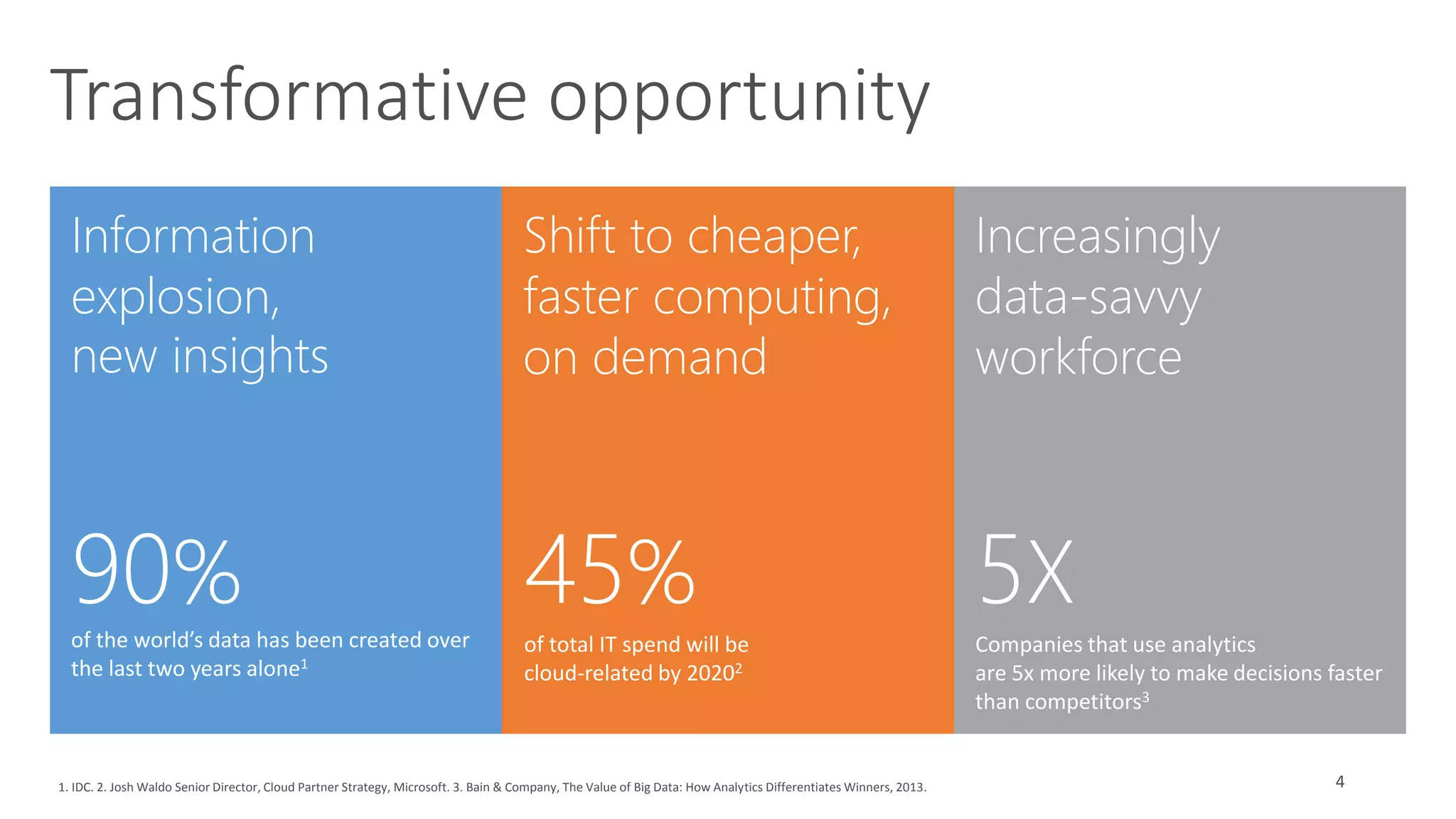
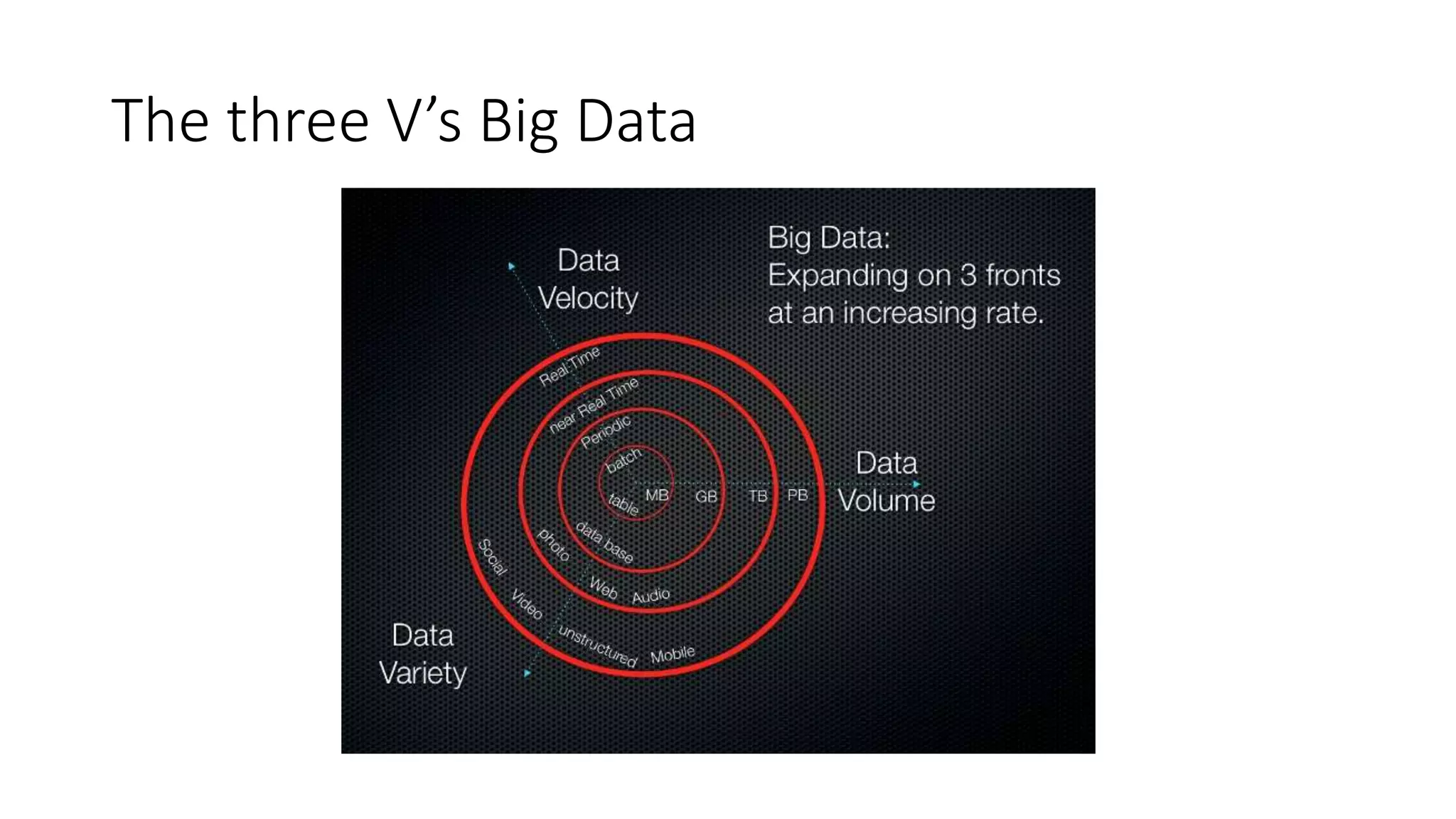
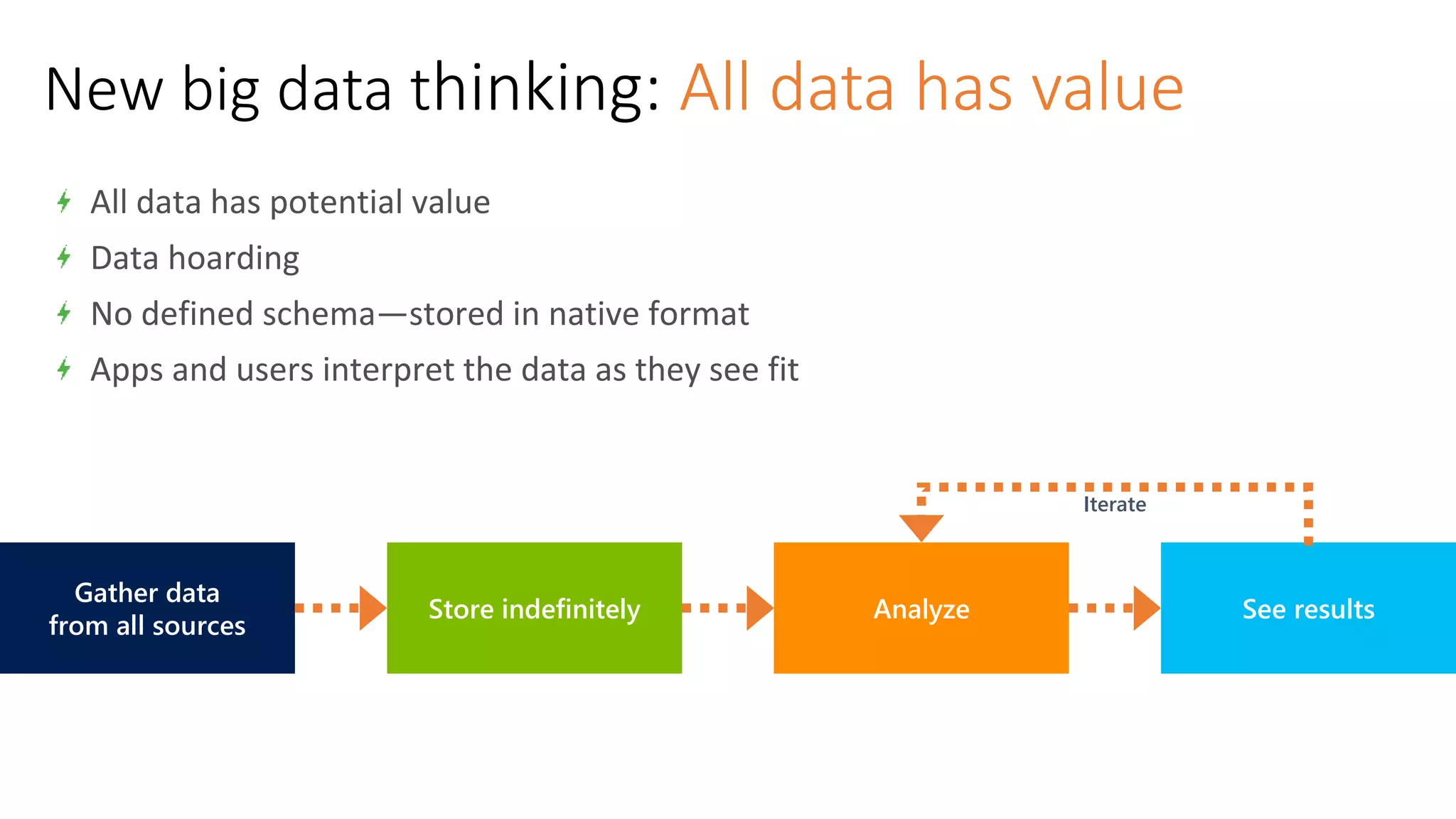
