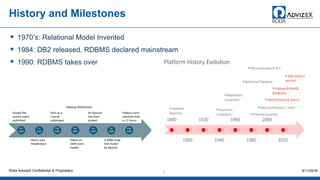
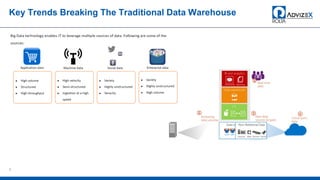
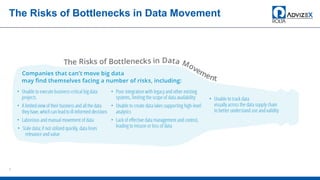
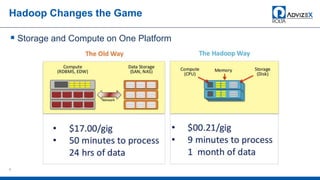
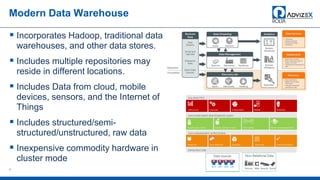
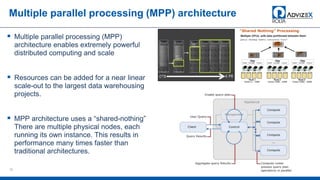
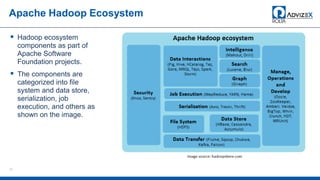
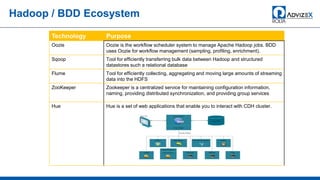
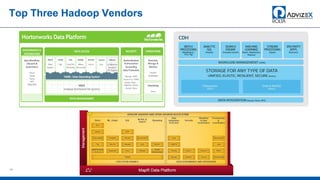
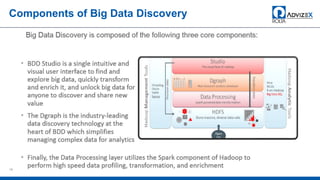
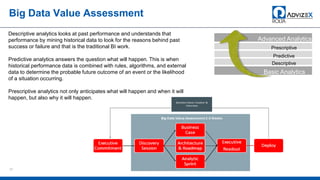
The document discusses the modern data warehouse and key trends driving changes from traditional data warehouses. It describes how modern data warehouses incorporate Hadoop, traditional data warehouses, and other data stores from multiple locations including cloud, mobile, sensors and IoT. Modern data warehouses use multiple parallel processing (MPP) architecture for distributed computing and scale-out. The Hadoop ecosystem, including components like HDFS, YARN, Hive, Spark and Zookeeper, provide functionality for storage, processing, and analytics. Major vendors like Oracle provide technical innovations on Hadoop for data discovery, exploration, transformation, discovery and sharing capabilities. The document concludes with an overview of descriptive, predictive and prescriptive analytics capabilities in a big data value assessment.