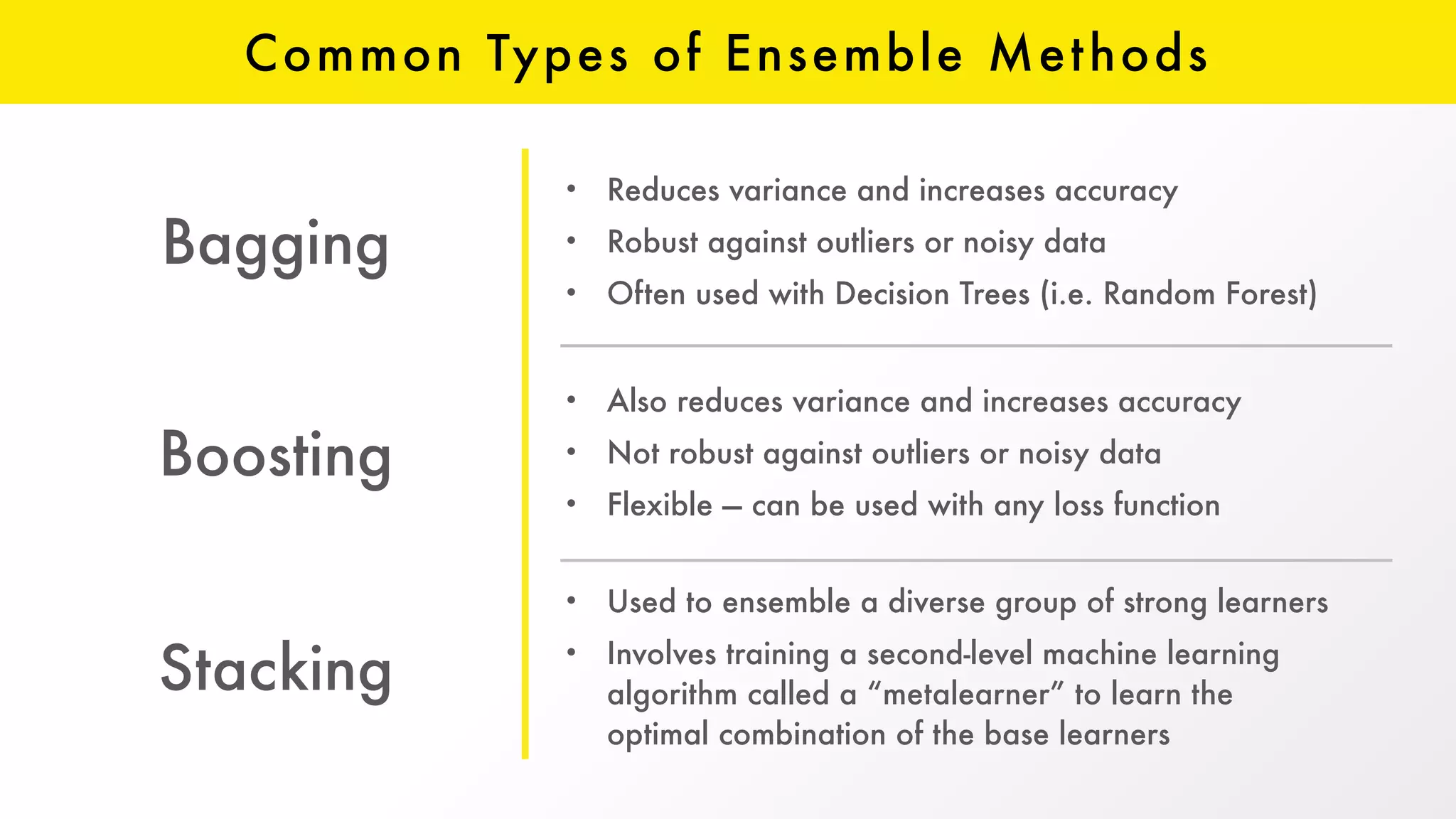
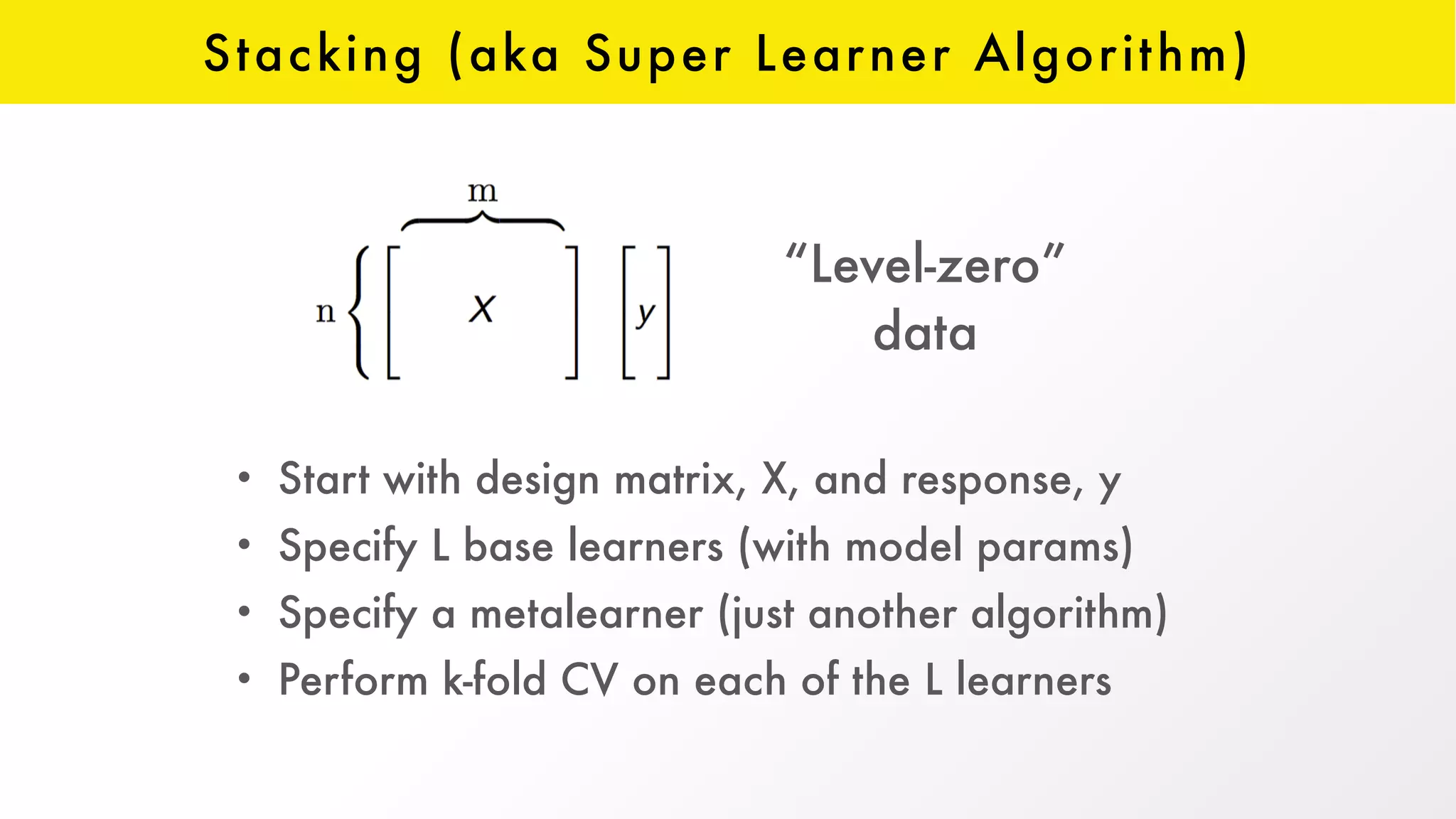
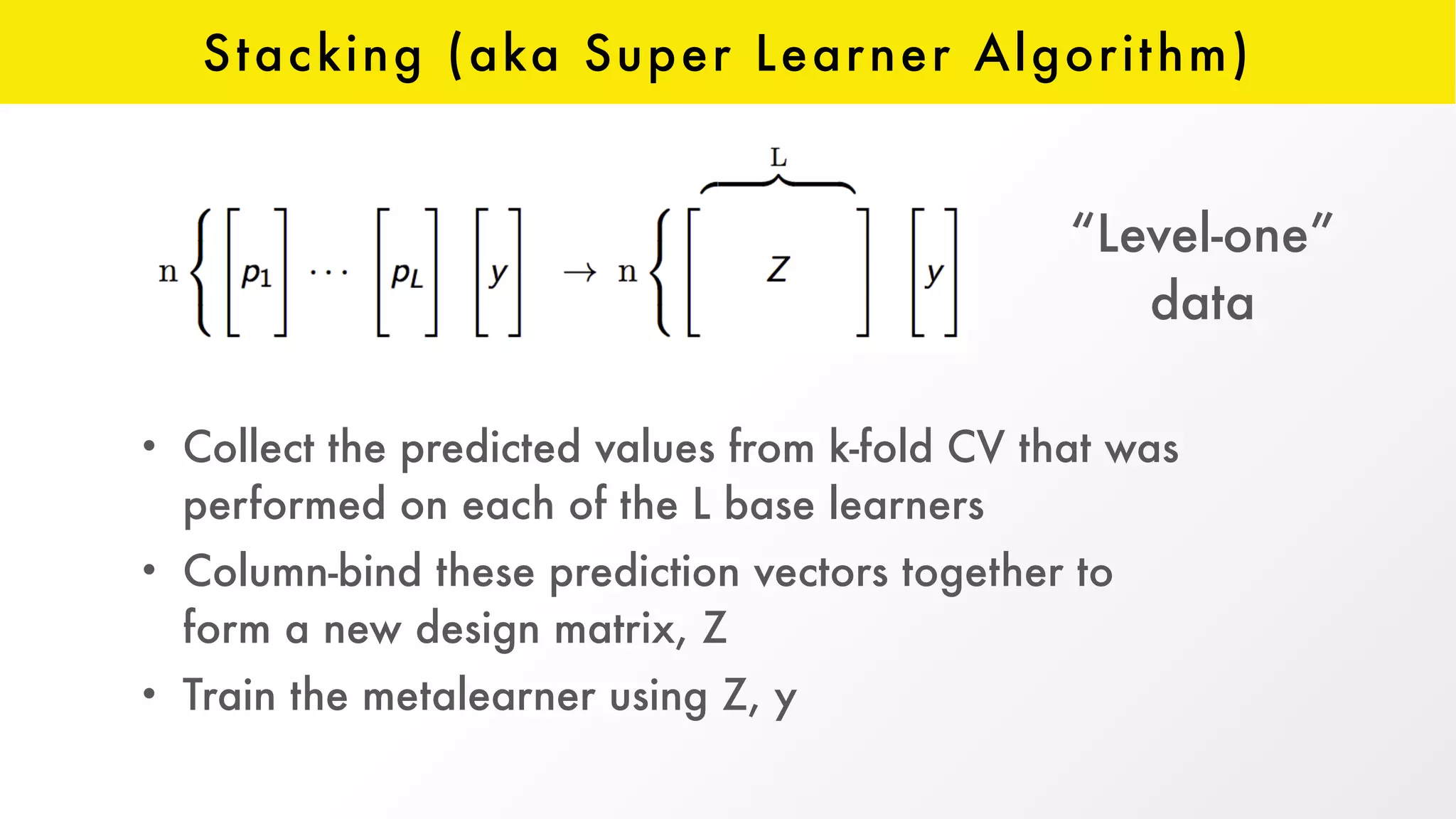
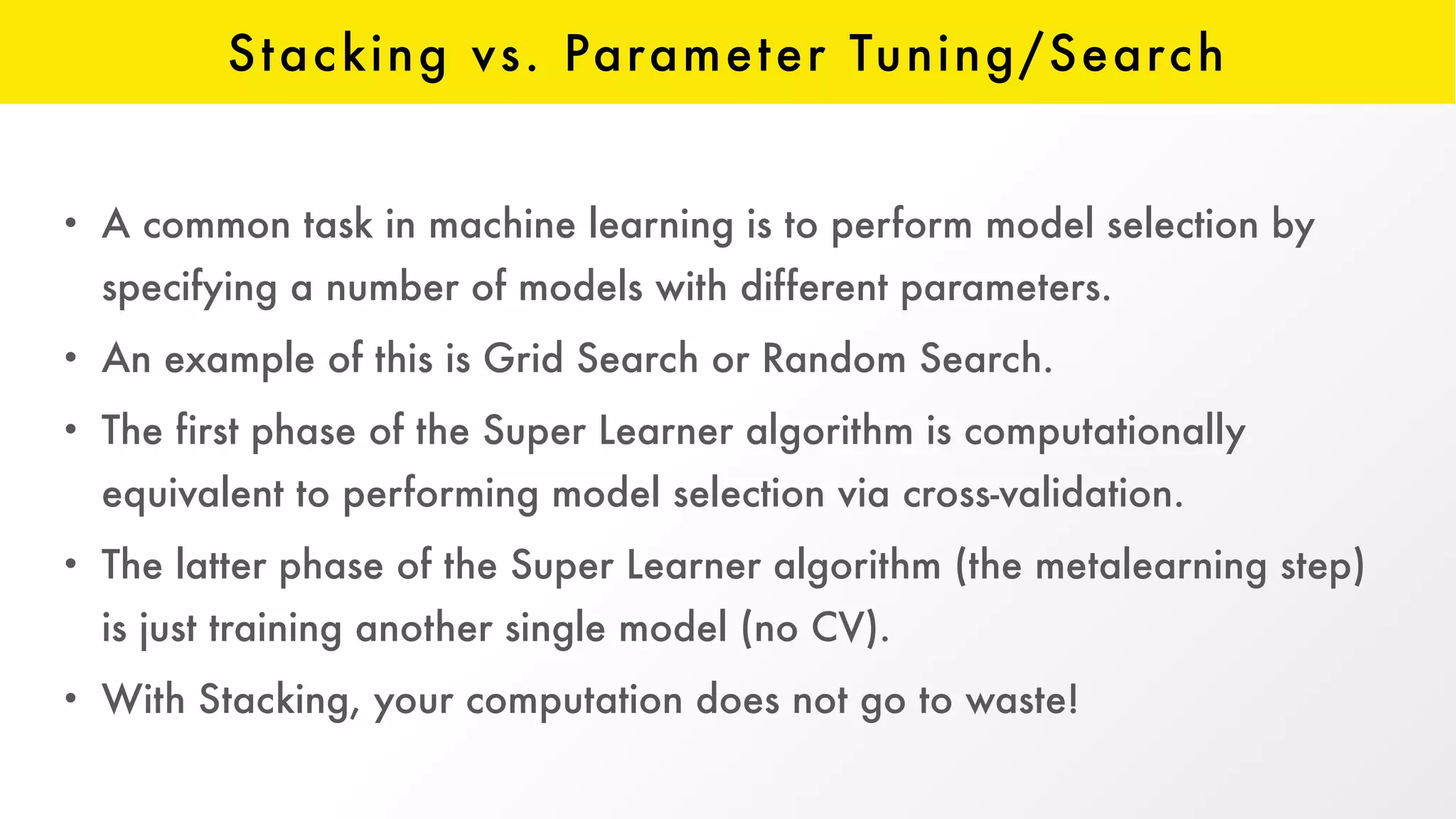
The document discusses H2O, an open-source platform for machine learning, founded in 2012, which facilitates ensemble learning through techniques like stacking to enhance predictive performance. It outlines the concept of stacking, involving both base learners and a 'metalearner', as well as the development of resources and integration with third-party algorithms like XGBoost. Additionally, it highlights advancements in H2O, such as the automl feature that automates parameter tuning and feature generation.