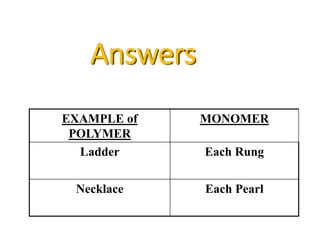
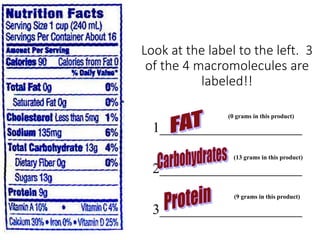
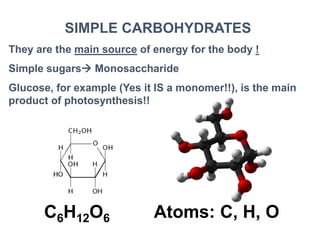
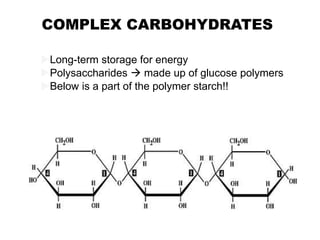
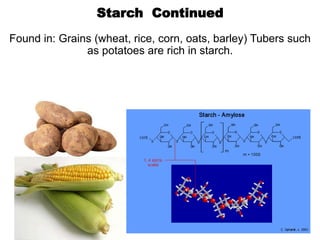
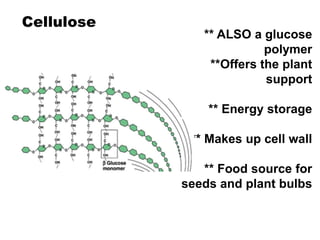
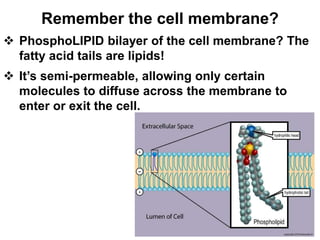
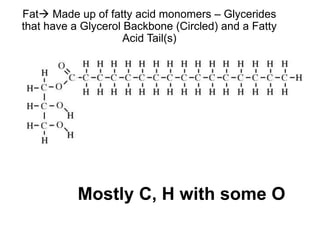
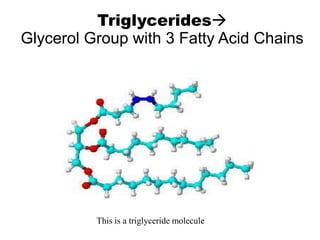
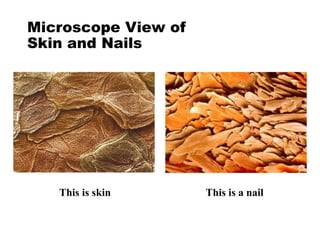
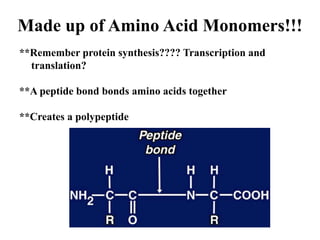
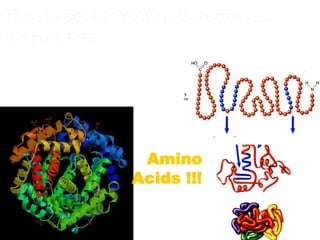
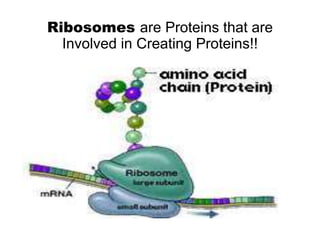
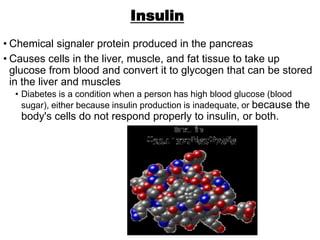
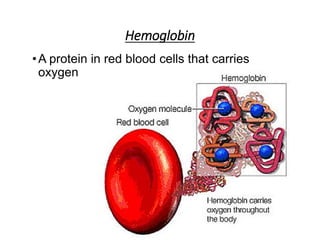
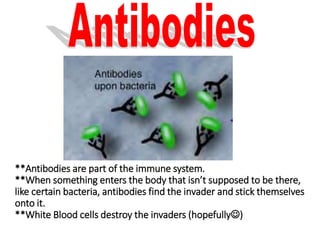
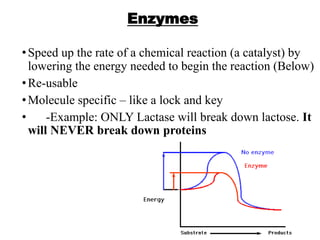
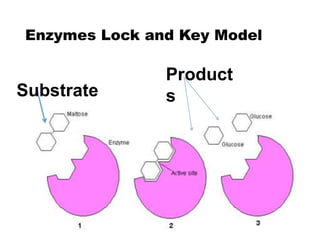
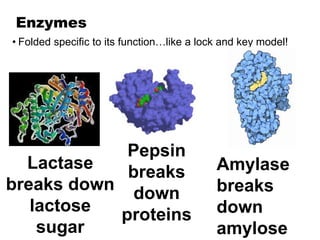
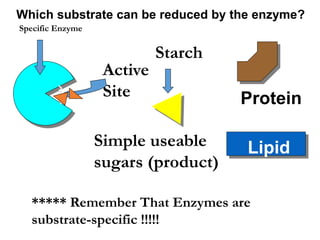
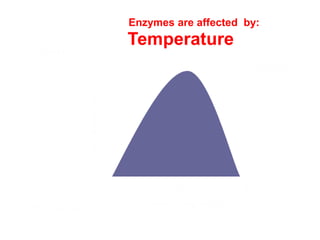
