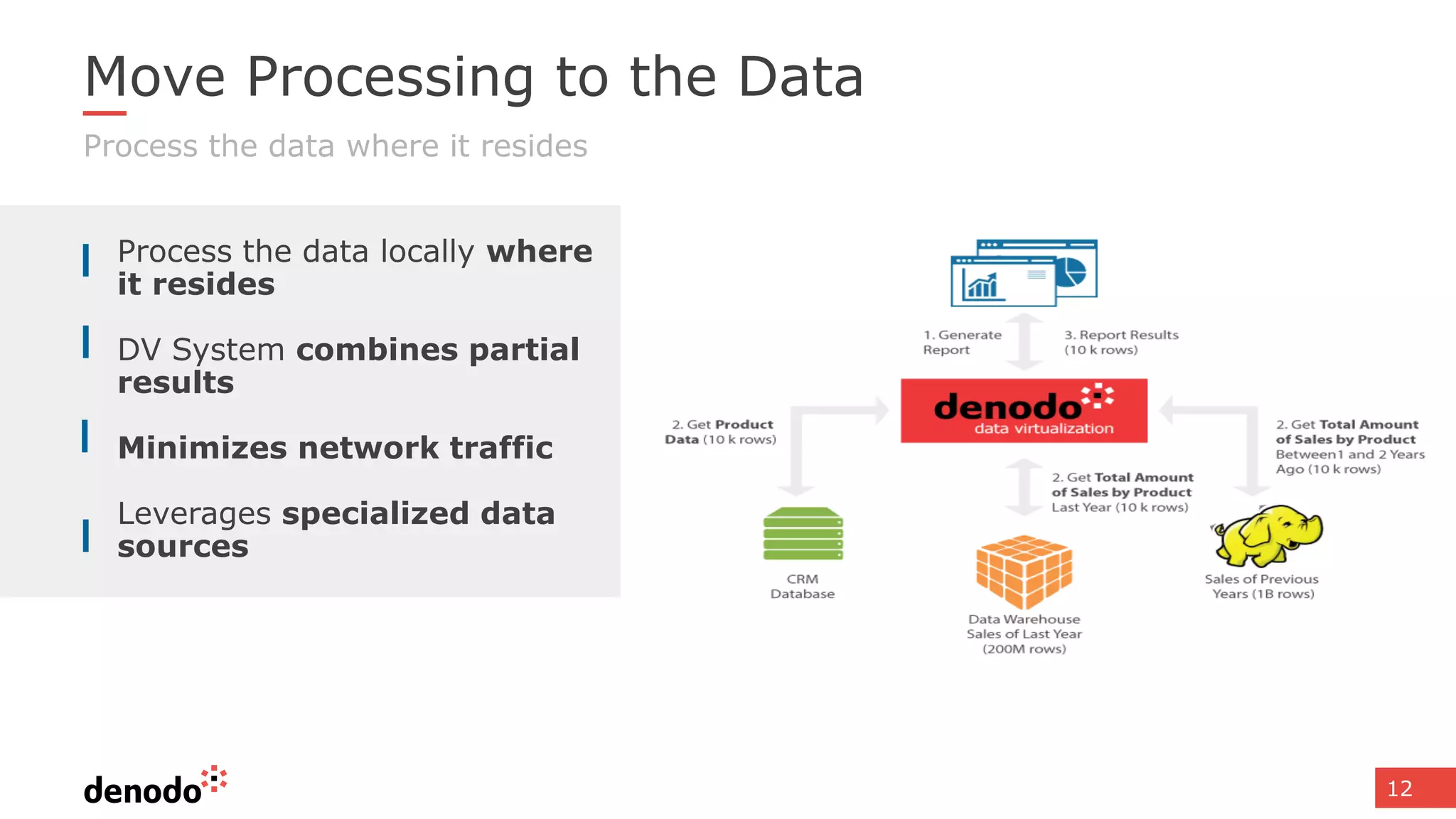
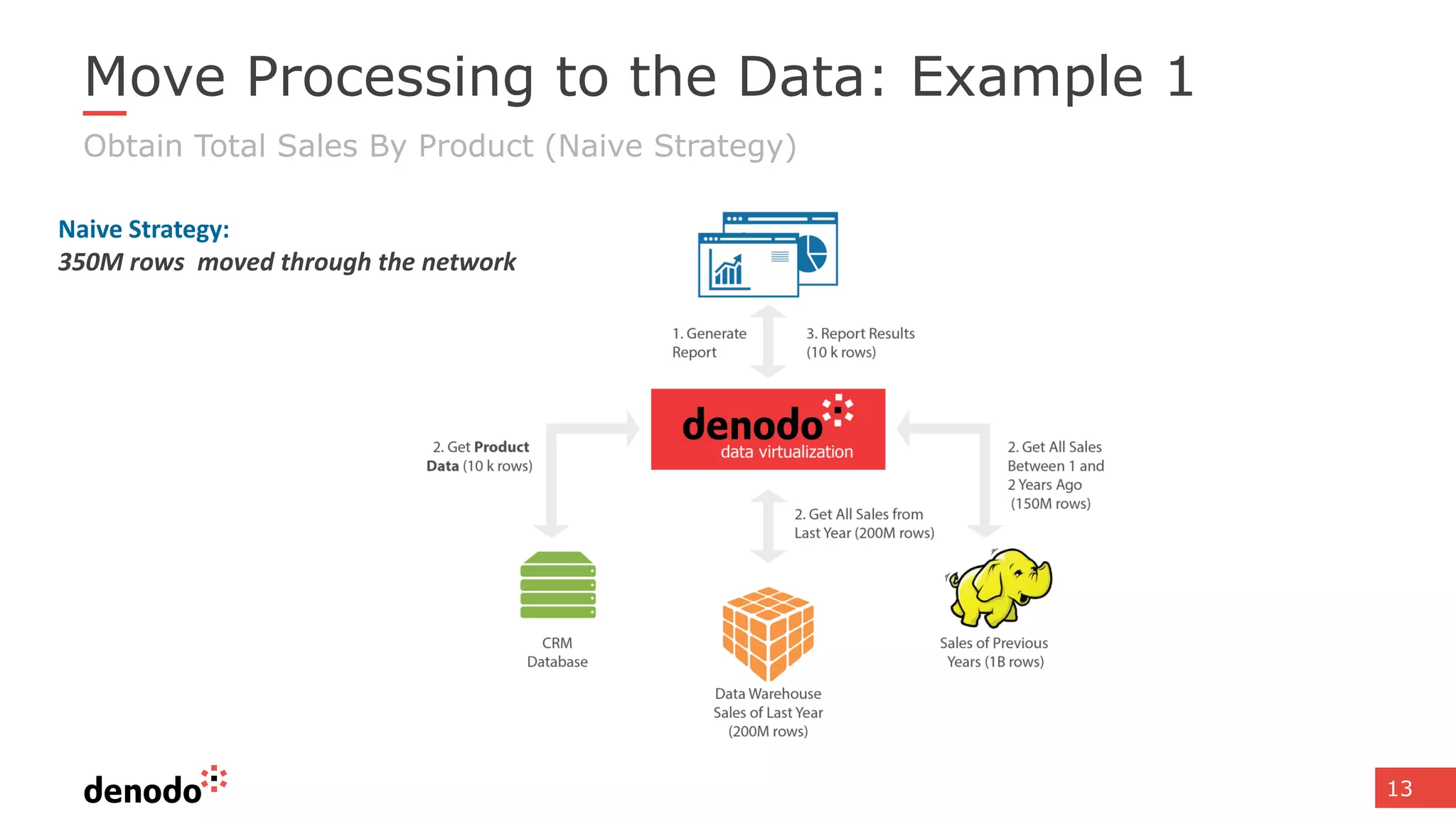
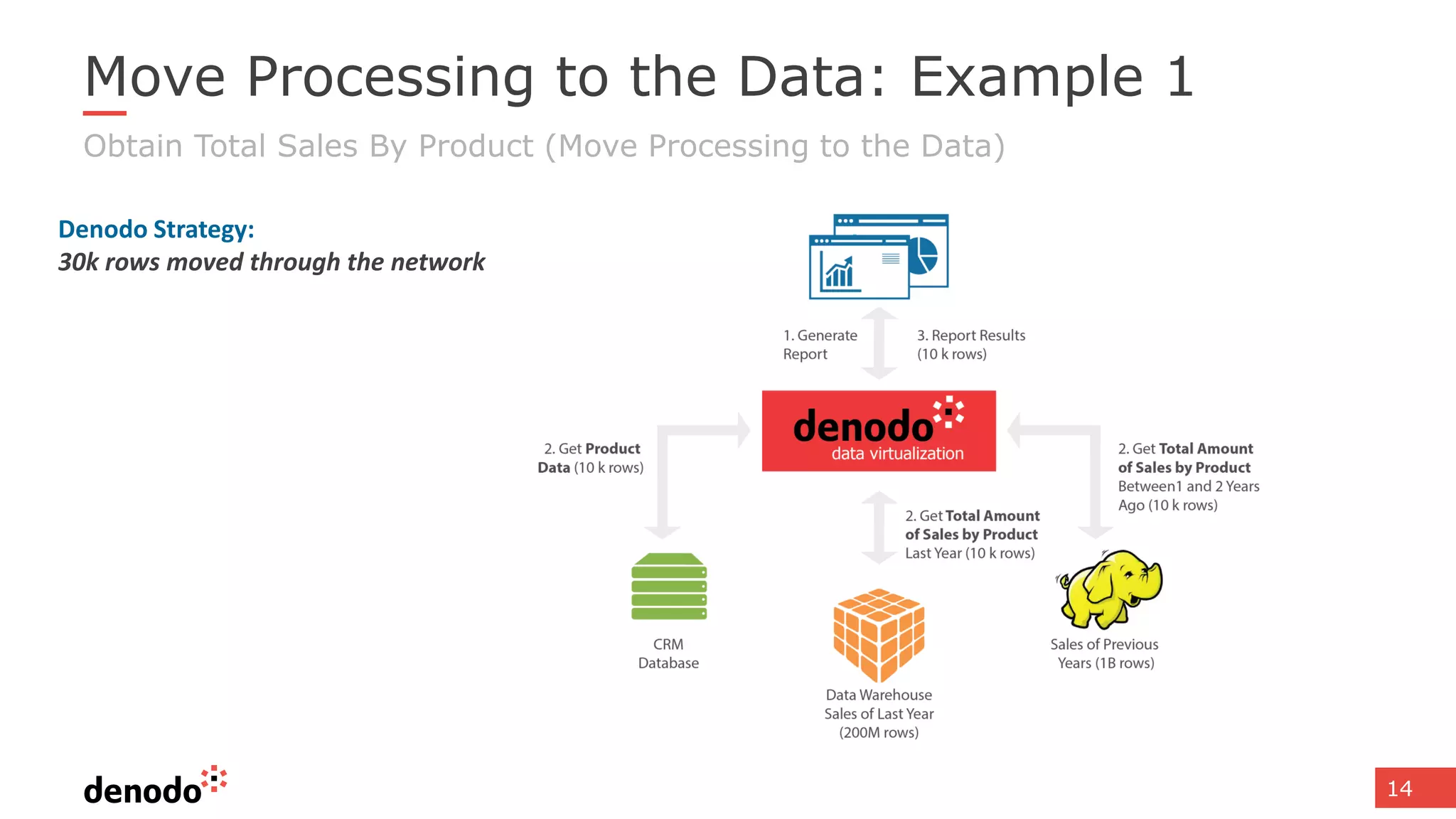
