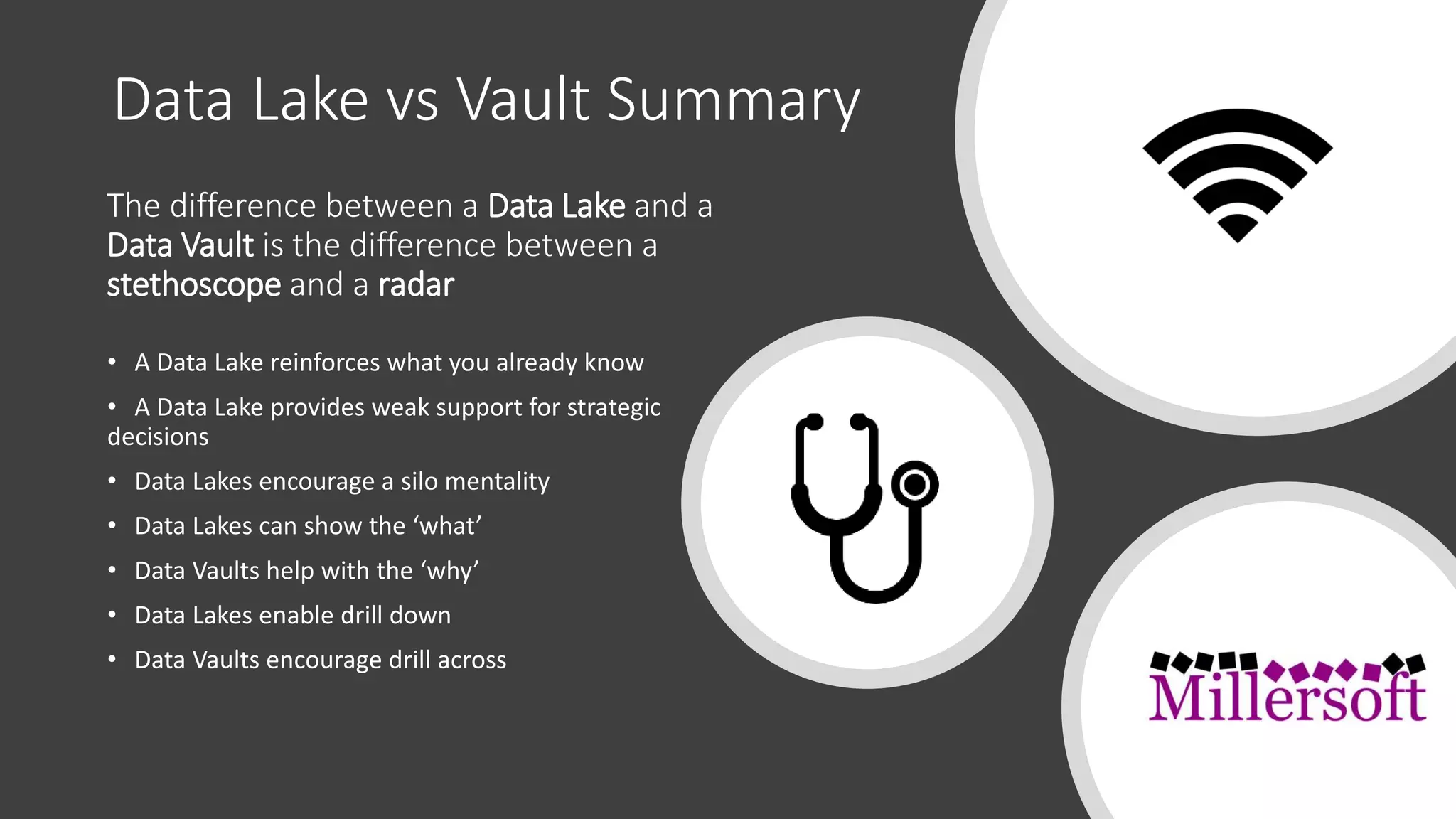
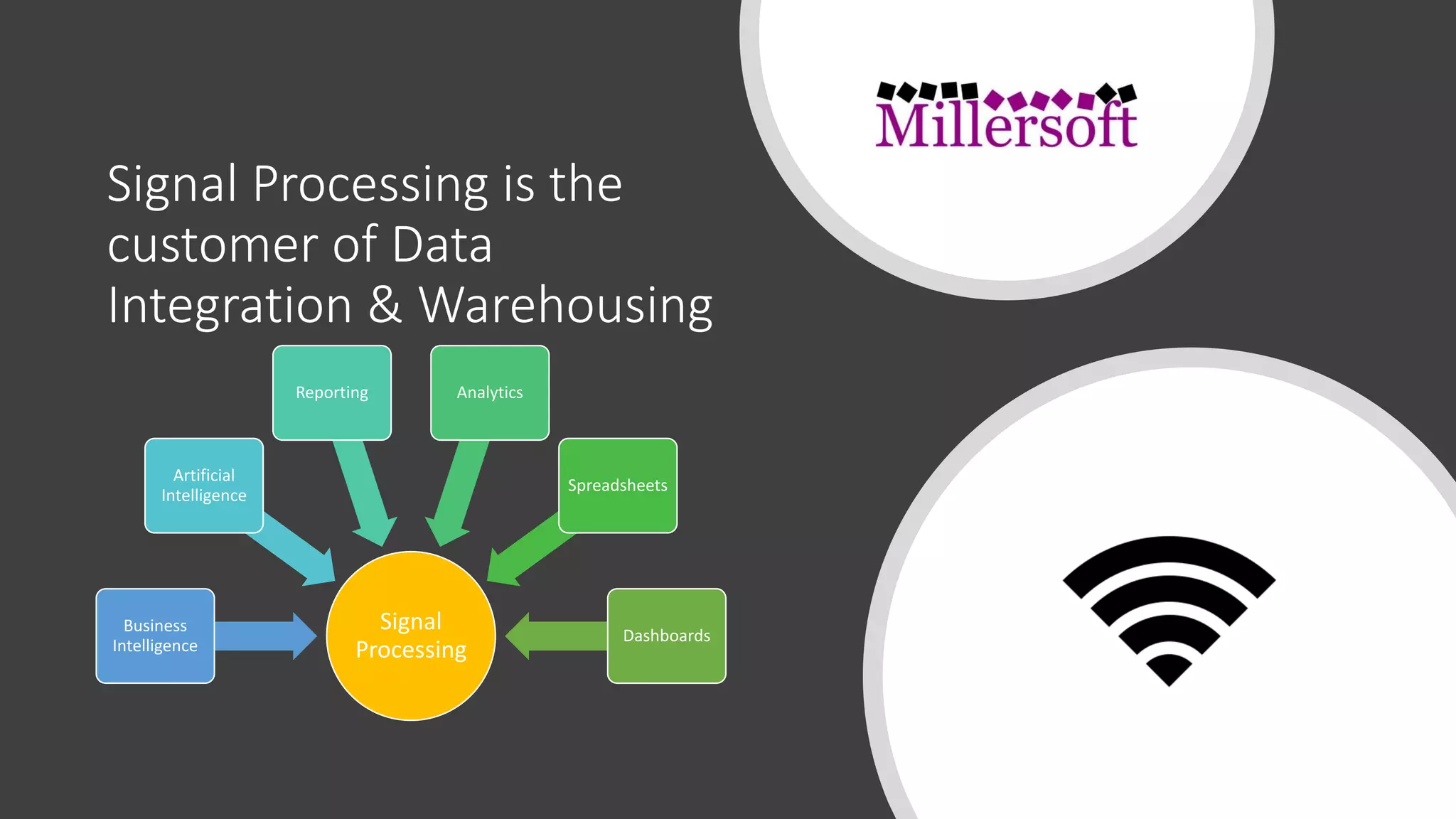
Data lakes and data vaults serve different purposes in data management; data lakes primarily show 'what' but can lead to silo mentalities and poor strategic support, while data vaults focus on 'why' and encourage comprehensive analysis. The document discusses the evolution of both systems, highlighting the growing importance of data integration and signal processing in cloud environments. Additionally, data lakes are suitable for tactical analysis, whereas data vaults are better for strategic insights.