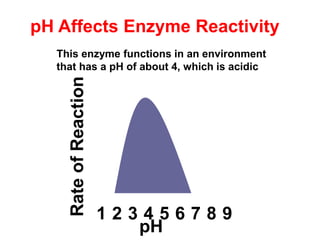
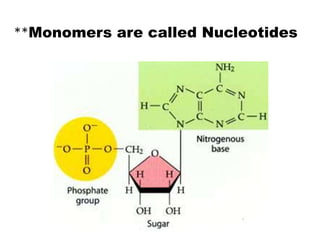
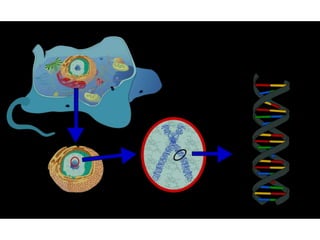
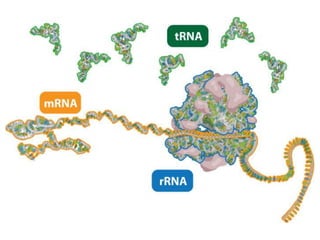
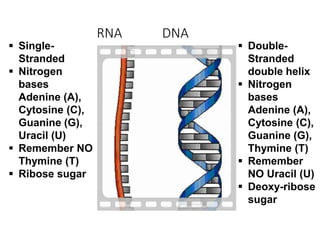
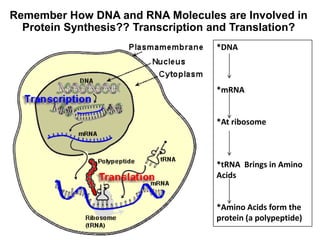
There are four classes of biological macromolecules: proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates include simple sugars like glucose and complex polysaccharides like starch, cellulose, and glycogen. Lipids function to store energy, insulate the body, and act as structural components of cell membranes. Proteins make up structures like hair, skin, and nails and perform functions as enzymes, antibodies, and hormones. Nucleic acids DNA and RNA contain genetic information and aid in protein synthesis, with DNA in the nucleus and RNA transcribing DNA before proteins are assembled from amino acids.