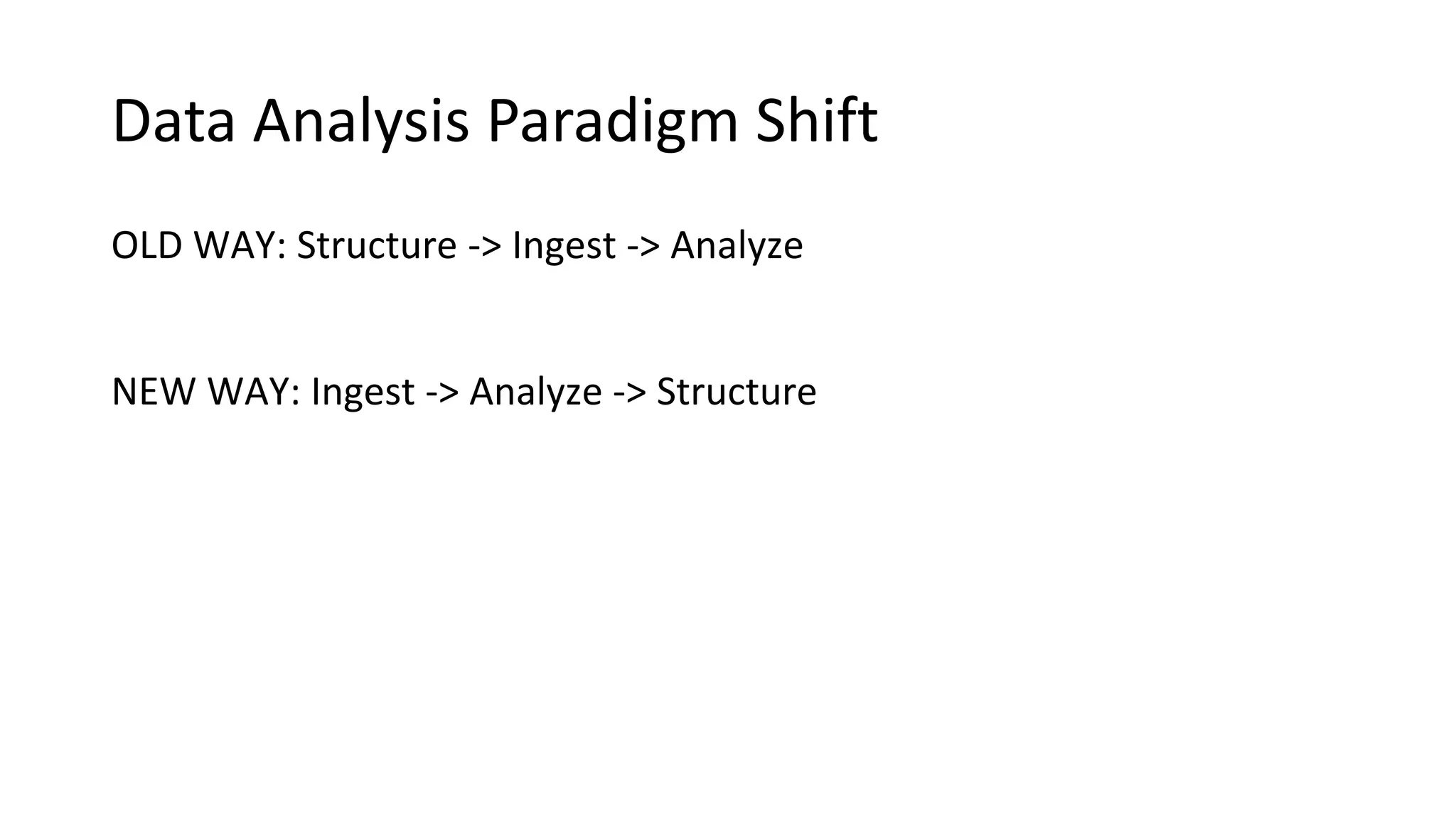
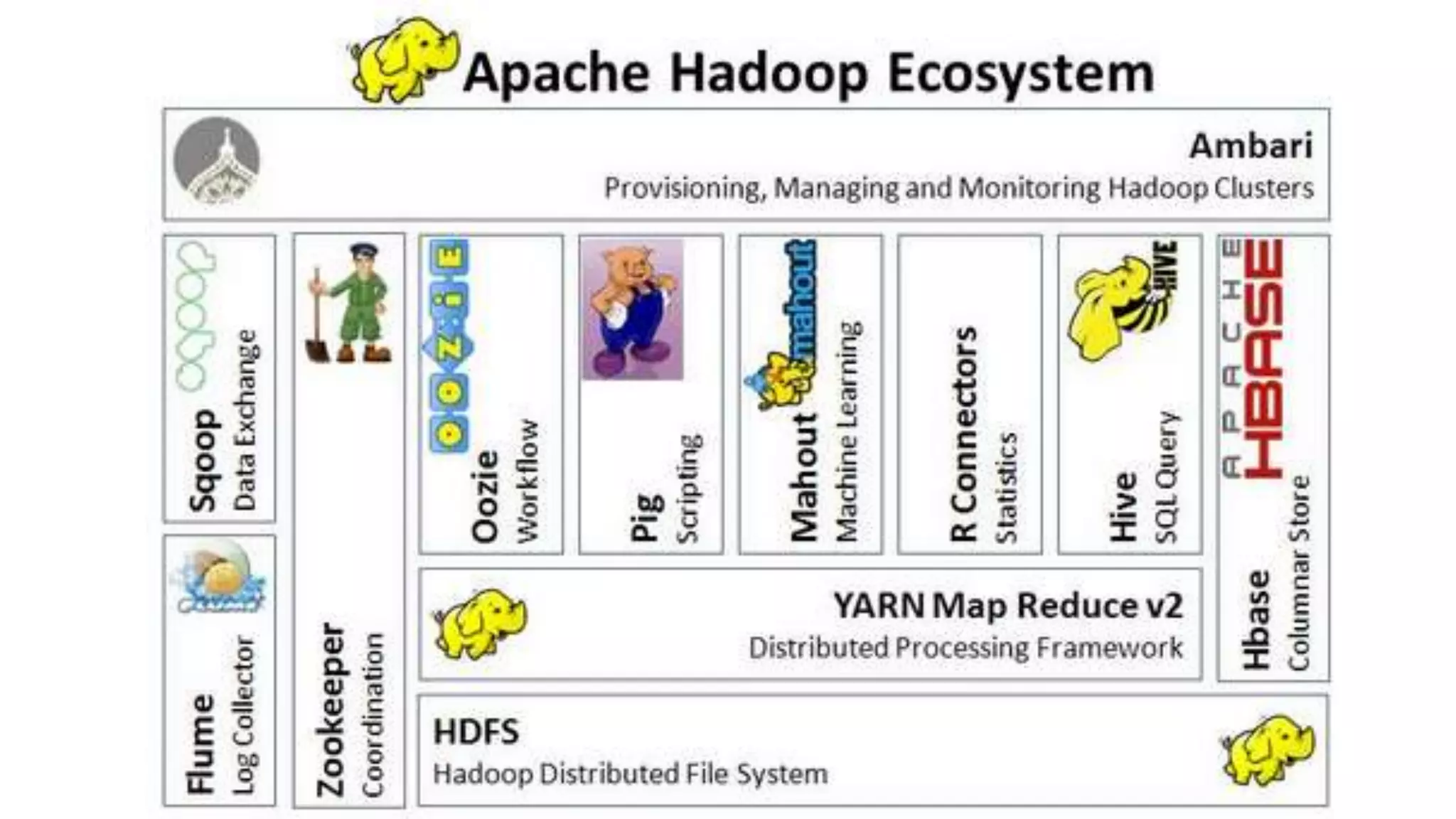
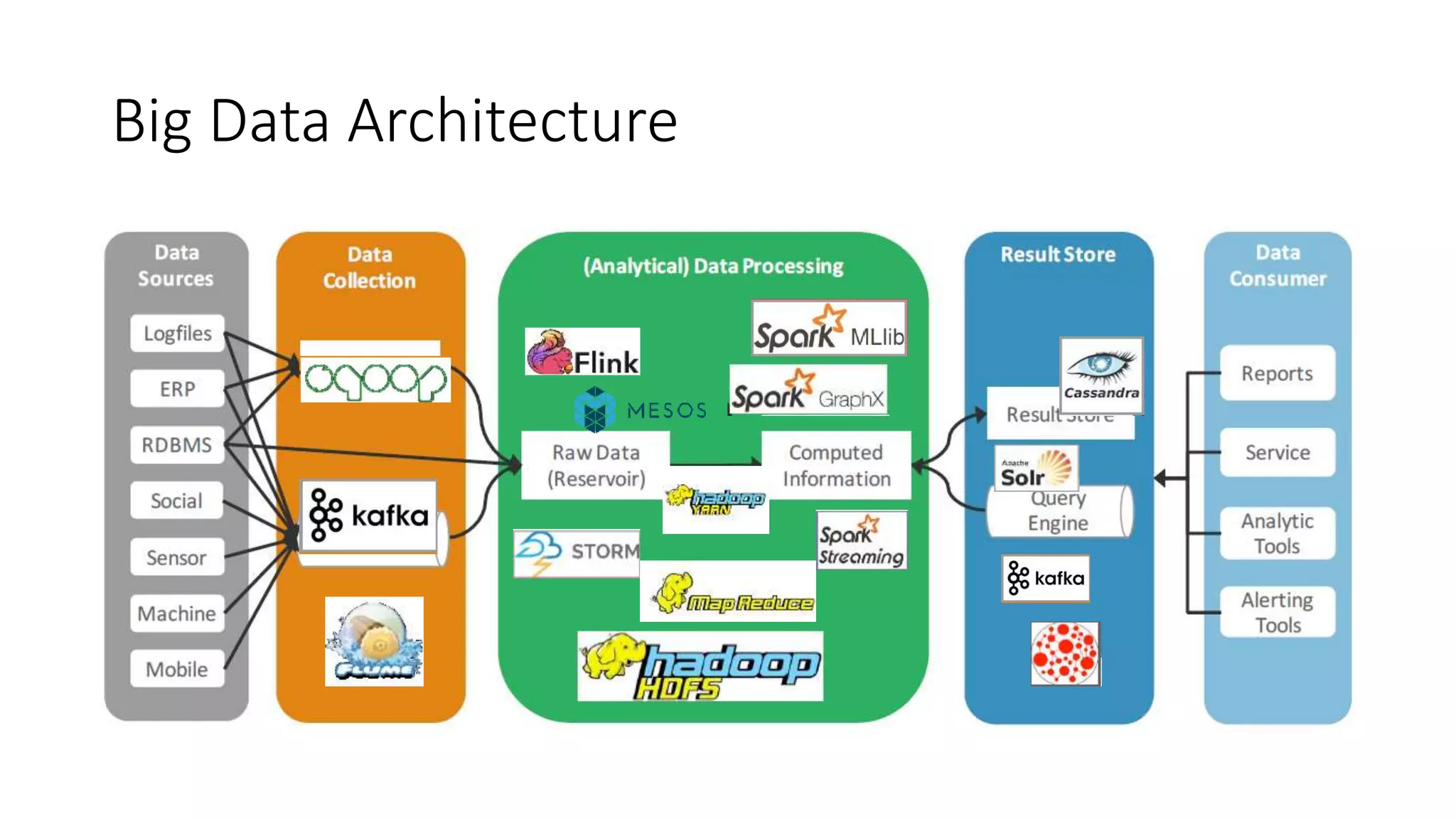