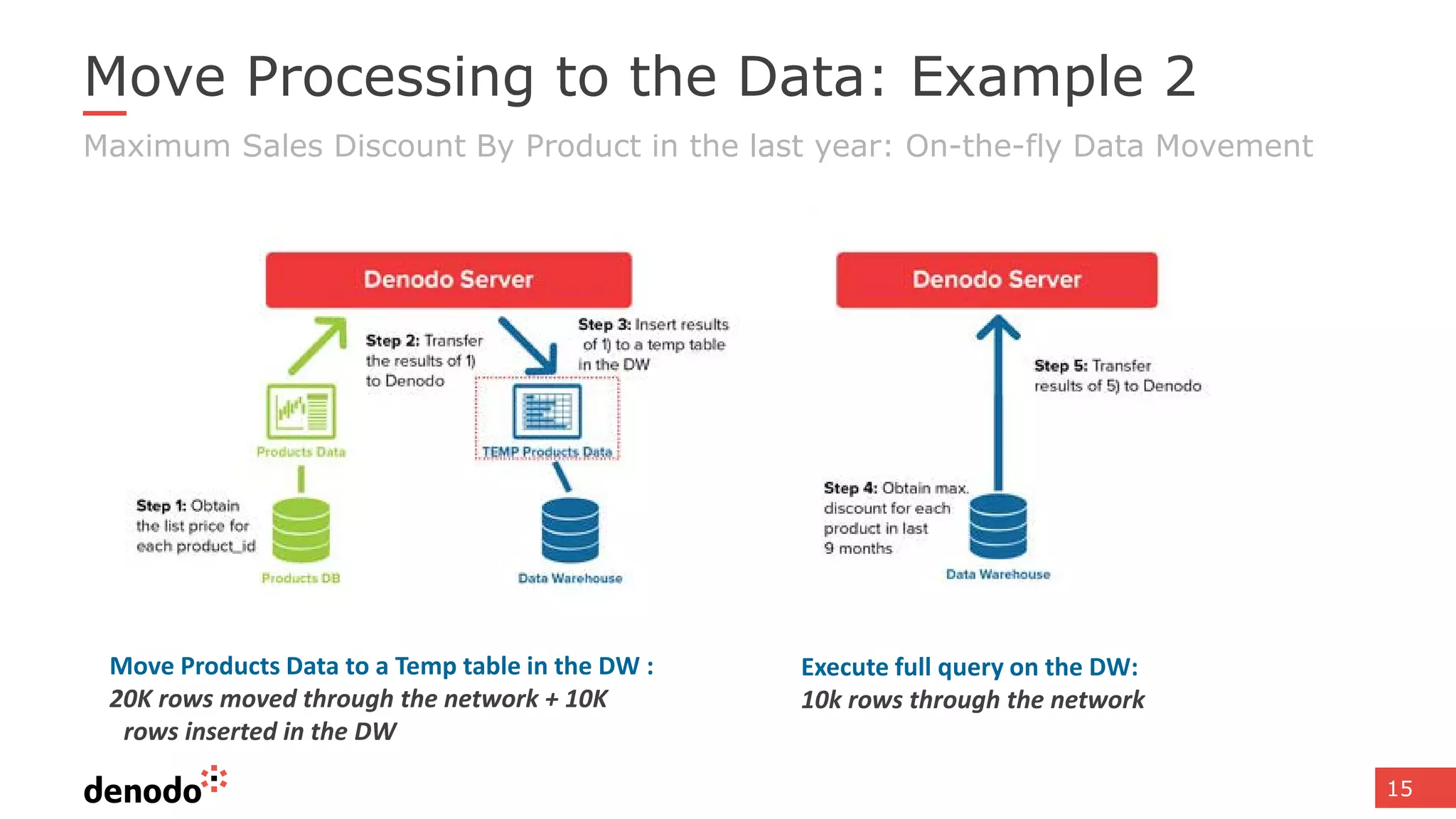
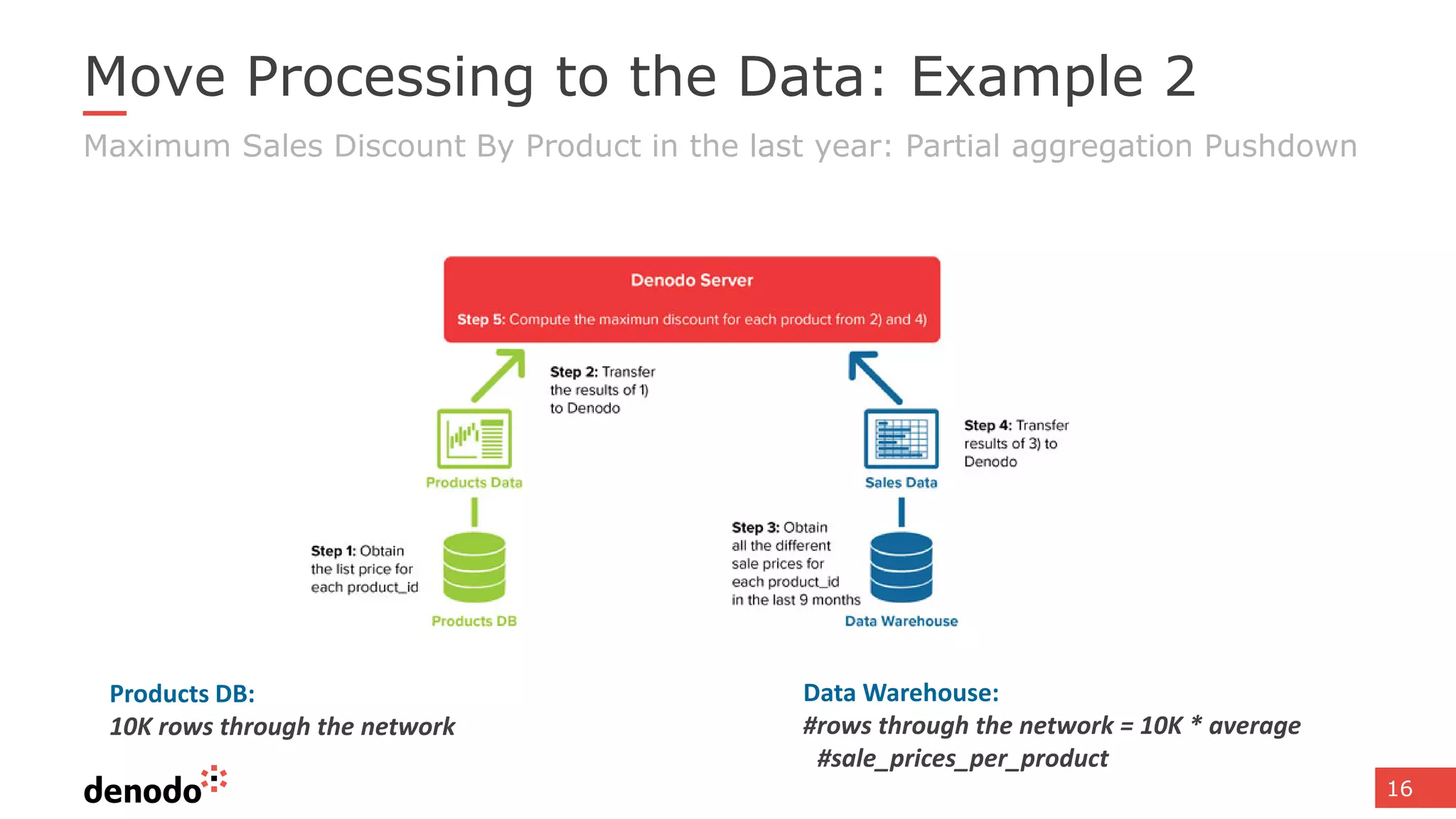
