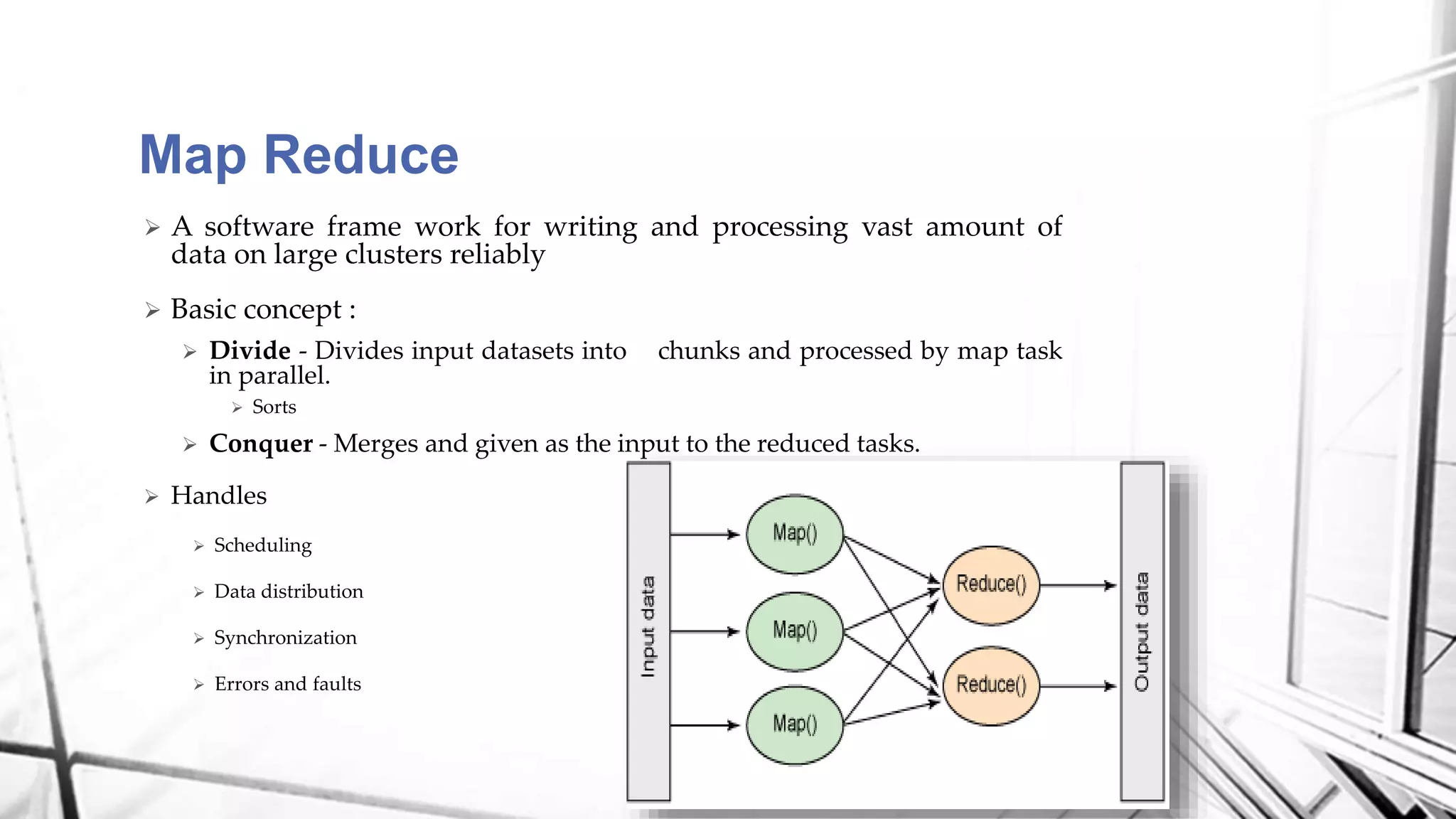
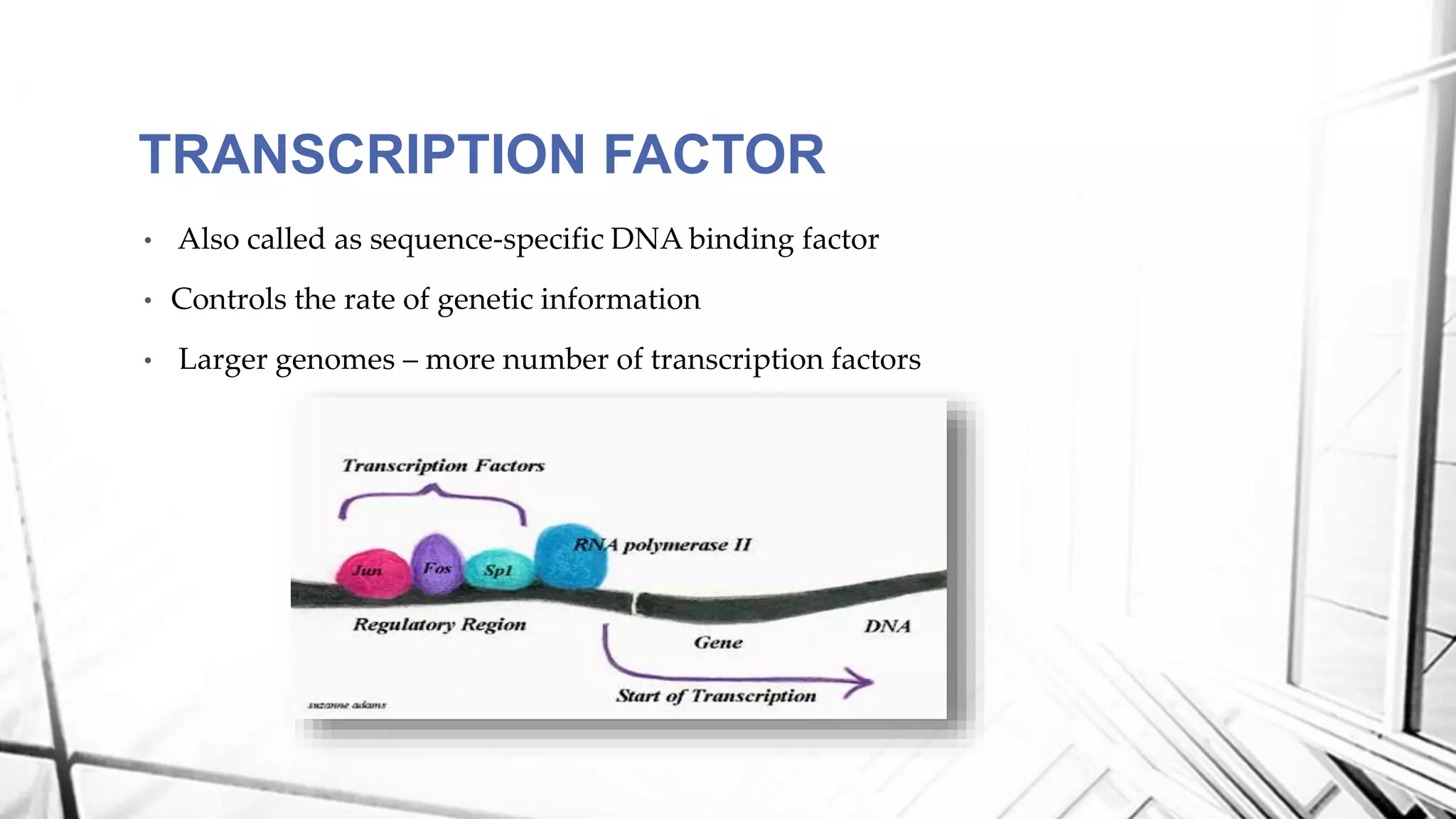
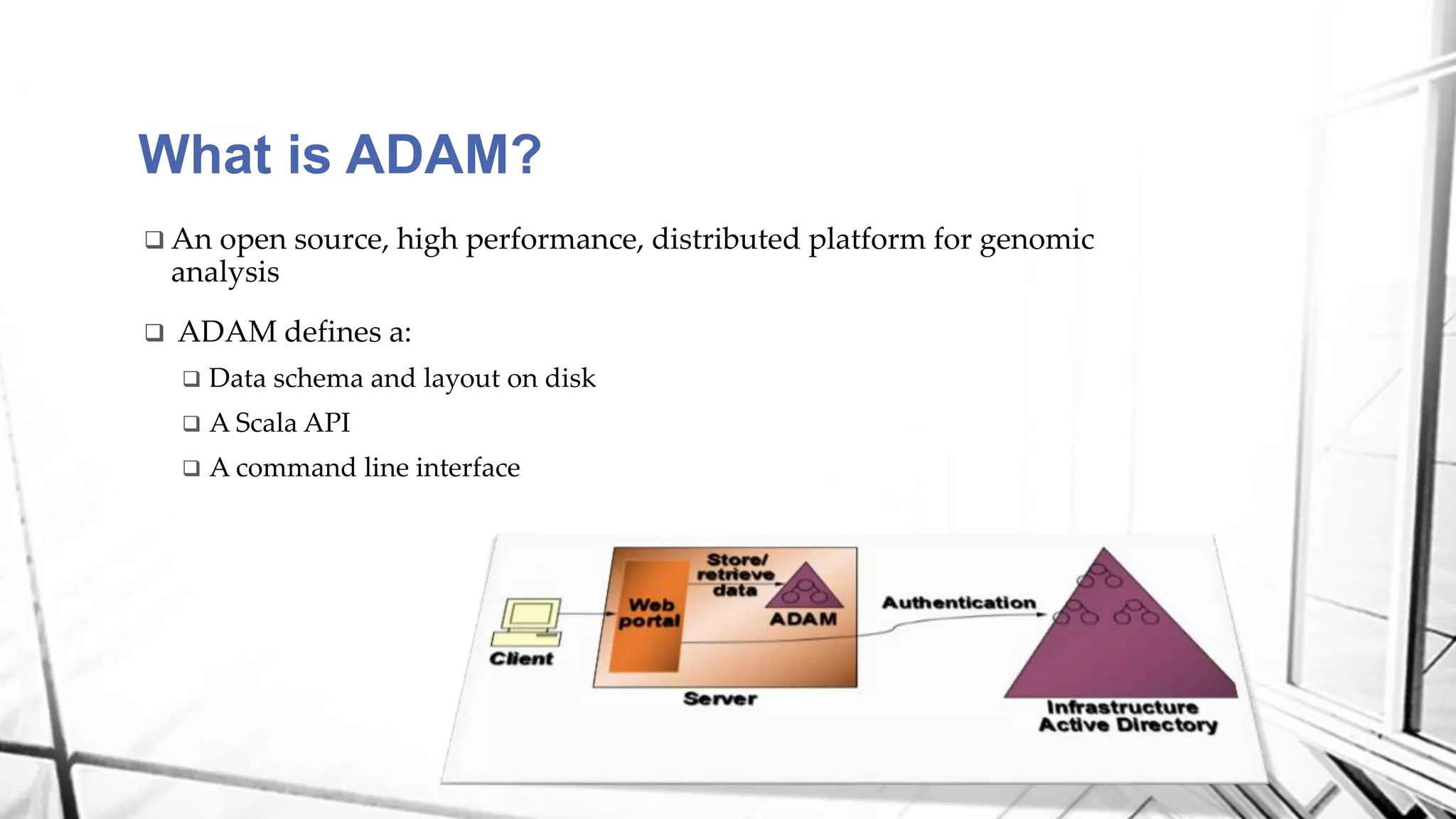