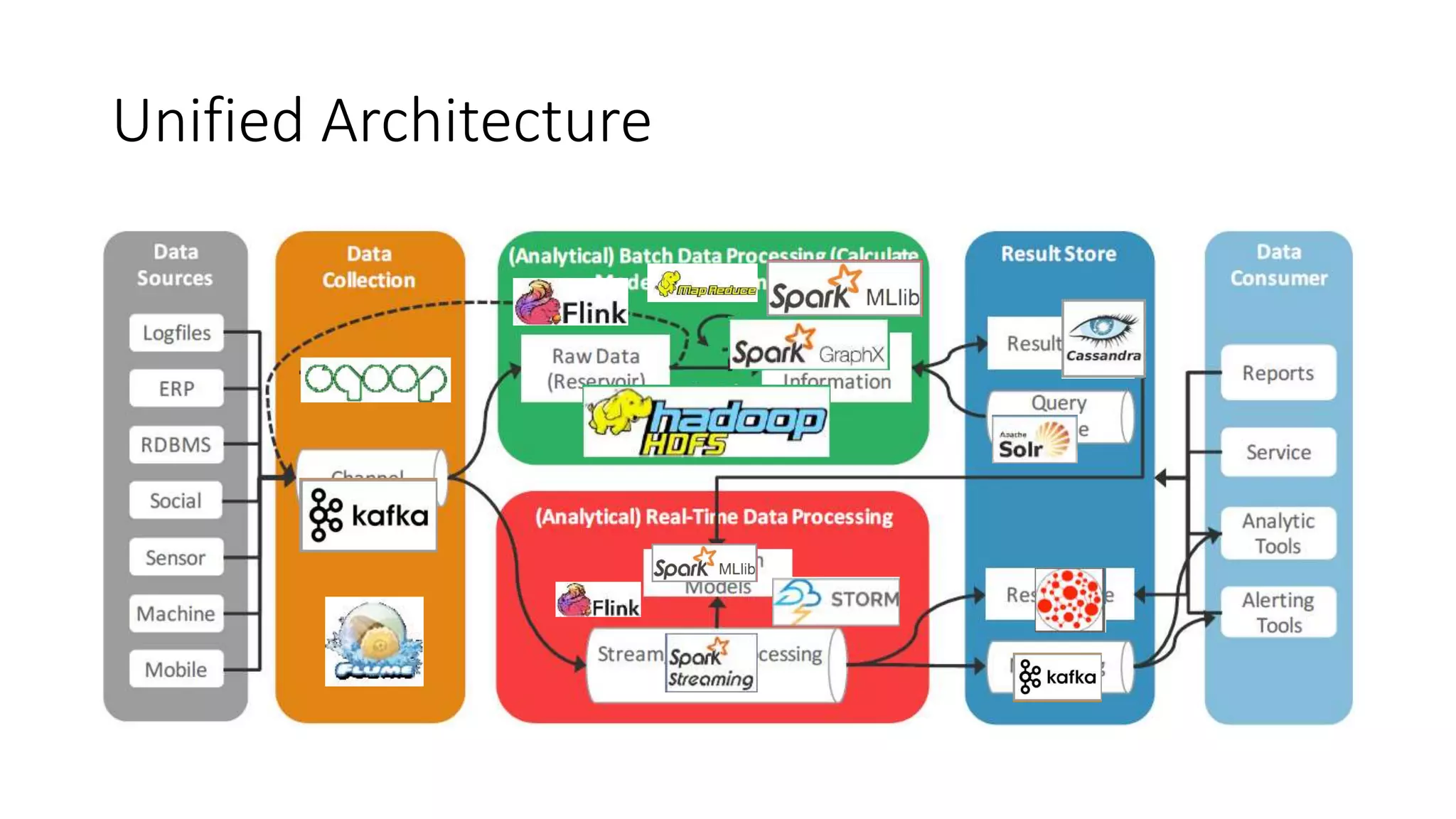
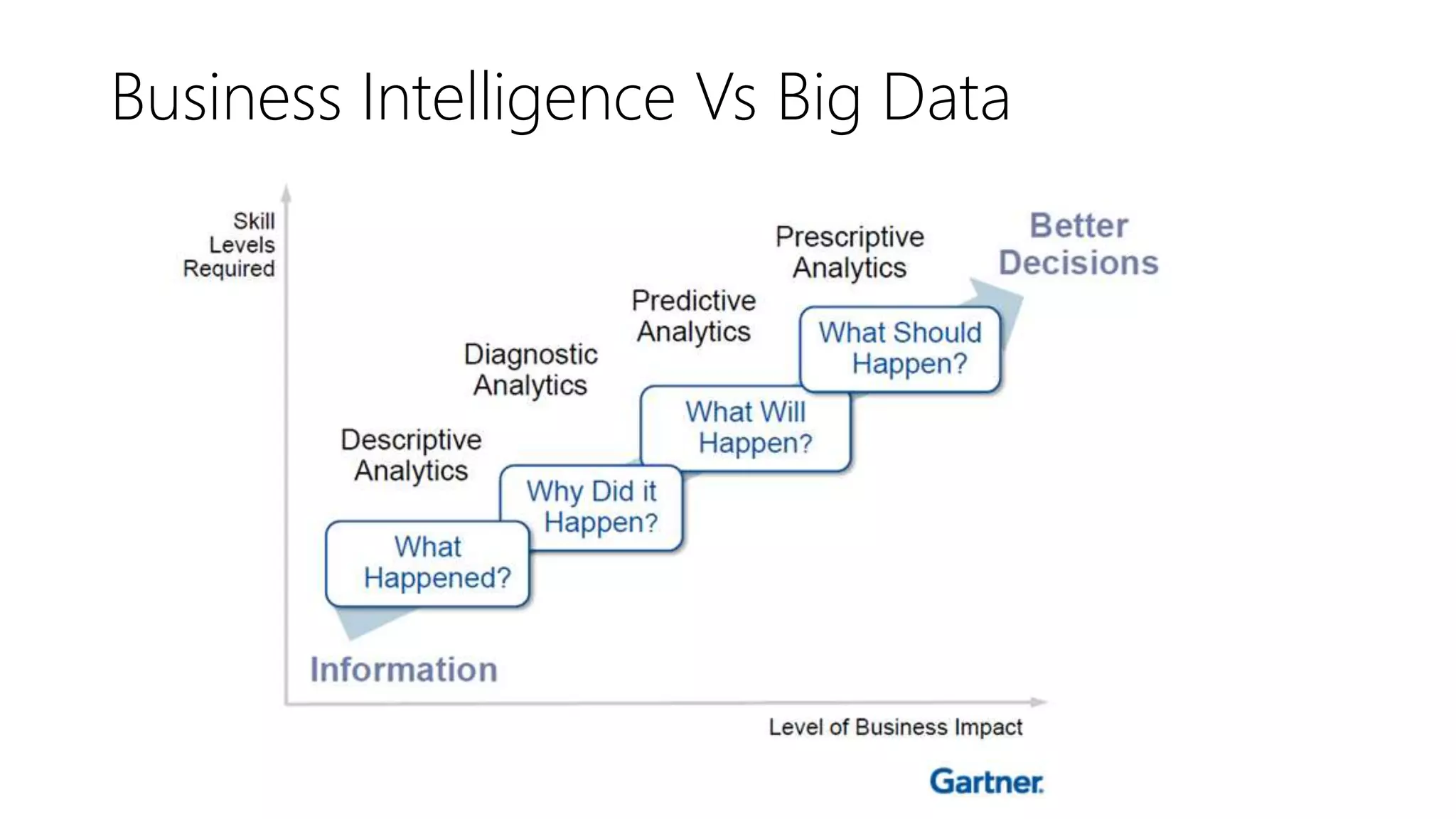
