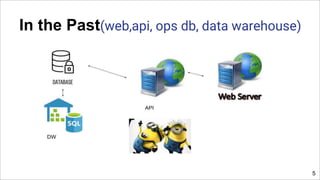
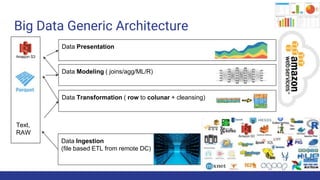
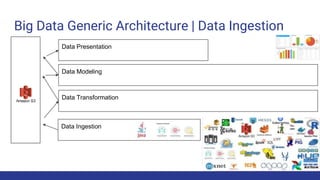
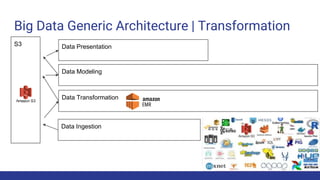
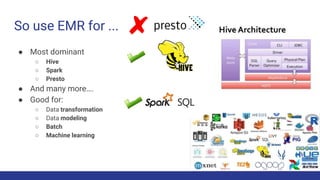
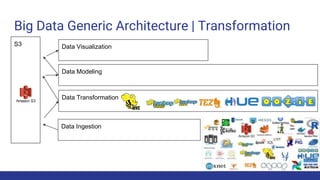
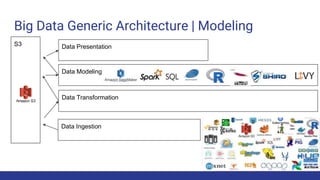
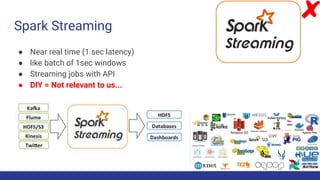
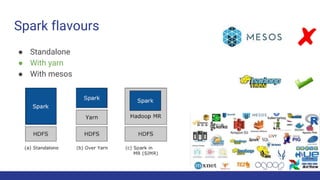
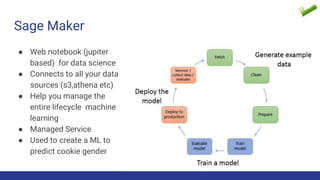
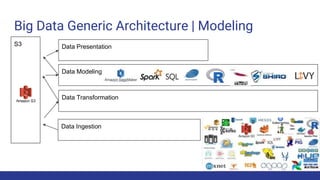
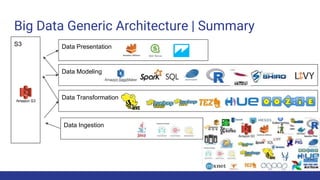
The document discusses the evolution of big data architecture, highlighting key concepts such as data ingestion, transformation, and modeling while addressing challenges related to velocity, volume, and veracity. It emphasizes the importance of defining business use cases and offers guidance on choosing between cloud and on-premises solutions, along with best practices for implementation. Additionally, it touches on various technologies and services available in AWS for managing big data effectively.