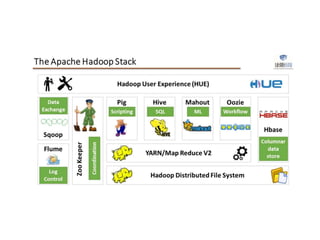
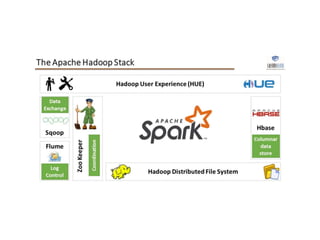
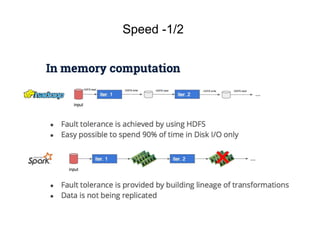
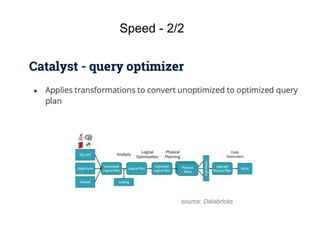
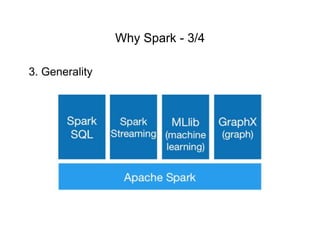
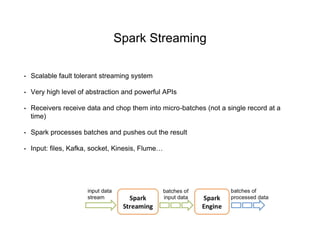
1. Apache Spark is an open source cluster computing framework for large-scale data processing. It is compatible with Hadoop and provides APIs for SQL, streaming, machine learning, and graph processing.
2. Over 3000 companies use Spark, including Microsoft, Uber, Pinterest, and Amazon. It can run on standalone clusters, EC2, YARN, and Mesos.
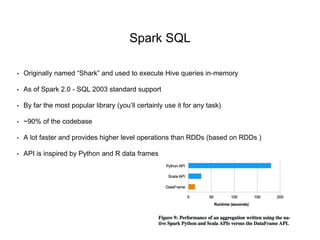
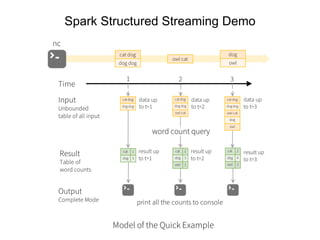
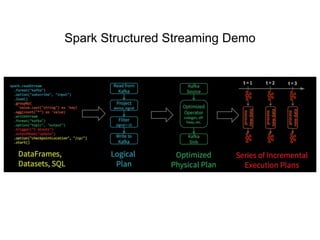
3. Spark SQL, Streaming, and MLlib allow for SQL queries, streaming analytics, and machine learning at scale using Spark's APIs which are inspired by Python/R data frames and scikit-learn.