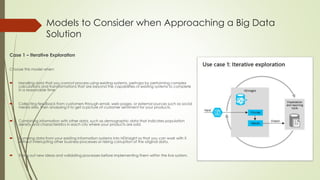
This document provides an overview of HDInsight and Hadoop. It defines big data and Hadoop, describing HDInsight as Microsoft's implementation of Hadoop in the cloud. It outlines the Hadoop ecosystem including HDFS, MapReduce, YARN, Hive, Pig and Sqoop. It discusses advantages of using HDInsight in the cloud and provides information on working with HDInsight clusters, loading and querying data, and different approaches to big data solutions.