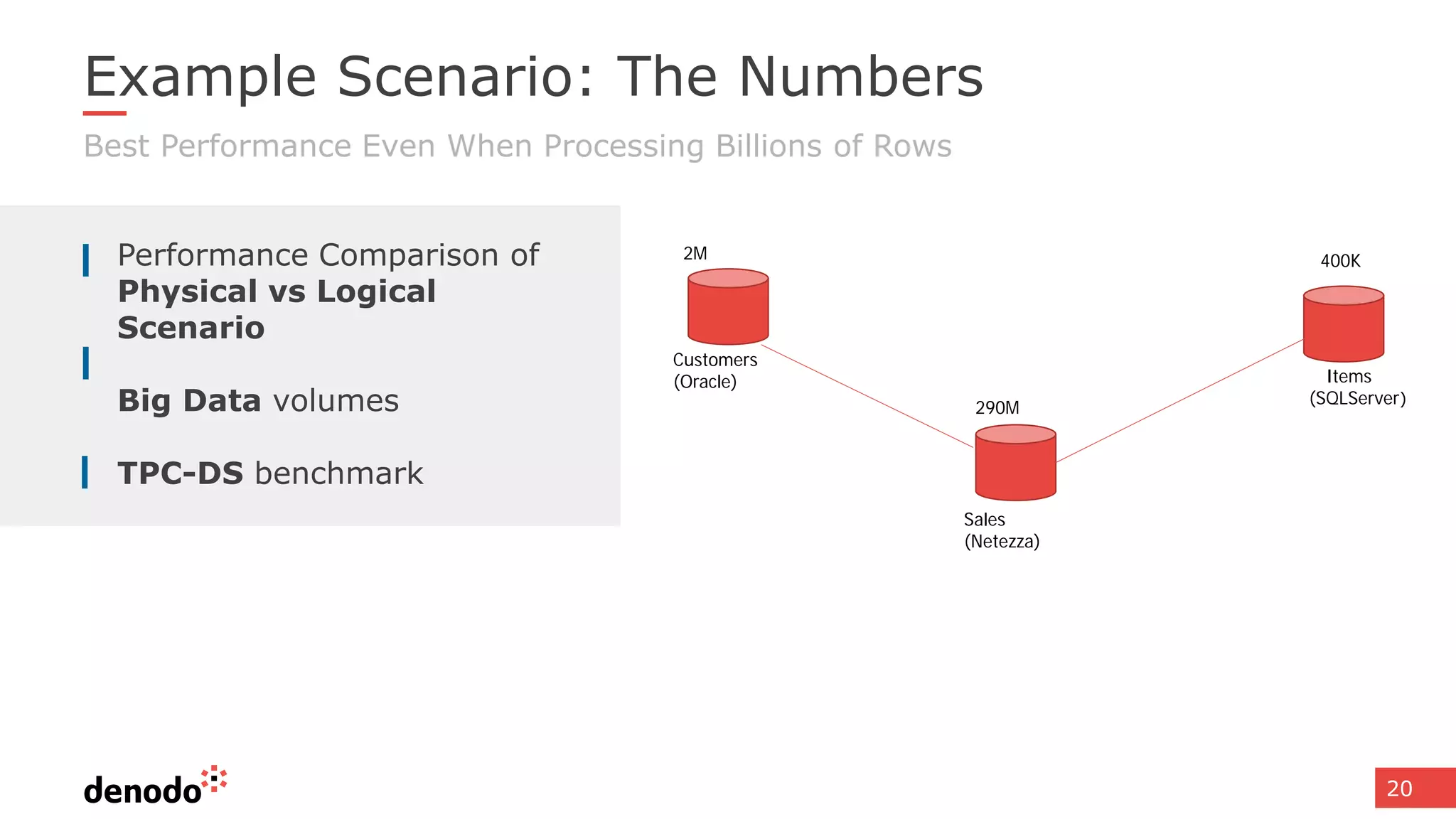
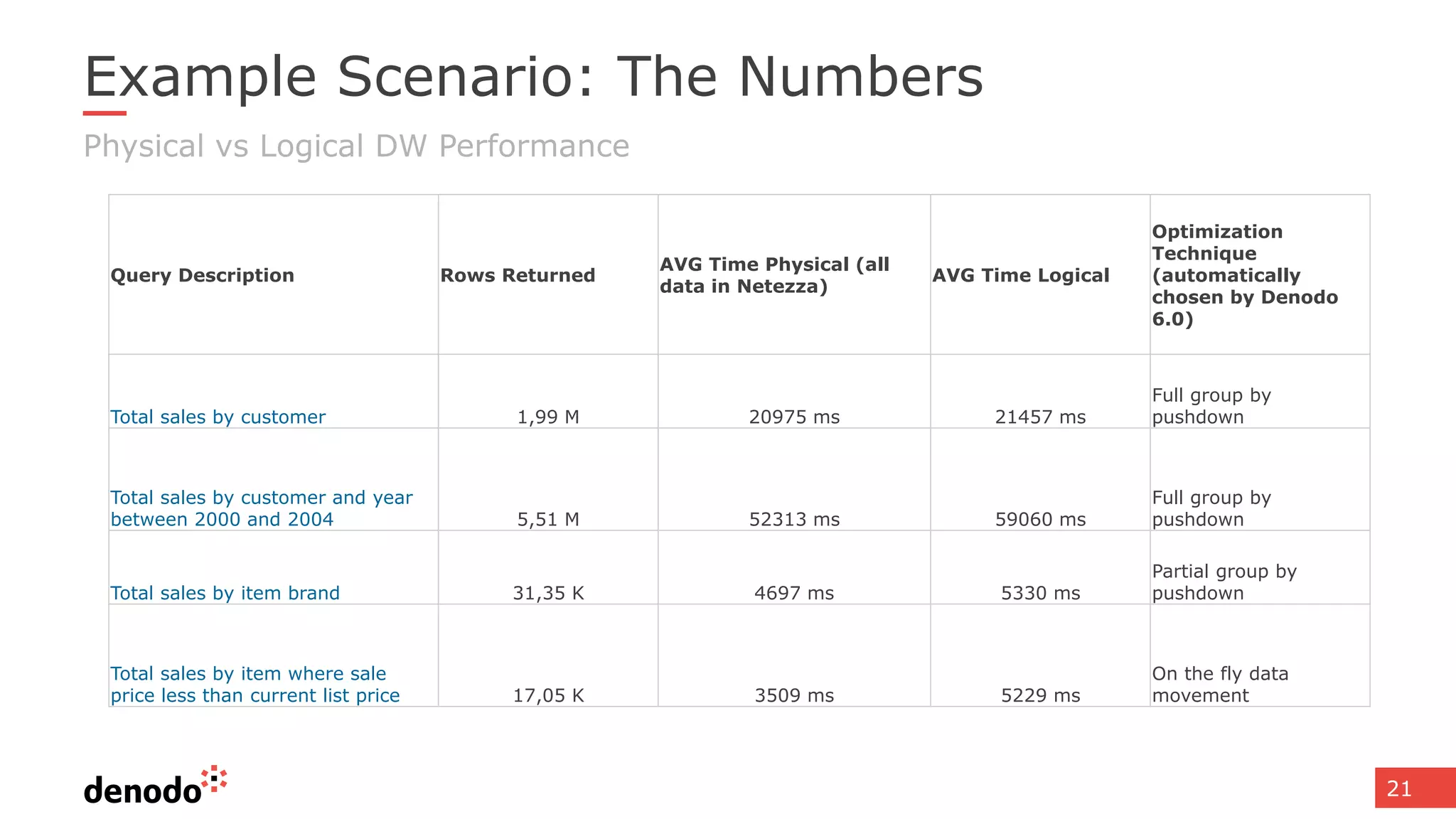
The document discusses architecture and performance considerations in a logical data lake, focusing on data virtualization and its impact on processing efficiency. It highlights the importance of moving processing close to data sources to reduce network traffic and enhance performance through optimized execution plans. Various components such as real-time decision management, data governance, and integration requirements are also addressed to create a cohesive data management strategy.