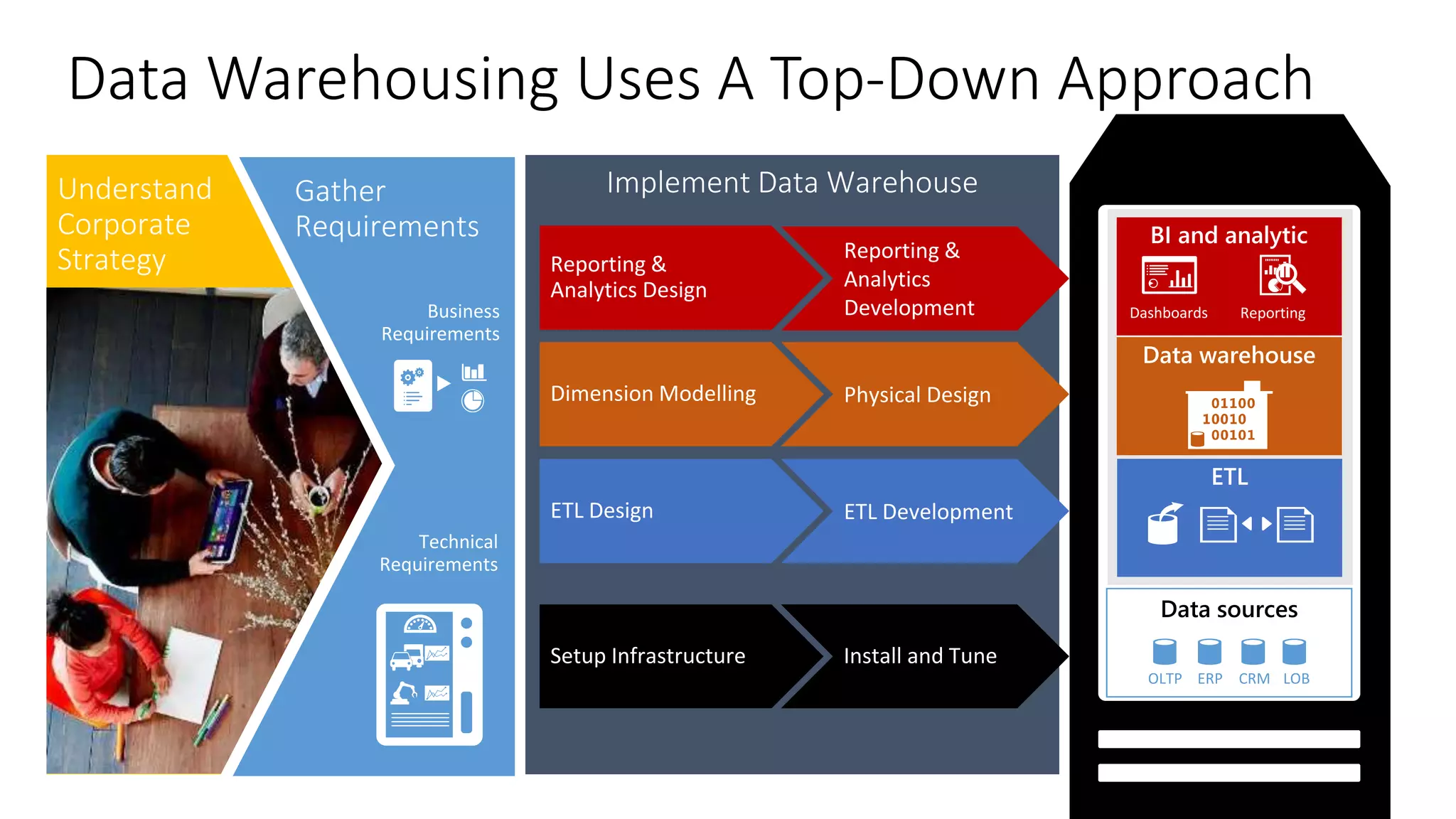
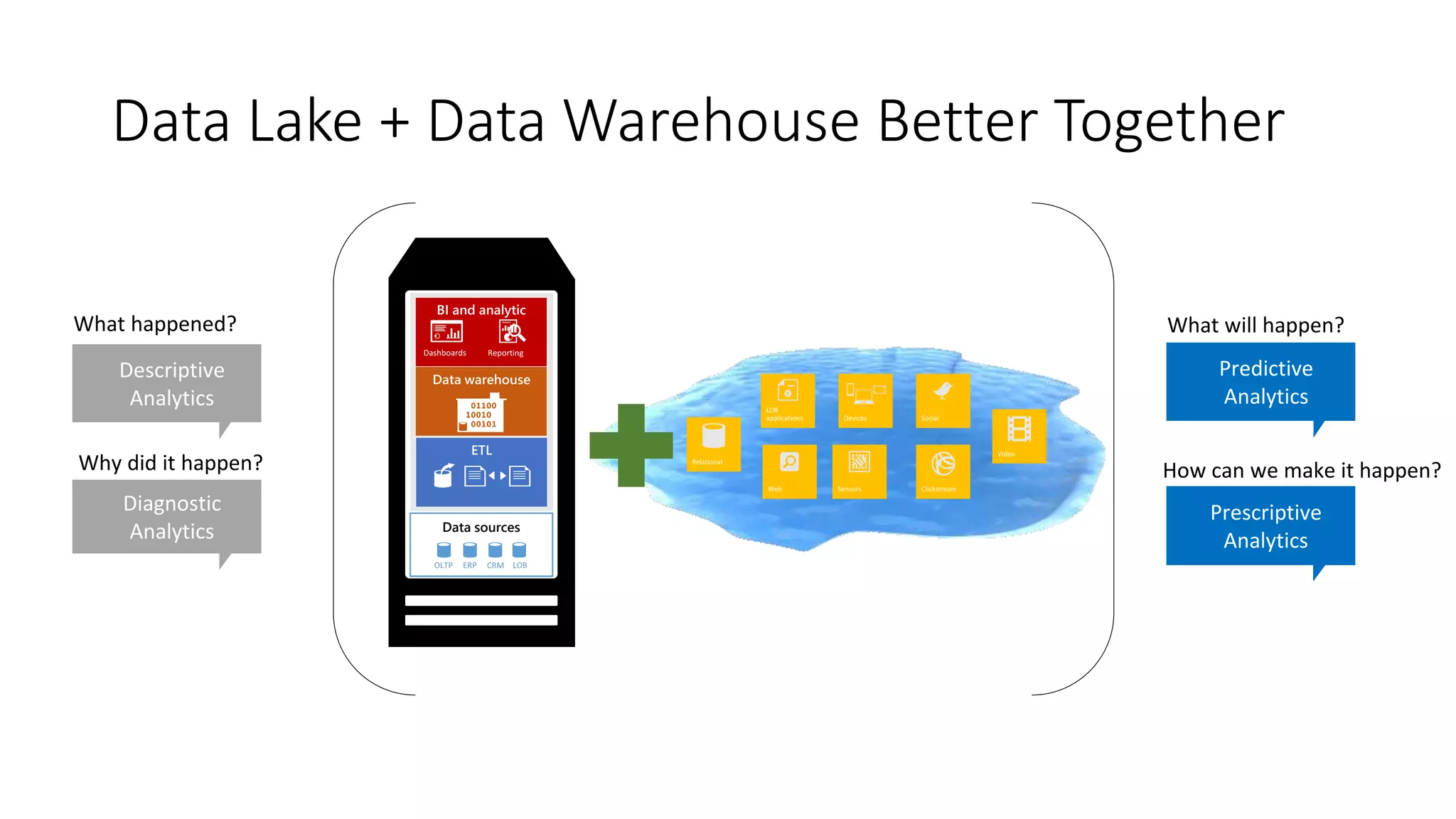
The document discusses the evolution and importance of data processing and management, highlighting concepts like data warehouses, data lakes, and big data pipelines. It emphasizes the value of big data for business decision-making and outlines the architecture and benefits of data lakes, such as quick ingestion and flexibility in data analysis. Additionally, it contrasts traditional data warehouse approaches with modern data lake strategies, emphasizing the growing need for scalable and efficient data solutions.