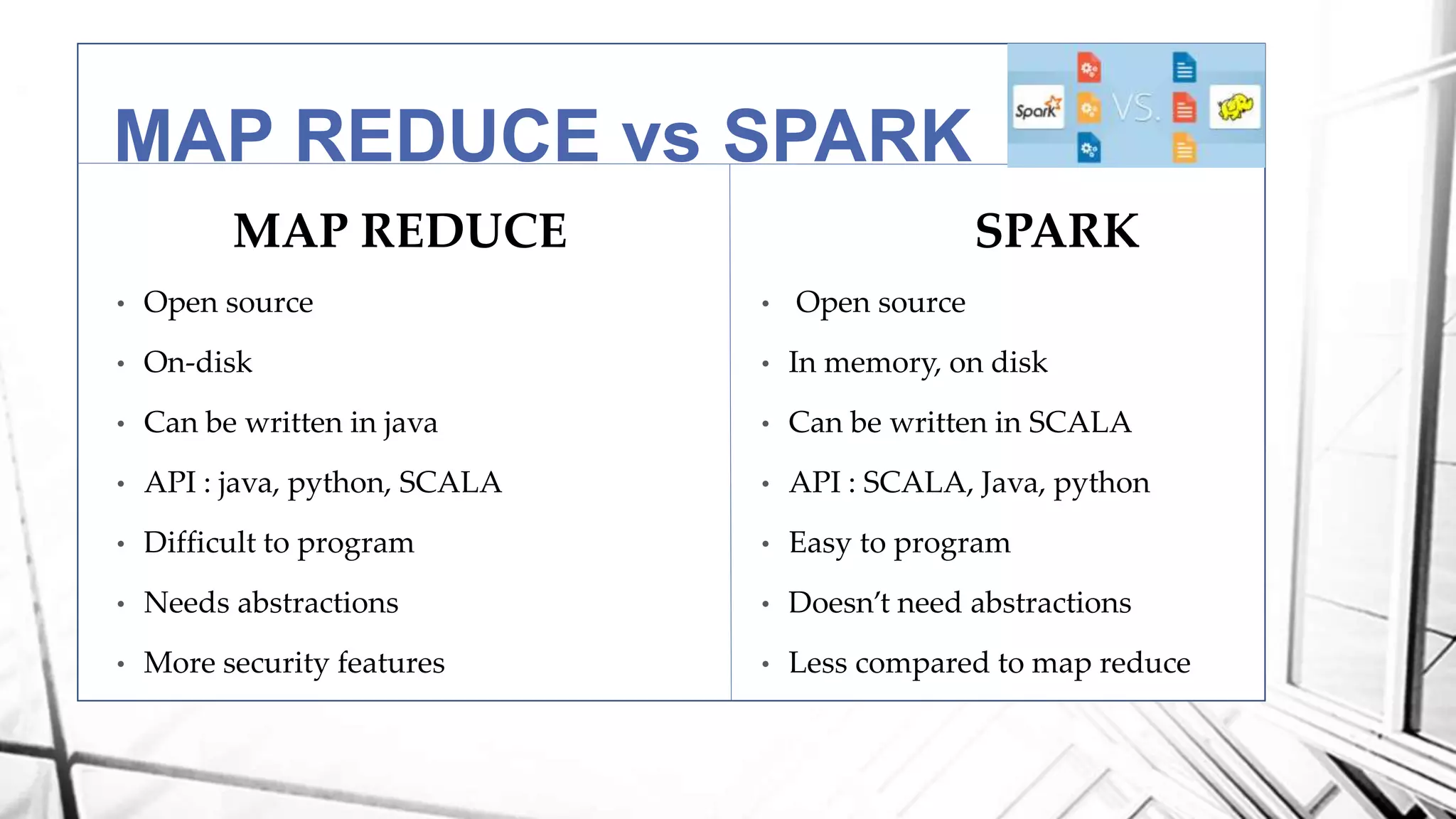
This document discusses a project analyzing genomics using big data techniques. It introduces Spark, a framework for large-scale data analysis, and ADAM, a Spark-based framework for genomic data. Key points covered include an overview of Spark and Hadoop, data types and formats in genomics, and using ADAM and Spark to perform genomic analysis and queries on large datasets like the 1000 Genomes Project.